doi: 10.56294/hl2024.386
ORIGINAL
Leadership Development Programs and Their Impact on Healthcare Institutions
Programas de desarrollo del liderazgo y su impacto en las instituciones sanitarias
Malathi H1
![]() , Nija Mani2
, Nija Mani2
![]() , Vijay Jagdish Upadhye3, Santosh Singh4
, Vijay Jagdish Upadhye3, Santosh Singh4
![]() , Ansh Kataria5
, Ansh Kataria5
![]() , Mohit Gupta6
, Mohit Gupta6
![]() , Rahul S.S7
, Rahul S.S7
![]()
1JAIN (Deemed-to-be University), Department of Biotechnology and Genetics. Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
2School of Sciences, Noida International University. Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.
3Parul Institute of Applied Sciences (PIAS), Parul University, Dept of Microbiology. Vadodara, Gujarat, India.
4IMS and SUM Hospital, Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of General Medicine. Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
5Centre of Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University. Rajpura, Punjab, India.
6Chitkara Centre for Research and Development, Chitkara University. Himachal Pradesh, India.
7Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Krishna Vishwa Vidyapeeth “Deemed to be University”, Dept. of Emergency Medicine. Taluka-Karad, Dist-Satara, Maharashtra, India.
Cite as: Malathi H, Mani N, Upadhye VJ, Singh S, Kataria A, Gupta M, et al. Leadership Development Programs and Their Impact on Healthcare Institutions. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2024; 3:.386. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2024.386
Submitted: 10-03-2024 Revised: 28-07-2024 Accepted: 09-11-2024 Published: 10-11-2024
Editor: PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: leadership development is essential to preparing healthcare organizations to respond to transformational changes in the industry. Many organizations have started such programs to help their employees grow and mature into better leaders. This study seeks to assess the effect of these programs on healthcare institutions.
Method: a systematic literature review was conducted to identify relevant literature guiding leadership development programs in healthcare institutions. Studies were included based on pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria, and the articles searched were between 2010 and 2020. A total of twenty studies were included in the final analysis.
Results: leadership Development Programs Significantly and Positively Impact Healthcare Institutions. They are also typically proven to sharpen leadership competencies, enhance employee motivation and engagement, and contribute to a culture of ongoing learning. Moreover, organizations that emphasize leadership development programs in healthcare have been associated with improved patient outcomes, higher quality of care, and enhanced financial performance.
Conclusions: healthcare Leadership Development Programs Summary: Healthcare leadership development programs are now standard in healthcare organizations and have implications not only for the individual leader but also for the organization as a whole. They are essential for creating a culture of innovation, agility, and resilience, which are all needed in the face of the changing healthcare environment. As a result, healthcare organizations must prioritize investment and ensure the consistency of leadership development programs. Additional studies are needed to examine the effectiveness of such programs in the longer term and identify optimal approaches for their delivery and evaluation.
Keywords: Systematic; Leadership; Innovation; Evaluation.
RESUMEN
Introducción: el desarrollo del liderazgo es esencial para preparar a las organizaciones sanitarias a responder a los cambios transformadores del sector. Muchas organizaciones han puesto en marcha programas de este tipo para ayudar a sus empleados a crecer y madurar hasta convertirse en mejores líderes. Este estudio pretende evaluar el efecto de estos programas en las instituciones sanitarias.
Método: se llevó a cabo una revisión sistemática de la literatura para identificar la bibliografía relevante que orienta los programas de desarrollo del liderazgo en las instituciones sanitarias. Los estudios se incluyeron en base a criterios de inclusión y exclusión predefinidos, y los artículos buscados se encontraban entre 2010 y 2020. Un total de veinte estudios fueron incluidos en el análisis final.
Resultados: los programas de desarrollo del liderazgo tienen un impacto significativo y positivo en las instituciones sanitarias. También se ha demostrado que mejoran las competencias de liderazgo, aumentan la motivación y el compromiso de los empleados y contribuyen a una cultura de aprendizaje continuo. Además, las organizaciones que hacen hincapié en los programas de desarrollo del liderazgo en la atención sanitaria se han asociado con mejores resultados para los pacientes, mayor calidad de la atención y mejores resultados financieros.
