doi: 10.56294/hl2024.397
ORIGINAL
The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Management and Rehabilitation of Depressive Disorders
La importancia de los ácidos grasos omega-3 en el tratamiento y la rehabilitación de los trastornos depresivos
Manisha Chandna1 ![]() , Sidhant Das2
, Sidhant Das2 ![]() , Malathi H3
, Malathi H3 ![]() , Neha Rana4
, Neha Rana4 ![]() , Geetika Madan Patel5
, Geetika Madan Patel5 ![]() , Snehanshu Dey6
, Snehanshu Dey6 ![]() , N.J.Patil7
, N.J.Patil7 ![]()
1Centre of Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Punjab, India.
2Chitkara Centre for Research and Development, Chitkara University, Himachal Pradesh, India.
3JAIN (Deemed-to-be University), Department of Biotechnology and Genetics, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
4School of Pharmacy, Noida International University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.
5Parul University, PO Limda, Tal. Waghodia, Department of Community Medicine, District Vadodara, Gujarat, India.
6IMS and SUM Hospital, Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of Psychiatry, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
7Krishna institute of Medical Sciences, Krishna Vishwa Vidyapeeth “Deemed to be University”, Department of Pathology, Taluka-Karad, Dist-Satara, Maharashtra, India.
Cite as: Chandna M, Das S, Malathi H, Rana N, Madan Patel G, Dey S, et al. The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Management and Rehabilitation of Depressive Disorders. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2024; 3:.397. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2024.397
Submitted: 13-03-2024 Revised: 01-08-2024 Accepted: 06-11-2024 Published: 07-11-2024
Editor: PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Omega-3 “polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)” supplementation in depressed individuals has been advocated as a way to reduce depression symptoms, however prior research has been unambiguous.
Objectives: to the latest meta-analysis of “randomized controlled trials (RCTs)” investigating the usefulness of omega-3 PUFAs in the treatment of depressive illnesses while accounting for clinical variations among the research patients.
Methods: RCTs employing PUFA omega-3 on individuals with depression symptoms were searched for in PsycINFO, Cochrane Database, MEDLINE, and EMBASE. The research to normalize average variation in psychological assessments for mental health intensity, investigate the use of omega-3 as monotherapy or in combination, concentrate on eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA] and docosahexaenoic acid [DHA]. Impacts of this research scope, initial level of depression, length of the hearings, omega-3 dose, and patient gender were evaluated using a meta-analysis.
Results: the considerable therapeutic advantage of PUFA omega-3 therapy in contrast to placebo was seen in a meta-analysis of 11 and 8 studies PUFA omega-3 on those who have of “major depressive disorder (MDD)” and patients through depressed symptoms without diagnosis of MDD. Ultimately effectiveness was modified using predominantly EPA relatively DHA in the formulation. When used as an auxiliary rather than a monotherapy, omega-3 PUFA has shown considerable beneficial effects. There was no association among investigation dimensions, beginning depressive extent, treatment time, client ages, or research effectiveness. Research on omega-3 PUFAs’ effectiveness in treating bipolar disorder, perinatal depression, and primary diseases is limited, highlighting the need for further investigations.
Keywords: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFA); Omega-3 Fatty Acids; Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA); Major Depressive Disorder (MDD).
RESUMEN
Introducción: la suplementación con «ácidos grasos poliinsaturados (PUFA)» omega-3 en individuos deprimidos se ha defendido como una forma de reducir los síntomas de la depresión, sin embargo, las investigaciones previas no han sido ambiguas.
Objetivos: realizar el último metaanálisis de los «ensayos controlados aleatorizados (ECA)» que investigan la utilidad de los PUFA omega-3 en el tratamiento de las enfermedades depresivas, teniendo en cuenta las variaciones clínicas entre los pacientes de la investigación.
Método: se buscaron ECA que emplearan AGPI omega-3 en individuos con síntomas de depresión en PsycINFO, Cochrane Database, MEDLINE y EMBASE. La investigación para normalizar la variación media en las evaluaciones psicológicas para la intensidad de la salud mental, investigar el uso de omega-3 como monoterapia o en combinación, concentrarse en el ácido eicosapentaenoico [EPA] y el ácido docosahexaenoico [DHA]. Mediante un metaanálisis se evaluaron los efectos del alcance de esta investigación, el nivel inicial de depresión, la duración de las audiencias, la dosis de omega-3 y el sexo del paciente.
Resultados: la considerable ventaja terapéutica de la terapia PUFA omega-3 en contraste con el placebo se observó en un meta-análisis de 11 y 8 estudios PUFA omega-3 en los que tienen de «trastorno depresivo mayor (TDM)» y los pacientes a través de los síntomas de depresión sin diagnóstico de TDM. En última instancia, la eficacia se modificó utilizando predominantemente EPA relativamente DHA en la formulación. Cuando se utilizan como auxiliar y no como monoterapia, los PUFA omega-3 han mostrado considerables efectos beneficiosos. No hubo asociación entre las dimensiones de la investigación, el grado depresivo inicial, el tiempo de tratamiento, las edades de los clientes o la eficacia de la investigación. La investigación sobre la eficacia de los AGPI omega-3 en el tratamiento del trastorno bipolar, la depresión perinatal y las enfermedades primarias es limitada, lo que pone de manifiesto la necesidad de realizar más investigaciones.
Palabras clave: Ácidos Grasos Poliinsaturados (PUFA); Ácidos Grasos Omega-3; Ácido Eicosapentaenoico (EPA); Trastorno Depresivo Mayor (TDM).
