doi: 10.56294/hl2024.384
ORIGINAL
Healthcare Management Strategies for Enhancing Patient Engagement
Estrategias de gestión sanitaria para mejorar la participación de los pacientes
Bhagwan Kulkarni1
![]() , Chandan Das2
, Chandan Das2
![]() , Pratibha Sharma3
, Pratibha Sharma3
![]() , Ashu Katyal4
, Ashu Katyal4
![]() , Jamuna K.V5
, Jamuna K.V5
![]() , Geetha Bhavani A6
, Geetha Bhavani A6
![]() , G.S. Karande7
, G.S. Karande7
![]()
1Parul institute of ayurveda and research, Ishwarpura campus, Parul University. Vadodara, Gujarat, India.
2IMS and SUM Hospital, Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of General Medicine. Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
3Centre of Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University. Rajpura, Punjab, India.
4Chitkara Centre for Research and Development, Chitkara University. Himachal Pradesh, India.
5JAIN (Deemed-to-be University), Department of Forensic science. Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
6Noida International University, Department of Chemistry, Greater Noida. Uttar Pradesh, India.
7Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Krishna Vishwa Vidyapeeth “Deemed to be University”, Dept. of Microbiology. Taluka-Karad, Dist-Satara, Maharashtra, India.
Cite as: Kulkarni B, Das C, Sharma P, Katyal A, Jamuna K, Geetha BA, et al. Healthcare Management Strategies for Enhancing Patient Engagement. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2024; 3:.384. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2024.384
Submitted: 09-03-2024 Revised: 27-07-2024 Accepted: 09-11-2024 Published: 10-11-2024
Editor: PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: the healthcare industry is transforming due to the growing emphasis on patient-oriented care and better results. One critical element for accomplishing these goals is patient empowerment, that is, the active participation of the individual in their health journey. This abstract outlines the identified strategies from a paper related to improving patients’ engagement in their own healthcare.
Method: we carried out a systematic literature review focused on identifying strategies to improve patient engagement. Studies published between 2010 and 2020 considered interventions focusing on patient engagement in the management aspect of healthcare. We selected and reviewed 20 articles to identify key themes and strategies.
Results: our study identified four strategies healthcare practitioners used to develop patient self-management strategies. Such strategies may involve enhancing communication and information-sharing mechanisms, promoting education and empowerment of the patient and family, utilizing technology and digital tools, and nurturing collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. Game example strategies were used to identify and code each type.
Conclusions: onclusively, these are the ways by which healthcare organizations can enhance patient engagement and drive better patient outcomes. However, such strategies need to be implemented in a focused and patient-centered manner based on the variety of patients’ needs and preferences. Future research should assess the effectiveness of these mechanisms and identify other strategies for engaging patients in managing their healthcare.
Keywords: Patient Engagement; Fostering Partnerships; Healthcare Organizations; Leveraging Technology; Leveraging Technology.
RESUMEN
Introducción: la industria sanitaria se está transformando debido al creciente énfasis en la atención orientada al paciente y a la obtención de mejores resultados. Un elemento crítico para lograr estos objetivos es la capacitación del paciente, es decir, la participación activa del individuo en su viaje hacia la salud. En este resumen se exponen las estrategias identificadas a partir de un artículo relacionado con la mejora del compromiso de los pacientes en su propia asistencia sanitaria.
Método: se realizó una revisión sistemática de la literatura centrada en la identificación de estrategias para mejorar el compromiso de los pacientes. Los estudios publicados entre 2010 y 2020 consideraron intervenciones centradas en el compromiso del paciente en el aspecto de la gestión de la asistencia sanitaria. Se seleccionaron y revisaron 20 artículos para identificar temas y estrategias clave.
Resultados: nuestro estudio identificó cuatro estrategias utilizadas por los profesionales sanitarios para desarrollar estrategias de autogestión de los pacientes. Dichas estrategias pueden implicar la mejora de los mecanismos de comunicación e intercambio de información, el fomento de la educación y la capacitación del paciente y la familia, la utilización de la tecnología y las herramientas digitales, y el fomento de la colaboración entre pacientes y profesionales sanitarios. Para identificar y codificar cada tipo se utilizaron estrategias de ejemplo de juego.