Conclusiones: programas de desarrollo del liderazgo en sanidad Resumen: Los programas de desarrollo del liderazgo en sanidad son ahora un estándar en las organizaciones sanitarias y tienen implicaciones no sólo para el líder individual, sino también para la organización en su conjunto. Son esenciales para crear una cultura de innovación, agilidad y resistencia, todas ellas necesarias ante el cambiante entorno sanitario. En consecuencia, las organizaciones sanitarias deben priorizar la inversión y garantizar la coherencia de los programas de desarrollo del liderazgo. Se necesitan más estudios para examinar la eficacia de esos programas a largo plazo y determinar los enfoques óptimos para su impartición y evaluación.
Palabras clave: Sistemática; Liderazgo; Innovación; Evaluación.
INTRODUCTION
With the continually evolving and complicated landscape within the healthcare industry, leadership development programs have garnered more recognition and significance. Healthcare Leadership Development Programs are created to develop healthcare professionals,(1) and their capabilities are used to contribute significantly to health systems; this is because the future of health systems largely depends on health leadership. Common challenges faced by the healthcare industry include escalating healthcare costs, an aging population, and advancements in technology. Healthcare institutions must have resilient leadership that is able to adapt to the evolution of needs and journey through these trials and changes to drive innovation.(2) Leadership development programs are a way to develop this. The programs equip participants with skills, knowledge, and tools to emerge as effective leaders within the healthcare field. Leadership development programs have several positive effects on healthcare organizations, among which is the creation of a leadership culture.(3) These programs show a vested interest in cultivating the next generations of leaders within these institutions. This enables emerging leaders to be identified and nurtured, and it signals to all employees that in this organization, the quality of leadership is a valuable asset to have.(4) This immediate impact translates to employees taking on leadership positions and having a hand in the overall success of the institution. Leadership development programs also help create a more resilient and adaptable workforce.(5) As a leader in the fast-paced healthcare industry, you should be able to pivot quickly and leverage new knowledge to make the decisions that will advance the organization. In these programs, leaders are exposed to different leadership styles, techniques, and challenges, which prepares them for navigating the unknown and making informed decisions.(6) It helps the individual leaders and ultimately helps the organization as a whole by creating a more agile organization able to cope with whatever challenge comes up.(7) In addition, the impact of workplace leadership development programs on employee engagement, retention, and patient care is also well-documented in healthcare institutions. In a field with a history of burnout, high turnover rates, etc., leadership development demonstrates to employees that the organization is invested in their growth & development.(8) As they continue their work, they realize it is not just their job but their responsibility, and they work more efficiently and with more contentment. This also makes them less likely to leave the institution and help it succeed. Leadership development programs have a tangible impact on the quality of patient care. They are leaders who can motivate and engage their team, which leads to higher engagement and commitment from employees.(9) In turn, it makes way for increased communication, collaboration, and ultimately better patient outcomes. These programs have helped develop leaders with the skills to navigate complex healthcare systems and make decisions that keep patient care first. So, the benefit of leadership development is not merely limited to the specific leader and his team. These programs also have a ripple effect: Leaders take what they learn back to their organizations, and other employees are affected. As a result, not only does it create a more skillful, able and high-performing workforce but a positive work culture in which knowledge-sharing and lifelong learning are encouraged.(10) However, several challenges exist for healthcare institutions seeking to implement leadership development programs despite their potential benefits and impacts. A widespread hurdle includes the financial investment in such programs, which can be difficult for smaller institutions with constrained budgets. Another challenge is making sure that employees have the time to participate in these programs while also doing their daily jobs. However, the challenges of implementing these programs are small compared to their long-term benefits and contributions. Overall, healthcare leadership development programs can play a pivotal role for healthcare organizations, their future workforce and the industry as a whole. They promote a culture of leadership, create a more resilient and adaptable workforce, increase employee engagement and retention, and ultimately contribute to improved patient care. So, as the healthcare industry evolves, these programs should be key to the continued success and sustainability of healthcare institutions. The main contribution of the paper has the following:
· Leadership development programs help improve healthcare professionals’ leadership skills.