INTRODUCTION
It is well acknowledged that omega-3 fatty acids in general and in particular, have a substantial impact on health. The health advantages of omega-3 fatty acids are due to their antimicrobial, hypolipidemic, antithrombotic, and antiarrhythmic properties. The outcome is various ailments, like heart problems and rheumatoid arthritis, are prevented and treated with the help of these fatty acids. For generations, presently had a drop in the taking in omega-3 fatty acids and a rise in the nutritional value of omega-6 fatty acids, which is thought to have harmed medical care.(1) PUFA are fatty acids with more one carbon-carbon bond pair throughout the particle that are not saturated with a hydrogen atom, PUFA can be divided to several classes. The term “PUFA” relates to a category of PUFA called omega-6 that share the twice bonded is located three carbons from the structure’s future (omega) carbon atom.(2)
All mammals’ cell membranes require PUFAs and omega-3 acids. Since numerous species fail to synthesize themselves, must be consumed dietary for the organs to operate normally. “Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA),” EPA, and DHA are all omega-3 fatty acid neighbors. Omega-3 fatty acids have already been shown to have a complex favorable influence on the health of organisms, including humans. As a result, several researches have been conducted on omega-3 fatty acids and their play in both treatment and prevention of various illnesses. Cardiovascular, immunological, and neurological tract disorders are the focus of the investigation. Since “spinal cord injuries (SCI)” generally cause problems with nerve tissue and the immune system during irritation, treating people with SCI presents a unique set of challenges for modern medicine.(3)
PUFA are fatty acids that have a minimum of two carbon-carbon bond doubles with the molecule that are not saturated through molecules of hydrogen. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are two types of PUFA that omega-3 PUFA group is made up of PUFA with a primary dual bond located three carbons from the final substance of the structure; the omega-6 PUFA family is made up of PUFA that share the last Recognizing backward toward the methyl conclusion the sixth bond is a double bond between carbon and carbon at the n-6 region. ALA, a dietary source of shorter-chain omega-3 fatty acids, synthesizes omega-3 PUFA to produce the more critical long-chain omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA.(4)
Significant contributions from fatty acids maintain hemodynamic wellness. Primary fundamental functions, including fuel retention and movement, genetic control, and thermal and electrical insulation in cells, are included in the section. Fatty acids also serve as the foundation for the exterior of cells and promote cellular signals. With their antibacterial, anticancer, antihypertensive, and hypoglycemic properties, fatty acids can have an immediate and wide range of positive effects on wellness.(5)
Important PUFAs like omega-3 and omega-6 influence brain development. Since n-3 PUFA and n-6 PUFA precursors are only available through nutrition for creatures and humans, food-based n-3 PUFA and n-6 PUFA composition play a significant role in brain development through pregnancy. Through influencing neurons equilibrium between n-6 and n-3 PUFAs while pregnancy impacts the cerebral cortex.(6)
Recommended course of treatment for depression in kids and teenagers with “depressive disorder (DD)” or “mixed anxiety and DD (MADD),” as well as to analyze fluid, fatty acid content and the omega-6/omega-3 FA proportion before and after the treatment. Sixty kids were randomly assigned 1:1 to the active comparative or interventional categories.(7)
“Major DD (MDD)” is a mental situation in a significant global impact and an absolute unfilled therapy requirement. Numerous systematic reviews later combined to multiple meta-analyses investigated the therapeutic benefits of omega-3 (n-3 PUFAs), particularly EPA and DHA, in addition to their medical safety features and impact on relevant indicators.(8)
Essential fats include omega-3 Lipids are fats. Nutritional omega-3 fatty acid deficiencies have been related to a variety of illnesses., such as dementia, cancer, head injuries, sadness, and “coronary heart disease (CHD)”. In highly active groups, like athletics and veterans, Omega-3 fatty acids have also demonstrated a reduction in the damage caused by exercise and hasten the recovery from “delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS)”. Additionally, consuming enough omega-3 fatty acids can improve the amino acid sensitivities for anabolism, which could benefit people with muscular damage.(9)
Linolenic acid, EPA, and DHA are examples of omega-3 fatty acids. Distinguished by having their initial pair of bonds on the next atomic level from the methyl end of the heavy acyl chain. This accumulates proof that its capacity to synthesize EPA, particularly DHA, is restricted. As a result, consuming manufactured EPA and DHA from resources like aquatic life, particularly fatty fish, or supplementation is advised.(10)
The objective of the research was to give a thorough and present assessment of the findings indicate the safety and efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids in the treatment of mental disorders. The popular of the data supporting the efficacy of EPA and DHA in treating the depressed symptoms of single-sided and bipolar depression has come from psychiatric illnesses. Research suggests using omega-3 fatty acids as therapies for illnesses such as borderline personality syndrome and situations marked by high impulsiveness and abuse.(11)
While numerous researchers have suggested that dietary FAs impact the biological rhythm, this investigation is the main circadian synchronizer. To update the data regarding the cellular processes underlying the circadian rhythm control by omega 3 FAs, a thorough literature analysis was undertaken using selected parameters. On the influence of omega-3 FAs on the circadian period, gathered experimental and medical analysis, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.(12)
The research a T-cell-mediated inflammatory condition with potential for malignant development is “oral lichen planus (OLP).”(13) Increasing data points to dental antigen-specific, not particular, and microbiome processes being implicated in the pathology of OLP, even if its etiology is unknown. While non-specific strategies involve “matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)”-9 up regulation, emotional stress, oxidative stress, unusual representation of this process, antigen-specific strategies involve presenting antigens nuclear factor-kappa B communicating, generation of cytokines, and stimulation of T cells. OLP therapy’s primary goal is symptomatic management since no known cure exists.