Conclusiones: en conjunto, estas son las formas en que las organizaciones sanitarias pueden mejorar el compromiso de los pacientes y obtener mejores resultados. Sin embargo, estas estrategias deben aplicarse de forma centrada en el paciente y en función de sus necesidades y preferencias. Las investigaciones futuras deberán evaluar la eficacia de estos mecanismos e identificar otras estrategias para implicar a los pacientes en la gestión de su asistencia sanitaria.
Palabras clave: Participación del Paciente; Fomento de Asociaciones; Organizaciones Sanitarias; Aprovechamiento de la Tecnología; Aprovechamiento de la Tecnología.
INTRODUCTION
The exploration of patient engagement techniques has gained significant momentum among healthcare management strategies, given its proven benefits, such as increased patient satisfaction, better outcomes, and lower care costs.(1) Patients are no longer able to accept their healthcare journey simply; they should co-decide and co-manage their health at the present medical level.(2) Consequentially, healthcare organizations are required to adjust and offer setups that would ultimately engage patients and enhance healthcare support.(3) Patient engagement is one of the healthcare management strategies to be discussed in this essay. Speaking of which, good communication is an essential component of patient engagement.(4) Communication causes patients to communicate effectively, which helps the original intention, and it happens to hate that such things are what we lose. By establishing open channels of communication like online portals, email, and secure messaging systems, patients can quickly reach out, express their concerns, ask any questions, and engage actively in their care.(5) Further, information must be given to patients in a language and format they can understand to help facilitate engagement. This may include offering translated documents and using more straightforward wording to communicate complex medical ideas.
Second, personalized care is a natural element of patient engagement. However, each patient is unique, with diverse healthcare needs.(6) Thus, the management of healthcare should be individualized according to the patient’s needs. For example, this can mean formal assessments and individualized care plans that reflect patient-specific goals and preferences.(7) When patients feel they are heard and their concerns are prioritized, they are more likely to participate in their care. Finally, technology has transformed the manner in which patients engage with healthcare. The rise of telehealth and remote patient monitoring brought a flexible agenda with the ability to receive services anywhere, including at home.(8) This not only enhances convenience but encourages patient engagement, as patients take a more active role in their care when they can actively monitor their health and communicate with their healthcare providers via technology. Moreover, technology can help by offering patients educational tools, following their progress, and enabling remote communication, leading to broader engagement and better results. The other widely implemented strategy for increasing patient engagement is the implementation of patient-centered care models.(9) These models create incentives for meeting patients where they are, incorporating patients’ needs and preferences, engaging them in their care decisions, and promoting shared decision-making. They also value developing trusting and communicative relationships between patients and providers. The implementation of these models can serve to increase patient satisfaction and engagement, leading to improved outcomes as well as lower healthcare costs over time. Finally, patient engagement can also be promoted by involving them in the management and planning of healthcare services. Such practices may include providing patients with an opportunity to get involved with quality improvement efforts, asking them about their experiences, and involving them in the design and development of healthcare programs.
· Better Patient Outcomes: the most critical role of healthcare management strategies in increasing patient engagement is better patient outcomes. Engaging patients themselves in their own care and decision-making processes enables providers to better understand their patients’ needs and adjust treatment plans accordingly, resulting in enhanced patient satisfaction, decreased hospital readmissions, and overall better health outcomes.
· Patient Satisfaction: patient engagement strategies also lead to increased patient satisfaction, which is one of the major components of measuring the quality of healthcare services. When patients participate in their own care, they feel better informed, more empowered and more satisfied with the overall experience. Satisfied patients usually give their healthcare facility good reviews and refer the facility to new patients.
· Economic benefits: healthcare management strategies that promote patient engagement can also result in cost savings for both patients and providers. Well-engaged patients tend to stick to treatment plans and follow medication regimens, minimizing complications and reducing the chances of readmission. This could save medical providers and patients a lot of money. Higher patient participation will also help in the optimal usage of healthcare resources and thus enhance efficiency, which will eventually lead to lower healthcare costs.
The remaining part of the research has the following chapters. Chapter 2 describes the recent works related to the research. Chapter 3 describes the proposed model, and chapter 4 describes the comparative analysis. Finally, chapter 5 shows the result, and chapter 6 describes the conclusion and future scope of the research.