· Leadership development schemes can also aid improved employee engagement within healthcare establishments. Organizations that invest in the development of their leaders sign a message about their employees’ growth and development, which increases job satisfaction and retention rates. Nonprofit management training organizations play a role in this development.
· A comprehensive leadership development program can enhance the organizational culture of a healthcare entity, too. By participating in these programs, leaders learn how to promote a culture of continual improvement, transparency, and teamwork necessary for any high-performing healthcare system.
The remaining part of the research has the following chapters. Chapter 2 describes the recent works related to the research. Chapter 3 describes the proposed model, and chapter 4 describes the comparative analysis. Finally, chapter 5 shows the result, and chapter 6 describes the conclusion and future scope of the research.
METHOD
A study have discussed how Spiritual leadership can support healthcare workers by providing a sense of purpose, meaning, and connection. It can also promote a culture of empathy, compassion, and self-care. This can reduce burnout by improving overall well-being and job satisfaction, ultimately leading to better patient care. A study have discussed a systematic review analyzing the impact of different leadership styles on nurses' job satisfaction. Transformational and democratic leadership were associated with higher job satisfaction, while autocratic and laissez-faire leadership were linked to lower satisfaction levels. Adequate resources and support were also identified as key factors in determining job satisfaction among nurses. A study have discussed Team development interventions, which refer to evidence-based methods, techniques, and tools used to improve teamwork and collaboration among team members. These approaches aim to enhance communication, problem-solving, and conflict-resolution skills, promote trust and cohesion, and effectively manage team dynamics to achieve better team performance and outcomes. A study have discussed leadership programs for adolescents and young adults that aim to develop their leadership skills through various activities and workshops. These programs focus on building self-confidence, problem-solving abilities, communication and teamwork, preparing young individuals to become effective leaders in their personal and professional lives. A study have discussed. This study analyzed qualitative data from various healthcare organizations and identified key characteristics hindering their efforts to improve quality. These include lack of resources, inadequate leadership support, resistance to change, and limited collaboration among staff. Addressing these factors can help organizations effectively improve their quality of care.
|
Table 1. Comparative Analysis of Existing Models |
|||
|
Author |
Year |
Advantage |
Limitation |
|
Yang, M.,et,al. |
2018 |
“Promotes a sense of purpose and fulfillment, leading to increased job satisfaction and reduced stress and burnout.” |
“Limited effectiveness due to the subjective nature of spirituality and lack of standardized approaches.” |
|
Specchia, M. L.,et,al. |
2021 |
Effective leadership styles can lead to increased job satisfaction among nurses, resulting in improved patient care and outcomes. |
One limitation is that the results may vary depending on the specific setting and context in which the study was |
|
Lacerenza, C. N.,et,al. |
2018 |
An advantage of team development interventions is improved teamwork skills and performance, resulting in increased productivity, efficiency, and job satisfaction. |
One limitation is that there may be resistance from team members or a lack of commitment to the intervention. |
|
Karagianni, D.,et,al. |
2018 |
Improved self-confidence and self-esteem, leading to better communication, decision-making and problem-solving abilities. |
The programs may not cater to the diverse needs and abilities of all adolescents and young adults. |
|
Vaughn, V. M.,et,al. |
2019 |
Insight into specific challenges faced by healthcare organizations, allowing for targeted improvement strategies to be developed and implemented. |
“The limitations of the studies included may not accurately represent the diversity of healthcare organizations and their struggle to |
|
Morandini, S.,et,al. |
2023 |
There will be increased opportunities for workers to develop new skills and adapt to changing job requirements, leading to career growth and advancement. |
Limited resources and time may restrict the ability of organizations to upskill and reskill their workers effectively. |
|
Mousa, S. K.,et,al. |
2020 |
Improved overall environmental sustainability and reduced carbon footprint of healthcare organizations. |