The research evaluated current research on a variety of anomalies, pathophysiology hazards, and biological hazards associated with aggression in persons with schizophrenia, mainly a focus on the metabolism of lipids.(14) That have concentrated on the changed cholesterol levels that potentially contributed to the emergence of violent schizophrenia sufferers’ attitudes. Discussed issues relating to the modulation of neuron action throughout the evolution of this terrible illness and the effects of abnormal lipid metabolism on cerebral development and functioning. Omega-3 fatty acids can decrease the onset of psychotic symptoms and function as a supplement to reduce aggression.
The review tries to clarify if x-3 PUFAs have supplemental, pharmaceutical, or combined effects on lung tumors. Data from a variety of cells, models of disease, and medical studies suggest that omega-3 PUFAs have therapeutic properties. Because essential mechanisms underpinning the development of complications of lung cancer are thought to be modulated by omega-3 PUFAs and their derivatives, this is a potential area requiring more research.(15)
Th analysis can discuss the most critical research about the benefits and risks of eating foods fats that are abundant in omega-3 and omega-6 for human wellness. Several types of PUFAs are available, and can be included in everyday meals for continued health. Defend against several illnesses, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and rheumatism. The main emphasis was the upland and aquatic ecosystems both include the PUFAs omega-3 (-3) and omega-6 (-6) fats.(16)
The investigation, problems following surgery in people with Crohn’s disease (CD) were evaluated about the effects of -3 PUFA-supplemented “parenteral nutrition (PN).” Chronic inflammation characterizes CD. Most CD patients need a procedure; however, surgical problems are more common in these people. Humans are thought to benefit from omega-3 (-3 PUFAs) regarding health, defenses, anti-inflammation, and gut microbiota equilibrium.(17)
The research was to ascertain if particularly, preoperative nutritional status and inflammatory status, would impact final results and difficulties in people living with cancer having lung removal. Sixty-eight individuals with non-small cell lung cancer in its initial phases can have operation. 68 patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer that was analyzed in this prospective assessment. A thorough analysis of the diet was done. The primary research variables were operational risks alongside 30-day mortality. A comprehensive logistic regression analysis was conducted.(18)
The research looked at how omega-3 fatty acids affected how severe dejection was in kids and teenagers. In 58 young people and teens with depression, lipid levels, “Paraoxonase 1 (PON1)” structure and permeability of the erythrocytes layer were the supplementary endpoints of the research, which also sought to determine how omega-3 fatty acids affected the tracked variables.(19)
The effectiveness of omega-3 fatty acids in treating psychosis, diseases of anxiety and bipolar, “post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD),” and depressive conditions is examined in this review.(20) Significant proof of major variation across contained research, and significant methodical shortcomings in featured studies make omega-3 fatty acid systematic reviews of studies with randomization for depression unclear.
The research examined omega-3 fatty acid impact on the variables being tracked along with the relationships between depression disorder manifestations and endothelial permeability, PON1 activity, lipid profile, and LDL- cholesterol subfractions in 58 depressed kids and teens.(21) The elements of depression were measured using the Children’s Depression Inventory (CDI), LDL subfractions were calculated using both Lipoprint technology and standard biological techniques. were used to determine the lipid composition. Fundamental metabolic indicators, like a lipid description, were in the physiological range when contrasted with levels in 20 healthy youngsters.
The investigation goal was to examine scientific and Investigations discusses how omega-3 fatty acids can help prevent and cure autoimmune-related chronic illnesses by controlling the bacteria in the intestines. For this, pure forms of omega-3 are offered, highlighting the significance of a balanced diet for maintaining the equilibrium of the organism and the enzymes reactions that these fatty acids with upon entering the cells.(22)
METHOD
A full investigation for every RCT employing PUFA omega-3 and sufferers with signs of depression was conducted on “MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, and the Expert Archives.” The following search terms were paired with others to find products that can be of attraction: angina, diabetes, depression, DD, depressed mood, CVD, post-partum, schizophrenia, Parkinson’s, perinatal, Alzheimer’, and bipolar. To choose the 192 products that were most pertinent for the evaluation, RCTs were found and verified by reviewing the entire manuscript in general or if required. It was also looked up in the references of the pertinent reports to additional trials had to be found. Figure 1 provides an overview of how problems were found and included. The following criteria were used for Participation: individual investigations, randomization designs, placebo controls, supplements containing omega-3 PUFAs whose relative amounts could be determined, and the investigation of alterations in mood disorders as a primary or secondary outcome. Here constituted excluded by standards: Research that (i) provided inadequate information or outcomes and (ii) used intervention with food strategy. The Jadad requirements and detailed data about (i) authorization of RCT before executing the investigation, (ii) sufficient investigators illuminating, (iii) using an assessment with intention-to-treat, (iv) regulation over their health nutrition, (v) evaluation of adherence with plasma fatty acid evaluation,(vi) substantial variations from the beginning, (vii) a reasonable sampling estimate, and (viii) a suitable sample size were all taken in consideration when determining the investigation to individually extracted information utilizing a same abstracting method for every recognized experiment. A pair of investigators carried out this approach separately, finally addressing and settling disagreements. In terms of the 59 investigations that were initially chosen, one was eliminated due to a non-randomized, non-placebo regulated layout; a pair was stopped due to the adoption of a nutritional therapy layout; five were destroyed since the depressed position was identified instead of an assessment magnitude, as a categorized parameter; two were eliminated due to an insufficient or inadequately equivalent grading achieved of depression was used, and two were eliminated due to weakly equivalent omega-3 PUFA or placebo substances. Forty-seven studies were ultimately chosen as suitable for inclusion in the current review of systems using this filtering technique.