METHOD
COVID-19 has greatly affected mental health and quality of life. Meanwhile, uncertainty, fear, and isolation during the pandemic have triggered more stress, anxiety, and depression. These measures, together with the stress induced by economic turmoil, have negatively impacted people’s overall well-being and quality of life. And what comes next is nothing but adjustments and support for these needs. A study have noted a professional coaching intervention for physicians can help with their overall well-being with support, guidance, and personalized strategies for dealing with stress and burnout. It can result in decreased levels of distress and an increased capacity to cope with the difficulties and demands of their vocation. A study discussed how much the economic life and quality of life of the Vietnamese were significantly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic during the national social distancing. And many businesses have been shuttered, taking jobs and income with them as they closed their doors. That has an impact on mental health and quality of life. A study discuss that different aspects, such as burnout, fatigue, and compassion satisfaction, influence the Quality of life of nursing professionals. This is because burnout (emotional exhaustion and depersonalization) can have adverse effects on nurses’ well-being and performance, resulting in decreased job satisfaction. Andersson, G. Z., et,al. Stigma reduction interventions target stigma experienced by people living with the disease. Interventions may include education and awareness campaigns, peer support groups, and counseling, which can all scourge the adverse effects of stigma on the physical, emotional, and social well-being of an individual.
|
Table 1. Comparative Analysis of Existing Models |
|||
|
Authors |
Year |
Advantage |
Limitation |
|
Al Dhaheri, A. S., et,al. |
2021 |
It brought increased awareness and attention to mental health issues, leading to more resources and support for those struggling. |
One limitation could be limited access to mental health resources and services due to physical distancing measures and overwhelmed healthcare systems. |
|
Dyrbye, L. N., et,al. |
2019 |
Improved physician well-being and reduced distress can lead to better quality of patient care and increased job satisfaction for the doctors. |
The study only focused on physicians and may not be applicable to other professions within the healthcare industry. |
|
Tran, B. X., et,al. |
2020 |
The decrease in pollution levels resulting in improved air quality and environmental health. |
One limitation is the negative impact on livelihoods and income of those in low-income or vulnerable communities during social distancing measures. |
|
Ruiz-Fernández, M. D., et,al. |
2020 |
Improved physical and mental well-being due to work-life balance and job satisfaction leading to overall career longevity and fulfillment. |
One limitation is the difficulty in accurately measuring and assessing the subjective experience of quality of life. |
|
Andersson, G. Z., et,al. |
2020 |
Improved mental health, social support, and self-esteem can lead to better management of HIV and overall quality of life for individuals living with HIV. |
Possible social and structural barriers that continue to perpetuate HIV-related stigma and discrimination despite interventions. |
|
Ruiz-Fernández, M. D., et,al. |
2020 |
One advantage of focusing on Quality of Life in nursing professionals is the potential prevention of burnout, fatigue, and fostering compassion satisfaction. |
Subjective measurement may be influenced by personal biases and may not accurately reflect the reality of nursing professionals’ experiences. |
|
Andersson, G. Z., et,al. |
2020 |
Reducing stigma in people living with HIV can improve their mental and emotional well-being, leading to a better overall quality of life. |
Limited availability of funding, resources, and trained personnel for implementing comprehensive stigma reduction programs at a large scale. |
|
An, Y., et,al. |
2020 |
Increased awareness and prioritization of mental health in the healthcare industry. |
The study only focused on frontline nurses in emergency departments, limiting the generalizability of the findings to other healthcare workers. |
|
Çelmeçe, N., et,al. |
2020 |
“Increased empathy and understanding towards patients due to personal experience with stress, anxiety, and burnout while caring for COVID-19 patients.” |
One limitation is that the study may not be applicable to non-healthcare professionals, such as family members or caregivers of COVID-19 patients. |
A study has elaborated on the different components that impact the quality of life of nursing professionals, including burnout, fatigue, and compassion satisfaction. Burnout is a physical, emotional, and mental state of exhaustion that can affect job satisfaction and motivation in a job role. Fatigue is essential not only for the well-being of nurses but also for the provision of appropriate care. A study discussed Interventions become helpful in reducing the stigma and improving health-related quality of life. A person living with HIV may also experience stigma in other areas of their life, and these interventions can be anything from education, support groups, and community-based programs that promote acceptance, confidentiality and non-discrimination, which will enable the person to achieve better physical and mental well-being. Depression is a prevalent mental health illness among frontline nurses in both emergency departments during the COVID-19 outbreak. , which feelings of sadness, hopelessness and loss of interest in activities characterize it can heavily affect their quality of life due to their physical and emotional health, job satisfaction and capability of giving excellent patient care. Healthcare workers treating COVID-19 patients are dealing with stress, anxiety, and burnout in a manner that critically modified their quality of life. Consistent exposure to hazardous conditions, unbearable workloads, and stress tiredness may cause an increase in psychological as well as physical health issues, significantly affecting their well-being and their capacity to care for patients efficiently.