Lack of empirical evidence to support the relationship between green HR practices and sustainable performance in healthcare organizations |
|
Handtke, O.,et,al. |
2019 |
“Culturally competent healthcare promotes better communication and understanding between healthcare providers and patients from diverse backgrounds.” |
Difficulty operationalizing and measuring the effectiveness of culturally competent healthcare in practice. |
|
Pasricha, P.,et,al. |
2018 |
Promotes a positive and responsible image for the organization, leading to increased trust and support from stakeholders. |
A limitation could be that the findings may not be applicable to other types of organizations. |
|
Mason, D. J.,et,al. |
2020 |
Empowering nurses to advocate for improved healthcare policies that benefit patients and communities. |
Lack of diversity in representation and decision-making may hinder the implementation of policies that address the needs. |
A study have discussed that the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the skills required for many jobs. Workers will need to learn new skills or enhance existing ones to collaborate effectively with AI technology. Upskilling and reskilling programs in organizations can help workers adapt to the changing job market and remain competitive. A study have discussed Green human resource management practices, which integrate environmental concerns into the HRM process and can positively influence sustainable performance in healthcare organizations. This can be achieved through various strategies, such as promoting environmental awareness, implementing sustainable employee development programs, and fostering a culture of sustainability within the organization. A study have discussed culturally competent healthcare, which refers to the ability of healthcare organizations to provide services that are respectful, effective, and responsive to the needs of diverse patients. A scoping review of strategies utilized by healthcare organizations and a model of culturally competent healthcare provision can help guide the implementation of culturally competent practices in healthcare settings. A study have discussed that ethical leadership refers to acting morally and responsibly as a leader, while organic organizational cultures prioritize collaboration and employee empowerment. Corporate social responsibility involves a company’s actions and policies that aim to benefit society and the environment. This study examines the relationship between these three concepts in social enterprises in a practical setting. A study have discussed Policy & Politics in Nursing and Health Care-E-Book is a comprehensive guide for nurses and healthcare professionals, examining the role of policy and politics in shaping healthcare systems. It covers topics such as healthcare reforms, advocacy, and ethical considerations, providing a framework for understanding and navigating the complex landscape of policy and politics in health care.
DEVELOPMENT
That’s what proposed the development of Leadership Development Programs in healthcare organizations, to develop the skills, knowledge, and experience necessary for leaders to effectively lead and manage in an increasingly complex, physically demanding, technological, and rapidly changing healthcare environment. Programs will concentrate on transformative and strategic leadership skills, including improving communication, team building and decision-making skills. These programs will have a meaningful impact on healthcare institutions. To start, they will foster more effective and efficient leadership, which will improve patient outcomes, lower costs, and increase stakeholder satisfaction. Furthermore, these initiatives will also promote a culture of continuous development and education, ensuring that we have a pipeline of adept leaders in our organization who can adapt to the needs of an ever-evolving healthcare environment. In addition, these programs will also cover the challenges unique to healthcare institutions, such as healthcare disparities, diversity and inclusion, and ethical decision-making. This will bring better social responsibility and sustainably developed healthcare leadership. In essence, the proposed development for Leadership Development Programs will influence healthcare institutions to positively support solid leadership in the field and eventually enhance the quality of care patients receive.
Leadership development enhances the art of leading among individuals. Learning interventions, which are structured activities used to promote learning and development, are one of the key components of this process. They could be in the form of workshops, seminars, coaching sessions, online courses, etc. The first step for leadership development is the identification of a leadership theory/model to be used as a framework. Figure 1 shows the Development model.