The medical result of interest was the standard deviation in outcomes on an anxiety assessment instrument between the beginning and ending for patients receiving PUFA omega-3 fatty acids versus patients taking a placebo. The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS), whether the 9-items short form, 17-items, 21-items, or 25-items scale, and Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), have been the preferred evaluations for determining the severity of depression. HDRS levels from each study were applied whenever became obtainable. In the absence of the HDRS, employed the MADRS. That utilized the clinician-rated stress measurement since the researchers specified its primary endpoint lacking HDRS or MADRS statistics.
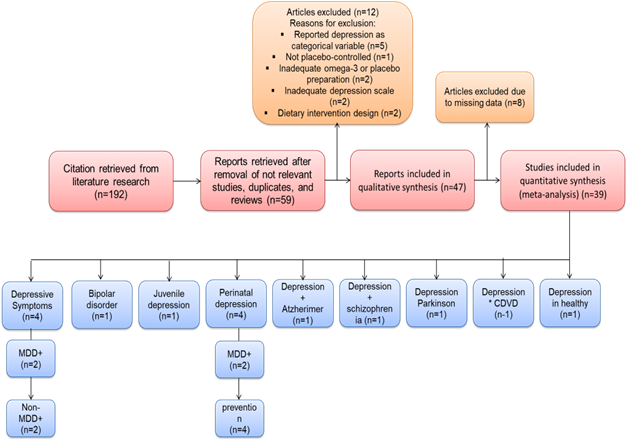
Figure 1. PRISMA structure diagram showing the search technique used in the current inquiry
Detailed investigation information was supplied through the researchers, five studies’ SDs and 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained from diagrams, one research’s information was averaged, three studies’ information was calculated to results from every trial that used an identical depression-related determine outlined globally. These researchers were chosen because that knew other tests did not, including indicates and variance. Thirty-nine articles participated in the investigation after eight studies were eliminated from the meta-analysis to dataset deficiencies.
|
Table 1. Ordered chronologically by kind of depression, regulated experiments examining the impact of omega-3 (PUFAs) on sadness are presented |
||||||||||
|
Author |
Year |
Participating Group |
Subjects, n (I/C) |
Type of treatment |
Outcome measure |
Intervention |
Duration (weeks) |
Study quality |
Daily dose |
Placebo |
|
MDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(23) |
2002 |
PzwithMDD |
20(10/10) |
Allbut1 used antidepressant |
HDRS |
E-EPA |
4 |
8 |
2 g |
NR |
|
(24) |
2003 |
PzwithMDD |
36(18/18) |
None |
MADRSHDRS |
DHA |
6 |
7 |
2 g |
NR |
|
Non-MDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bipolar disorder |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(25) |
1999 |
Pz with bipolar disorder |
30(14/16) |
Heterogeneous |
HDRS |
EPA+DHA |
16 |
8 |
6,2gEPA+3,4 g DHA |
Olive oil |
|
(26) |
2004 |
Pz with bipolar disorder |
21(12/9) |
Heterogeneous |
HDRS |
EPA+DHA |
4 |
4 |
5–5,2gEPA+3–3,4 gDHA or 1,3g EPA+0,7g DHA |
NR |
|
Depressive symptom sinpz with Alzheimerd isease or mild cognitive impairment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(27) |
2008 |
Pz with Alzheimer Disear or mild Cognitive impairment
|
46(24/22) |
Unclear |
MMSE,HDRS |
EPA+DHA |
24 |
9 |
1,08gEPA+0,72 g DHA |
Olive oil Ethyl esters |
|
Depressive symptom sinpz with schizophrenia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(28) |
2001 |
Pz with schizophrenia |
8/ (43/44) |
All dul used neuroleptic |
Madres |
E-EPA |
1b |
10 |
3u |
Mineral oil |
|
MDD inpz with Parkinson’s disease |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(29) |
2008 |
Pz with Parkinson’s disease and MDD |
29[NAD:13(6/7) AD:16(8/8)] |
26 levodopa, 19 pramipexol,5 amantadine, 4 COM Tinhibitors, 6SSRI, 4 tricyclics, 2 trazodone |
MADRS, BDI, CGI |
EPA+DHA |
12 |
10 |
0,72 gEPA. 0,48 gDHA |
Mineral oil |
Experiments were organized based on the statistically significant medical features of the population on which that were conducted to examine outcomes related to respondent evaluation: (i) People with depression, (ii) Patients with bipolar disorder, (iii) Adolescents or kids with bipolar disorder or depression (iv) Women who have perinatal depressive symptoms (v) those suffering from moderate Cognition issues (vi) Patients with schizophrenia (vii) Parkinson’s condition sufferers (vii) Patients with concurrent cardiovascular diseases and (ix) Patients in excellent condition.