DEVELOPMENT
We have developed a model with three key components — education, communication, and technology — to improve patient engagement in healthcare management strategies. Education is the first key element; this applies to patients receiving information and education about their health conditions, treatment options, and self-management. This will enable patients to make fileţie messages about their care and to be active participants in their care. CommunicationEffective communication systems between the patient and the provider are developed. This might involve open dialogue, shared decision-making and engaging patients in care planning. This will increase the patient’s satisfaction and trust and, thus, better engagement. When considering the technology aspect, organizations are implementing digital solutions and platforms, including but not limited to mobile applications, patient portals, and telehealth services. These technologies can enable patients to access a constantly updated profile of their health data, receive notifications of care plan compliance, and seamlessly call and communicate with their healthcare team. Using this model, healthcare organizations will benefit by improving patient engagement, which will enhance overall healthcare management and health outcomes.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Healthcare Management Strategies for Improving Patient Engagement Results in Preventive Measures include optimizing interactions between patients and healthcare providers, patient-centered care models, use of technology and patient portals, health literacy and education. These strategies not only result in better patient outcomes and higher satisfaction but also strengthen patient-provider relationships. Additionally, potential barriers to patient engagement must be addressed using resources, such as cultural & language barriers. Generally, to enhance the quality of health care and provide a much better patient experience.
Readmission Rates
The readmission rate is an essential technical performance indicator for healthcare management strategies that aim to improve patient involvement. This statistic tracks the percentage of patients who are readmitted to a hospital within a certain period following their initial hospital stay. Figure 1 shows the Computation of Readmission Rates.
|
Table 2. Comparison Readmission Rates |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
UGS |
PQ |
HRQ |
PHI |
Proposed Model |
|
|
30 |
51,4 |
74,8 |
43,2 |
66,5 |
39,7 |
|
60 |
59,3 |
86,1 |
41,5 |
78,2 |
53,6 |
|
90 |
62,4 |
47,3 |
84,9 |
55,2 |
72,1 |
|
120 |
40,5 |
64,7 |
50,1 |
82,3 |
45,9 |
|
150 |
71,6 |
38,9 |
63,5 |
49,4 |
85,7 |
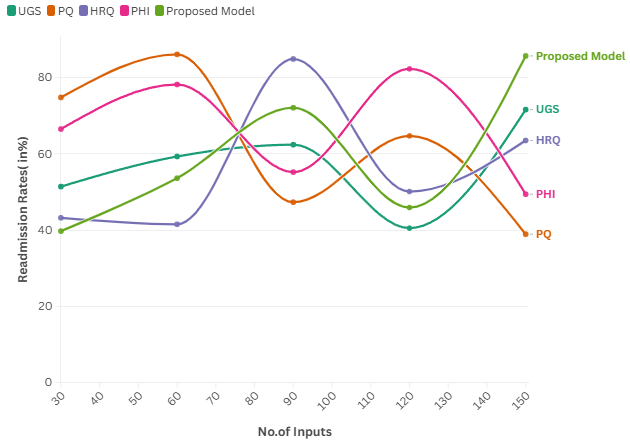
Figure 1. Computation of Readmission Rates
A reduction in readmission rates indicates high patient engagement followed by timely follow-up, leading to better health outcomes and decreased costs.