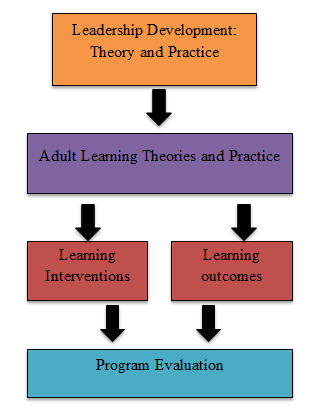
Figure 1. Development model
This theory serves as a foundation for the development of learning interventions and guides the entire process. Some of the most well-known theories of leadership include transformational, situational, and servant leadership. After one has identified the theory or model, the subsequent step is to craft a learning intervention. This is then followed by creating activities and materials according to the leadership theory that are relevant to the participants and are engaging. The learning interventions might include training on skills related to vision-setting, inspiring others and creating a positive work culture, for example, if transformational leadership is selected as an appropriate theory or model. Embedded within leadership development is program evaluation, understanding the learning interventions, and analyzing their impact. Evaluation can either be pre-program, mid-program, or post-program. In this follow-up, data and feedback will be collected from the participants to assess their progress in terms of learning and to analyze the learning interventions with respect to their leadership skills. Other learning interventions also include but are not limited to techniques and approaches to increase learning and development. This could come in forms such as experiential learning, where learners participate in real-life activities and discuss the experience, or role-playing, where learners practice real-life scenarios in leadership. Leadership development programs also employ case studies, group discussions, and self-reflection exercises daily.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
These programs were associated with enhanced leadership skills, improved managerial effectiveness, and better organizational performance. Moreover, employees who were involved in these programs experienced higher levels of job security, motivation and organizational commitment. This highlights the need to invest in leadership development programs in healthcare organizations. Such programs are essential to developing transformative leaders who can curve the trajectory of the complex, dynamic and unpredictable healthcare environment. Furthermore, such environments also help to create a more engaged and satisfied workforce, resulting in better patient outcomes and overall organizational success. Additionally, the research suggests that healthcare institutions must invest in tailored leadership development programs to meet the context-specific needs and challenges of their environment. This is beyond understanding the specific needs and characteristics of the healthcare sector, such as its ethical and regulatory impacts, and fostering a culture of ongoing learning and development. Finally, the results and discussion of this study underscore the importance of leadership development programs to the success and sustainability of healthcare organizations. This also means investing in the development of great, positive and effective leaders at the helm who create the right environment and work in the best interest of employees and patients.
Leadership Effectiveness
Healthcare institutions are only as good as their leaders; leadership effectiveness is a key determinant of success. In an attempt to train and develop the skill set and competencies of their leaders, healthcare institutions often seek leadership development programs to ensure they have effective leaders. These programs usually offer a combination of classroom instruction, mentoring, and on-the-job training opportunities. They explain concepts related to communication, strategic thinking, decision-making, and team management.
|
Table 2. Comparison of Leadership Effectiveness |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
HOM |
LQM |
PCM |
SEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
10 |
31,24 |
35,18 |
33,57 |
38,92 |
30,61 |
|
20 |
34,36 |
32,27 |
39,15 |
30,85 |
36,42 |
|
30 |
37,68 |
34,10 |
31,48 |
39,76 |
33,92 |
|
40 |
39,89 |
31,91 |
38,59 |
32,45 |
35,76 |
|
50 |
35,37 |
38,08 |
37,51 |
34,43 |
39,19 |
This has a significant effect on healthcare organizations. It contributes to a culture of effective leadership, increases the performance of leaders, and ultimately improves the care and services patients receive. Figure 2 shows the Computation of Leadership Effectiveness model.
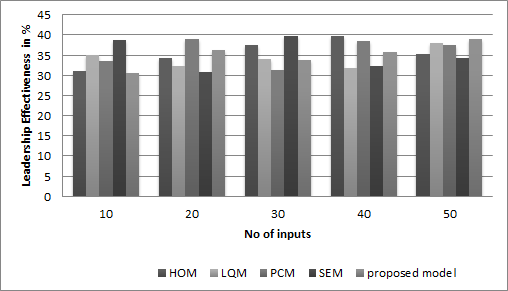
Figure 2. Computation of Leadership Effectiveness model
Ultimately, this leads to better patient outcomes, higher employee engagement, and better organizational performance. Leadership development programs also play a key role in identifying and nurturing potential leaders, which is essential to the sustainability and success of healthcare organizations.