A variety of information was acquired, including the type of evaluation, the total quantity of participants in the trial, the type of substance utilized for the treatment, the sort of a placebo, everyday dose, the length of the treatment, measurements of the results, and data to determine the research’s level of quality. In the combined evaluations, RCTs indicating multiple compositions or dosages of omega-3 PUFA were treated as separate trials. Since several groups were examined in a single research investigation, every group was treated as its research group in the meta-analyses.
Analytical Statistics
Regular information appears in explanatory tables with the mean and standard deviations indicated. The averages and SDs of all depression assessments for both groups of participants were merged. For each investigation, the standardized mean effects were computed utilizing Hedges corrected g to account for little sampling biases. The total impact quantity was calculated using both random- and fixed-effects approaches. Heterogeneity was examined by applying the Higgins I2 estimate. The unpredictable impact categories were chosen over alternative approaches, while study outcomes were heterogeneous.
Using the funnel plot to examine for funnel plot asymmetrical and depending on the number of studies allowed researchers to investigate potential publication bias for their evaluation of RCTs that included MDD patients versus those who weren’t confirmed with the condition according to DSM-IV criteria. A linear approach was used to accomplish the meta regression using the factors that matter, while the impact magnitude standardized mean difference (SMD) as the dependent factor and serving as the independent factor. Experiments were weighted using the general inverted variation technique. While applying meta-regression using normalized initial depression ratings, average ages of those who participated, and our adjusted Jadad scores of the research, accordingly, impacts related to the intensity age of individuals, the severity of feelings of depression, and the caliber of the research studied. The investigations were grouped into others utilizing mainly EPA, with others involving exclusively DHA as part of an investigation and a qualitative examination of the treatment employed. The population was divided into three groups: predominantly EPA, pure EPA, and primarily DHA supplemented for second research. Additionally, the treatment method has been studied by combining investigations employing omega-3 and medicines for depression or maintenance. An examination of the applied EPA and DHA using meta-regression dosages was utilized to calculate the quantitative analysis of the dosage.
According to reviewing software version 5,2, Higgins’ I2, woodland, and funnel graphs, random- and fixed-effects models estimates were carried out; in SPSS version 17, meta-regression analysis was carried out.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Broader Research
Table 1 lists the investigations that were a part of the systemic evaluation and meta-analysis’s most significant characteristics. Significant variations between research were discovered for each feature considered, and a possible score of the quality of the investigations averaged roughly an out of a potential. The average length of the trials was around weeks, and studies utilized pure EPA while studies used pure DHA. In comparison, 1,94 g of EPA+DHA had a moderate dosage of 1,38 g.
Table 1 displays the typical dosages of pure DHA and EPA. The Montgomery- Asberg depressive scale and the Hamilton Depressive Grading Factor were the primary outcome measures employed in most RCTs. Four investigations performed on bipolar depressed patients reported no apparent distinctions in any outcome determined within the EPA and placebo categories; single research on diabetics; and two studies on patients with the condition and chronic tiredness, respectively, reported nothing important effects of fatty acids omega-3 against placebo.
Depression
To determine to reveal the outcomes are changed when taking into account a mood-improving impact on depressed non-organic disease sufferers’ signs, metabolism, or genetically associated neurologic illness, a general evaluation involving the two categories was done. Assuming a fixed-effects approach, the combined variance of averages was 0,27 SD, while utilizing random-effects analysis, the conflict was 0,39 SD. Heterogeneity, though, was evident. Figure 2 depicts the funnel plot that was created to evaluate this heterogeneity. There was little inequality proof in the funnel graph. There existed no link within the meta-regression research impact and survey quantity, showing that the population of participant’s portion had no bearing on its conclusions.
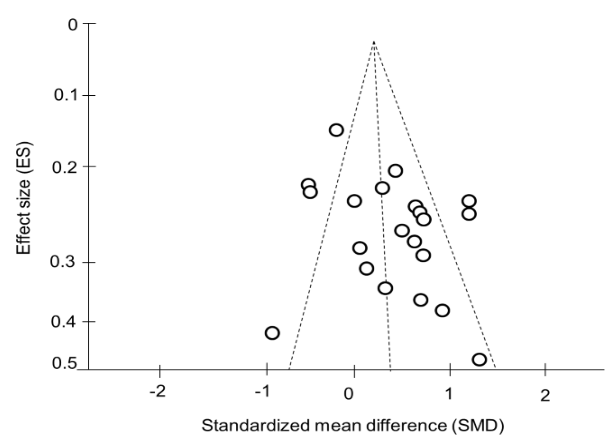
Figure 2. Effectiveness calculations in particular experiments performed on individuals with severe depression who had no additional illnesses are shown in a funnel-shaped graph
Psychotic Illness
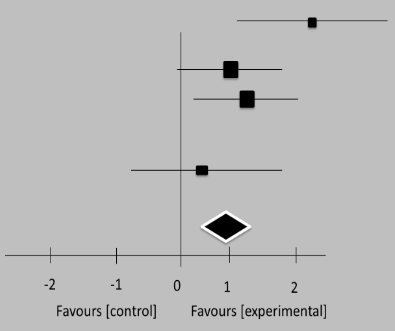
The gathered clinical experiments involving bipolar illness users for comprehensive analysis. One investigation that made up more than 70 % of the weight of the evaluation’s three aggregated investigations showed omega-3 fatty acids considerably impact reducing bipolar disorder in adults with depressed symptoms.