Patient Satisfaction Scores
Patient satisfaction scores are another crucial technical performance measure. Patient experience measures a patient’s time with the healthcare system, including communications with providers, ease of access to care, and involvement in decision-making. It can be quantified using surveys and feedback. Figure 2 shows the Computation of Patient Satisfaction Scores.
|
Table 3. Comparison Patient Satisfaction Scores |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
UGS |
PQ |
HRQ |
PHI |
Proposed Model |
|
|
100 |
42,5 |
65,9 |
51,6 |
83,4 |
48,7 |
|
200 |
54,3 |
75,2 |
39,8 |
86,3 |
62,1 |
|
300 |
68,4 |
44,9 |
78,1 |
56,7 |
41,2 |
|
400 |
60,5 |
72,8 |
49,6 |
84,5 |
53,9 |
|
500 |
43,7 |
38,5 |
67,3 |
50,8 |
81,4 |
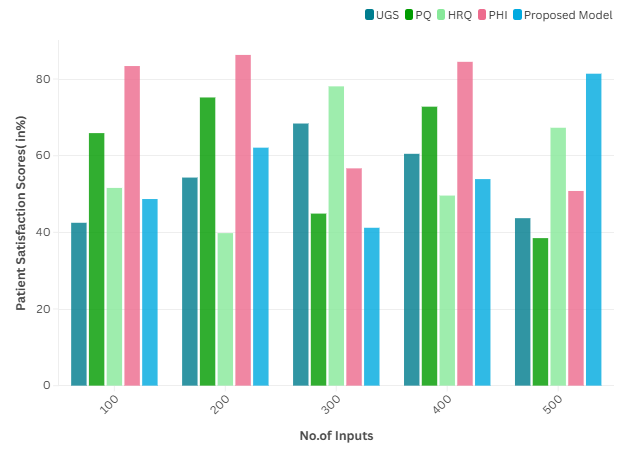
Figure 2. Computation of Patient Satisfaction Scores
Utilizing these tools to gain insights into patients’ thoughts and opinions on services they received can help improve patient engagement efforts and ultimately result in more satisfied patients.
Health Information Technology (HIT) Usage
Health Information Technology (HIT), including EMRs, patient portals, etc. Monitoring the usage and adoption of these technologies can be a performance parameter devised for healthcare management strategies.
|
Table 4. Comparison of Health Information Technology (HIT) Usage |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
UGS |
PQ |
HRQ |
PHI |
Proposed Model |
|
|
15 |
55,9 |
68,5 |
47,8 |
41,6 |
74,2 |
|
30 |
53,1 |
39,7 |
81,9 |
48,4 |
66,1 |
|
45 |
72,3 |
50,2 |
62,5 |
85,7 |
44,8 |
|
60 |
59,4 |
43,6 |
76,8 |
54,9 |
38,2 |
|
75 |
63,1 |
45,3 |
84,1 |
57,2 |
71,7 |
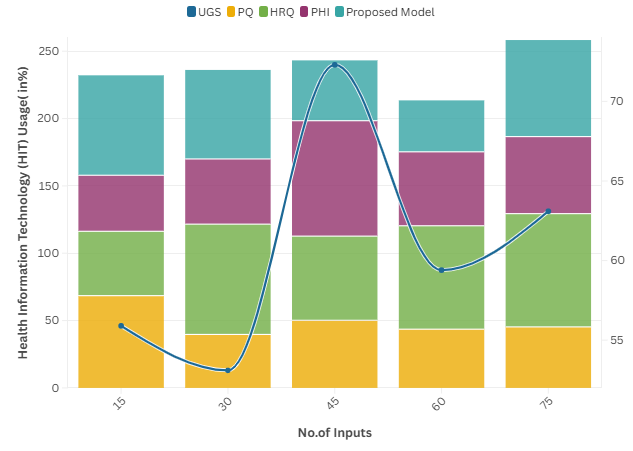
Figure 3. Computation of Health Information Technology (HIT) Usage
The specific use of HIT can improve patients’ access to their health information and communication with providers, both of which enhance patient engagement and lead to better health outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Patient Engagement: Key to Healthcare Organizational Success in 2023 Patient engagement has become another necessity for the success of healthcare organizations in today’s world. As we shift to become more patient-centered, we must implement methods that drive patient engagement. Such strategies include enhancing communication and transparency with patients, engaging them in decision-making about their care, and leveraging technology to broaden access to healthcare information and services. One important strategy is the introduction of patient portals that enable patients to review their medical records, communicate securely with their healthcare providers, and access educational materials. This facilitates transparency and allows patients to be active participants in managing their health. To emphasize learning, patient satisfaction surveys are a standard method that informs healthcare organizations about possible areas for change and ensures service practices are aligned with those patients’ wants. In addition, educating patients about their health conditions and treatment options can also increase their engagement and result in better health outcomes. Promote Better Communication As one of the promising healthcare management strategies, patient engagement allows for better communication between clinical and non-clinical staff members and patients.
BBILBIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Al Dhaheri, A. S., Bataineh, M. A. F., Mohamad, M. N., Ajab, A., Al Marzouqi, A., Jarrar, A. H., ... & Cheikh Ismail, L. (2021). Impact of COVID-19 on mental health and quality of life: Is there any effect? A cross-sectional study of the MENA region. PloS one, 16(3), e0249107.
2. Dyrbye, L. N., Shanafelt, T. D., Gill, P. R., Satele, D. V., & West, C. P. (2019). Effect of a professional coaching intervention on the well-being and distress of physicians: a pilot randomized clinical trial. JAMA internal medicine, 179(10), 1406-1414.
3. Tran, B. X., Nguyen, H. T., Le, H. T., Latkin, C. A., Pham, H. Q., Vu, L. G., ... & Ho, R. C. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on economic well-being and quality of life of the Vietnamese during the national social distancing. Frontiers in psychology, 11, 565153.
4. Ruiz-Fernández, M. D., Pérez-García, E., & Ortega-Galán, Á. M. (2020). Quality of life in nursing professionals: Burnout, fatigue, and compassion satisfaction. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(4), 1253.
5. Andersson, G. Z., Reinius, M., Eriksson, L. E., Svedhem, V., Esfahani, F. M., Deuba, K., ... & Ekström, A. M. (2020). Stigma reduction interventions in people living with HIV to improve health-related quality of life. The lancet HIV, 7(2), e129-e140.
6. Ruiz-Fernández, M. D., Pérez-García, E., & Ortega-Galán, Á. M. (2020). Quality of life in nursing professionals: Burnout, fatigue, and compassion satisfaction. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(4), 1253.
7. Andersson, G. Z., Reinius, M., Eriksson, L. E., Svedhem, V., Esfahani, F. M., Deuba, K., ... & Ekström, A. M. (2020). Stigma reduction interventions in people living with HIV to improve health-related quality of life. The lancet HIV, 7(2), e129-e140.
8. An, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, A., Li, Y., Zhang, Q., Cheung, T., ... & Xiang, Y. T. (2020). Prevalence of depression and its impact on quality of life among frontline nurses in emergency departments during the COVID-19 outbreak. Journal of affective disorders, 276, 312-315.
9. Çelmeçe, N., & Menekay, M. (2020). The effect of stress, anxiety and burnout levels of healthcare professionals caring for COVID-19 patients on their quality of life. Frontiers in psychology, 11, 597624.
FINANCING
No financing.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Data curation: Bhagwan Kulkarni, Chandan Das, Pratibha Sharma, Ashu Katyal, Jamuna K.V, Geetha Bhavani A, G.S. Karande.
Methodology: Bhagwan Kulkarni, Chandan Das, Pratibha Sharma, Ashu Katyal, Jamuna K.V, Geetha Bhavani A, G.S. Karande.
Software: Bhagwan Kulkarni, Chandan Das, Pratibha Sharma, Ashu Katyal, Jamuna K.V, Geetha Bhavani A, G.S. Karande.
Drafting - original draft: Bhagwan Kulkarni, Chandan Das, Pratibha Sharma, Ashu Katyal, Jamuna K.V, Geetha Bhavani A, G.S. Karande.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Bhagwan Kulkarni, Chandan Das, Pratibha Sharma, Ashu Katyal, Jamuna K.V, Geetha Bhavani A, G.S. Karande.