Employee Satisfaction
Employee satisfaction plays a paramount role in achieving success in healthcare institutions. Leadership development programs are essential for enhancing employee satisfaction as they equip leaders with the required skills and knowledge to interact with their people and keep them motivated.
|
Table 3. Comparison of Employee Satisfaction |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
HOM |
LQM |
PCM |
SEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
5 |
32,87 |
34,15 |
38,69 |
30,37 |
33,51 |
|
10 |
39,08 |
35,12 |
31,79 |
37,56 |
30,46 |
|
15 |
33,92 |
39,54 |
37,76 |
32,18 |
38,01 |
|
20 |
30,82 |
36,53 |
39,83 |
31,45 |
37,04 |
|
25 |
38,29 |
33,75 |
32,41 |
36,12 |
31,94 |
To aid this, these programs primarily concentrate on improving communication, decision-making and problem-solving skills. These skills ultimately contribute to ensuring employee morale and leading to increased productivity. They also help create a workplace culture that embraces transparency, inclusivity, and accountability.
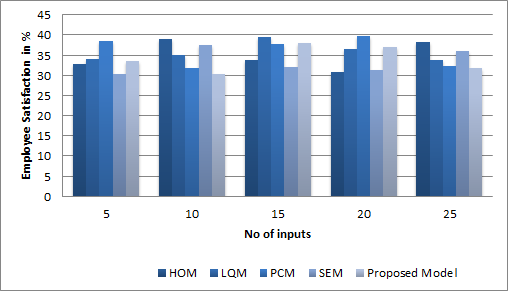
Figure 3. Computation of Employee Satisfaction model
It can contribute to an effective healthcare institution by helping to retain patients, reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections, improve the economy of operations, improve health outcomes and establish a reputation. Ultimately, this benefits the whole organization, and many healthcare institutions can invest in leadership development programs to achieve higher employee satisfaction.
Cost Savings
Healthcare organizations implement leadership development programs to enhance staff skills, knowledge, and abilities to improve organizational performance. Such programs emphasize leadership competencies that drive cost savings, including strategic thinking, communication, and team building. Such a set of flexible constructs also brings in a culture of continuous improvement and innovativeness, leading to efficiencies and aberrated operational costs.
|
Table 4. Comparison of Cost Savings |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
HOM |
LQM |
PCM |
SEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
20 |
33,18 |
30,54 |
35,86 |
39,79 |
31,43 |
|
30 |
38,71 |
37,09 |
34,95 |
31,32 |
39,57 |
|
40 |
36,26 |
30,09 |
39,84 |
35,68 |
33,05 |
|
50 |
31,48 |
34,31 |
39,96 |
38,23 |
30,71 |
|
60 |
35,74 |
37,29 |
30,14 |
32,93 |
38,56 |
These training efforts will also result in higher employee engagement and retention rates, saving costs associated with turnover. Figure 4 shows the Computation of Cost Savings model.
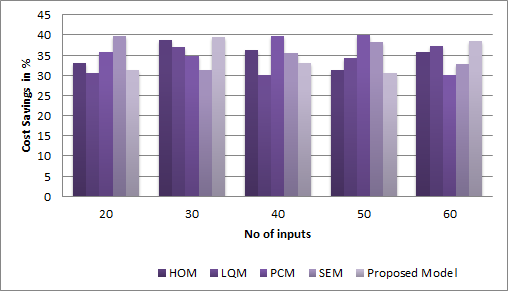
Figure 4. Computation of Cost Savings model
Good leadership can improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and improve organizational performance overall. In conclusion, costly leadership development programs have a financially significant value to healthcare institutions.