|
Table 2. Individual and cumulative effect size estimates, as well as 95 % confidence intervals, are shown in a forest plot for three researches including individuals with bipolar depression |
||||||||||
|
|
Control |
Experimental |
|
Std. Mean difference |
|
|
||||
|
Study or division |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Weight |
IV. Random. 95 % |
CI Year |
|
|
Stoll 199 |
16,7 |
9,5 |
15 |
4,9 |
5,7 |
17 |
17,4 % |
1,40 [055,2.20] |
1999 |
|
|
Frangou 2006 |
12,4 |
6,8 |
24 |
9,8 |
6,6 |
25 |
36,1 % |
0,55 [-0,01, 1,24] |
2006 |
|
|
Frangou 2006 |
12,3 |
5,4 |
25 |
9,4 |
5,1 |
22 |
33,6 % |
0,65 [0,11,1,26] |
2006 |
|
|
Frangou 2007 |
11 |
5,1 |
8 |
11 |
2,3 |
9 |
11,1 |
0,44 [-0,61,1,51] |
2007 |
|
|
Total (95 % CI) |
|
|
72 |
|
|
73 |
100,0 % |
0,77 [0,35,1,14] |
|
|
Depression Perinatal
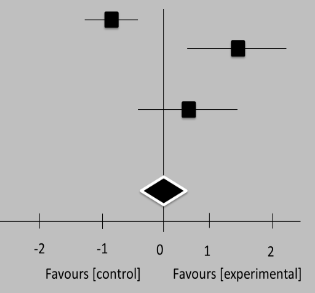
Six research were undertaken to look at the effects of omega-3 PUFA on prenatal stress. This separated between studies on pregnant MDD moms versus on women with first prophylaxis who looked to be effective. Both evaluations, though, produced conflicting findings. Fatty acids such as omega-3 can be useful in reducing despair during childbirth. In addition to the clinical effectiveness of omega-3, it is significant to emphasize indicated every research found that supplementing with the tolerability of omega-3 fatty acids effectively and had no adverse effects on treating participants or neonates. Tests on “moderate cognitive impairment (MCI),” schizophrenia, and were undertaken for individuals with primary diseases besides sadness.
|
Table 3. Individual and cumulative effect size estimates, as well as 95 % confidence intervals, are shown in a forest plot for three studies including pregnant women suffering severe depressive disorders |
||||||||||
|
|
Control |
Experimental |
|
Std. Mean difference |
|
|
||||
|
Study or division |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Weight |
IV. Random. 95 % |
CI Year |
|
|
Freeman 2008 |
10,1 |
5,6 |
29 |
12,8 |
6,4 |
32 |
34,4 % |
-0,55 [1,07,-0,03] |
2008 |
|
|
Su 2008 |
15,5 |
5,1 |
19 |
10,11 |
5,2 |
19 |
33,11 % |
1,02 [0,32, 2,72] |
2008 |
|
|
Rees 2008 |
10,2 |
6,2 |
14 |
8,1 |
6,2 |
14 |
32,5 % |
0,37[-0,41,1,13] |
2008 |
|
|
Total (95 % CI) |
|
|
63 |
|
|
55 |
100,0 % |
0,24 [-0,75, 1,24] |
|
|
|
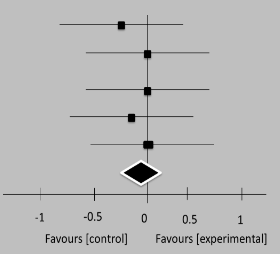
Table 4. Forest plot displaying separate and combining estimates of effect sizes and 95 % confidence intervals for three studies done on asymptomatic pregnant women for the prevention of depression after childbirth. |
||||||||||
|
|
Experimental |
Control |
|
Difference std and mean |
|
|
||||
|
Study or division |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Weight |
IV. Random. 95 % |
CI Year |
|
|
Llorente 2003 |
4,9 |
5,7 |
17 |
16,7 |
9,5 |
15 |
17,4 % |
1,40 [055,2.20] |
2003 |
|
|
Doombos 2009 |
2 |
47 |
44 |
6 |
54 |
35 |
18,2 % |
0,02 [-0,42, 0,45] |
2009 |
|
|
Doombos 2009 |
6 |
6 |
43 |
5 |
3 |
34 |
41 |
-0,12 [-0,55., 033] |
2009 |
|
|
Mozurkewich 2013 |
7,1 |
5,5 |
41 |
6,1 |
7,1 |
45 |
18,4 % |
-0,11 [-0,55, 0,31] |
2009 |
|
|
Mozurkewich 2013 |
6,5 |
5,2 |
38 |
5,5 |
7,1 |
45 |
21,9 % |
0,02 [-0,42, 0,45] |
2013 |
|
|
Total (95 % CI) |
|
|
207 |
|
|
200 |
100,5 % |
0,05[-0,35,1,14] |
|
|
|
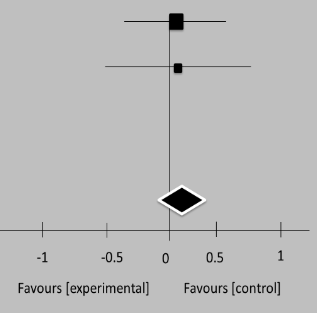
Table 5. Forest plot displaying independent and aggregate estimates of effect sizes and 95 % confidence intervals for two studies done on individuals with Alzheimer’s or moderate cognitive dysfunction |
||||||||||
|
|
Control |
Experimental |
|
Std. Mean difference |
|
|
||||
|
Study or division |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Mean |
SD |
Total |
Weight |
IV. Random. 95 % |
CI Year |
|
|
Freund-Levi 2007 |
1,4 |
2,1 |
105 |
1,4 |
2,4 |
104 |
88,9 % |
0,04 [-0,22, 0,33] |
2008 |
|
|
Chiu 2008 |
3,07 |
5,51 |
12 |
2,75 |
2,55 |
20 |
13,1 % |
0,11[-0,62 |
2008 |
|
|
Total (95 % CI) |
|
|
117 |
|
|
124 |
100,0 % |
0,05[-0,35,1,31] |
|
|
In contrast, outcomes for patients with various illnesses, good health, and premature babies had been insufficient. That showed that using omega-3 PUFA as medication had been successful for persons with a medical history of Effects MDD and on sufferers of depression who are not MDD-diagnosed. The assessment of research on bipolar disease found a favorable benefit of omega-3 PUFA; nevertheless, the quality of the proof is diminished because several studies that can have an impact on the supplement’s overall impact were not included in the statistical evaluation. The overall beneficial effect of omega-3 PUFA was discovered if the investigations that involved individuals who do not have MDD or others who have patients with depressive symptoms were fully assessed by clinicians combined.
CONCLUSIONS
The investigations eliminated from this systematic review needed to be more understanding regarding the technique that employed, necessitating their elimination to attempt to narrow the gap between RCTs and enhance the standard of information provided. These trials can be closely related to the subject of the current investigation, and an extensive review could reinforce the findings in this systematic review. Spoke regarding the caliber of the research and probable causes for independence in a particular segment of the e-discussion. While performing a reasonable combination of tests, a non-modifiable measure of variation resulting from certain traits in every tested subject nonetheless undermined the pooled analysis of this research. Adding all of the upgraded RCTs subsequently reinforced the findings on the beneficial the impact of omega-3 PUFA ingestion on depression when compared to previous research.
REFERENCES
1. Giacobbe J, Benoiton B, Zunszain P, Pariante CM, Borsini A. The anti-inflammatory role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolites in pre-clinical models of psychiatric, neurodegenerative, and neurological disorders. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 28;11:450833. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00122
2. Wolters M, von der Haar A, Baalmann AK, Wellbrock M, Heise TL, Rach S. Effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in the prevention and treatment of depressive disorders—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2021 Mar 25;13(4):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041070
3. Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski ŁA, Turczyn P, Frasuńska J, Paradowska-Gorycka A, Tarnacka B. Significance of Omega‐3 Fatty Acids in the Prophylaxis and Treatment after Spinal Cord Injury in Rodent Models. Mediators of Inflammation. 2020;2020(1):3164260. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3164260
4. Bozzatello P, Brignolo E, De Grandi E, Bellino S. Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids in psychiatric disorders: a review of literature data. Journal of clinical medicine. 2016 Jul 27;5(8):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5080067
5. Ouyang WC, Sun GC, Hsu MC. Omega-3 fatty acids in cause, prevention and management of violence in schizophrenia: Conceptualization and application. Aggression and violent behavior. 2020 Jan 1;50:101347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2019.101347
6. Rodríguez-Iglesias N, Nadjar A, Sierra A, Valero J. Susceptibility of female mice to the dietary omega-3/Omega-6 fatty-acid ratio: effects on adult hippocampal neurogenesis and glia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022 Mar 21;23(6):3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063399
7. Trebatická J, Hradečná Z, Surovcová A, Katrenčíková B, Gushina I, Waczulíková I, Sušienková K, Garaiova I, Šuba J, Ďuračková Z. Omega-3 fatty-acids modulate symptoms of depressive disorder, serum levels of omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6/omega-3 ratio in children. A randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Psychiatry research. 2020 May 1;287:112911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112911
8. Guu TW, Mischoulon D, Sarris J, Hibbeln J, McNamara RK, Hamazaki K, Freeman MP, Maes M, Matsuoka YJ, Belmaker RH, Marx W. A multi-national, multi-disciplinary Delphi consensus study on using omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) for the treatment of major depressive disorder. Journal of affective disorders. 2020 Mar 15;265:233-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.050
9. Rittenhouse M, Sambuughin N, Deuster P. Optimization of Omega-3 Index Levels in Athletes at the US Naval Academy: Personalized Omega-3 Fatty Acid Dosage and Molecular Genetic Approaches. Nutrients. 2022 Jul 20;14(14):2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142966
10. Tomczyk M, Jost Z, Chroboczek M, Urbański R, Calder PC, Fisk HL, Sprengel M, Antosiewicz J. Effects of 12 wk of Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in Long-Distance runners. Medicine and science in sports and exercise. 2022 Sep 27;55(2):216. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000003038
11. Checa-Ros A, D’Marco L. Role of omega-3 fatty acids as non-photic zeitgebers and circadian clock synchronizers. International journal of molecular sciences. 2022 Oct 12;23(20):12162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012162
12. van Verseveld M, Mocking RJ, Scheepens D, Ten Doesschate F, Westra M, Schoevers RA, Schene AH, van Wingen GA, van Waarde JA, Ruhé HG. Polyunsaturated fatty acids changes during electroconvulsive therapy in major depressive disorder. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 2023 Apr 1;160:232-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.02.028
13. Xia DN, Tan YQ, Yang JY, Zhou G. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: a promising approach for the management of oral lichen planus. Inflammation Research. 2020 Oct;69:989-99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01388-0
14. Ouyang WC, Sun GC, Hsu MC. Omega-3 fatty acids in cause, prevention and management of violence in schizophrenia: Conceptualization and application. Aggression and violent behavior. 2020 Jan 1;50:101347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2019.101347