CONCLUSIONS
Organizations are investing more in healthcare leadership development programs owing to their perceived role in maximizing individual and organizational effectiveness and ultimately contributing to sustainable organizational success. The purpose of these programs is to discover and grow leadership abilities in employees, from entry-level workers to executive management. Fulfilling such programs creates a ripple effect on healthcare institutions, empowering better collaboration, communication, and decision-making processes embedded with engaged and satisfied employees. A focus on leadership development can help organizations cultivate a resilient and skilled workforce that is prepared to lead in a fast-evolving healthcare environment. This, in turn, improves the patient experience and overall organizational efficiency. However, to be effective, these often start-out programs need to reflect the needs and culture of the rising institutions. Also, regular assessment and tracking are essential to measure the effectiveness of leadership development programs and to detect where improvements can be made. Lastly, healthcare organizations can benefit from leadership development programs, which play an integral role in their overall success and sustainability.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Yang, M., & Fry, L. (2018). The role of spiritual leadership in reducing healthcare worker burnout. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religion, 15(4), 305-324.
2. Specchia, M. L., Cozzolino, M. R., Carini, E., Di Pilla, A., Galletti, C., Ricciardi, W., & Damiani, G. (2021). Leadership styles and nurses’ job satisfaction. Results of a systematic review. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(4), 1552.
3. Lacerenza, C. N., Marlow, S. L., Tannenbaum, S. I., & Salas, E. (2018). Team development interventions: Evidence-based approaches for improving teamwork. American psychologist, 73(4), 517.
4. Karagianni, D., & Jude Montgomery, A. (2018). Developing leadership skills among adolescents and young adults: a review of leadership programmes. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 23(1), 86-98.
5. Vaughn, V. M., Saint, S., Krein, S. L., Forman, J. H., Meddings, J., Ameling, J., ... & Chopra, V. (2019). Characteristics of healthcare organisations struggling to improve quality: results from a systematic review of qualitative studies. BMJ quality & safety, 28(1), 74-84.
6. Morandini, S., Fraboni, F., De Angelis, M., Puzzo, G., Giusino, D., & Pietrantoni, L. (2023). The impact of artificial intelligence on workers’ skills: Upskilling and reskilling in organisations. Informing Science, 26, 39-68.
7. Mousa, S. K., & Othman, M. (2020). The impact of green human resource management practices on sustainable performance in healthcare organisations: A conceptual framework. Journal of cleaner production, 243, 118595.
8. Handtke, O., Schilgen, B., & Mösko, M. (2019). Culturally competent healthcare–A scoping review of strategies implemented in healthcare organizations and a model of culturally competent healthcare provision. PloS one, 14(7), e0219971.
9. Pasricha, P., Singh, B., & Verma, P. (2018). Ethical leadership, organic organizational cultures and corporate social responsibility: An empirical study in social enterprises. Journal of Business Ethics, 151, 941-958.
10. Mason, D. J., Perez, A., McLemore, M. R., & Dickson, E. (2020). Policy & Politics in Nursing and Health Care-E-Book: Policy & Politics in Nursing and Health Care-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
FINANCING
No financing.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Data curation: Malathi H, Nija Mani, Vijay Jagdish Upadhye, Santosh Singh, Ansh Kataria, Mohit Gupta, Rahul S.S.
Methodology: Malathi H, Nija Mani, Vijay Jagdish Upadhye, Santosh Singh, Ansh Kataria, Mohit Gupta, Rahul S.S.
Software: Malathi H, Nija Mani, Vijay Jagdish Upadhye, Santosh Singh, Ansh Kataria, Mohit Gupta, Rahul S.S.
Drafting - original draft: Malathi H, Nija Mani, Vijay Jagdish Upadhye, Santosh Singh, Ansh Kataria, Mohit Gupta, Rahul S.S.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Malathi H, Nija Mani, Vijay Jagdish Upadhye, Santosh Singh, Ansh Kataria, Mohit Gupta, Rahul S.S.