15. Kapoor B, Kapoor D, Gautam S, Singh R, Bhardwaj S. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs): Uses and potential health benefits. Current nutrition reports. 2021 Sep;10:232-42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-021-00363-3
16. Liang Z, Lou Y, Li Z, Liu S. Causal relationship between human blood omega-3 fatty acids and the risk of epilepsy: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Frontiers in Neurology. 2023 Mar 9;14:1130439. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2023.1130439
17. Zailani H, Satyanarayanan SK, Liao WC, Liao HF, Huang SY, Gałecki P, Su KP, Chang JP. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in managing comorbid mood disorders in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023 Apr 2;12(7):2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072653
18. Déniz C, Raba-Parodi C, García-Raimundo E, Macía I, Rivas F, Ureña A, Muñoz A, Moreno C, Serratosa I, Masuet-Aumatell C, Escobar I. Preoperative omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio could predict postoperative outcomes in patients with surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Current Oncology. 2022 Sep 28;29(10):7086-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100556
19. Katrenčíková B, Vaváková M, Waczulíková I, Oravec S, Garaiova I, Nagyová Z, Hlaváčová N, Ďuračková Z, Trebatická J. Lipid profile, lipoprotein subfractions, and fluidity of membranes in children and adolescents with depressive disorder: Effect of omega-3 fatty acids in a double-blind randomized controlled study. Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 8;10(10):1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101427
20. Perić I, Lješević M, Beškoski V, Nikolić M, Filipović D. Metabolomic profiling relates tianeptine effectiveness with hippocampal GABA, myo-inositol, cholesterol, and fatty acid metabolism restoration in socially isolated rats. Psychopharmacology. 2022 Sep;239(9):2955-74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-022-06180-y
21. González AP, Flores-Ramírez A, Gutiérrez-Castro KP, Luévano-Contreras C, Gómez-Ojeda A, Sosa-Bustamante GP, Caccavello R, Barrera-de León JC, Garay-Sevilla ME, Gugliucci A. Reduction of small dense LDL and Il-6 after intervention with Plantago psyllium in adolescents with obesity: a parallel, double blind, randomized clinical trial. European journal of pediatrics. 2021 Aug;180:2493-503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-021-04064-5
22. Zorgetto-Pinheiro VA, Machate DJ, Figueiredo PS, Marcelino G, Hiane PA, Pott A, Guimarães RD, Bogo D. Omega-3 fatty acids and balanced gut microbiota on chronic inflammatory diseases: A close look at ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2022 Apr 1;25(4):341-54. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2021.0012
23. Frasure-Smith N, Lespérance F, Julien P. Major depression is associated with lower omega-3 fatty acid levels in patients with recent acute coronary syndromes. Biological psychiatry. 2004 May 1;55(9):891-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.01.021
24. Ciappolino V, Delvecchio G, Agostoni C, Mazzocchi A, Altamura AC, Brambilla P. The role of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3PUFAs) in affective disorders. Journal of affective disorders. 2017 Dec 15;224:32-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.12.034
25. Freeman MP, Hibbeln JR, Wisner KL, Davis JM, Mischoulon D, Peet M, Keck Jr PE, Marangell LB, Richardson AJ, Lake J, Stoll AL. Omega-3 fatty acids: evidence basis for treatment and future research in psychiatry. Journal of Clinical psychiatry. 2006 Dec 15;67(12):1954.
26. Turnbull T, Cullen-Drill M, Smaldone A. Efficacy of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on improvement of bipolar symptoms: a systematic review. Archives of psychiatric nursing. 2008 Oct 1;22(5):305-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnu.2008.02.011
27. Li GR, Sun HY, Zhang XH, Cheng LC, Chiu SW, Tse HF, Lau CP. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit transient outward and ultra-rapid delayed rectifier K+ currents and Na+ current in human atrial myocytes. Cardiovascular research. 2009 Feb 1;81(2):286-93. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvn322
28. O’Neill B, Hafiz MA, De Beer DA. Corrosion of Penlon sevoflurane vaporisers. Anaesthesia. 2007 Apr;62(4):421-. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2007.05048.x
29. Harvey MG, Cave GR. Intralipid infusion ameliorates propranolol-induced hypotension in rabbits. Journal of Medical Toxicology. 2008 Jun;4:71-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160958
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None.
FINANCING
None.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Manisha Chandna, Sidhant Das, Malathi H, Neha Rana, Geetika Madan Patel, Snehanshu Dey, N.J.Patil.
Investigation: Manisha Chandna, Sidhant Das, Malathi H, Neha Rana, Geetika Madan Patel, Snehanshu Dey, N.J.Patil.
Methodology: Manisha Chandna, Sidhant Das, Malathi H, Neha Rana, Geetika Madan Patel, Snehanshu Dey, N.J.Patil.
Writing - original draft: Manisha Chandna, Sidhant Das, Malathi H, Neha Rana, Geetika Madan Patel, Snehanshu Dey, N.J.Patil.
Writing - review and editing: Manisha Chandna, Sidhant Das, Malathi H, Neha Rana, Geetika Madan Patel, Snehanshu Dey, N.J.Patil.