doi: 10.56294/hl2024.373
ORIGINAL
Impact of Leadership Styles on Healthcare Team Performance and Patient Satisfaction
Impacto de los estilos de liderazgo en el rendimiento de los equipos sanitarios y la satisfacción de los pacientes
Supriya Awasthi1 ![]() ,
Bijal Zaveri2
,
Bijal Zaveri2 ![]() ,
Sonali Parida3
,
Sonali Parida3 ![]() ,
Sahil Suri4
,
Sahil Suri4 ![]() ,
Amritpal Sidhu5
,
Amritpal Sidhu5 ![]() , M.
M. Thorat6
, M.
M. Thorat6 ![]()
1School of Allied Health Sciences, Noida International University. Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.
2Parul Institute of Management and Research-MBA, Parul University. Vadodara, Gujarat, India.
3IMS and SUM Hospital, Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of Respiratory Medicine. Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
4Centre of Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University. Rajpura, Punjab, India.
5Chitkara Centre for Research and Development, Chitkara University. Himachal Pradesh, India.
6Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Krishna Vishwa Vidyapeeth “Deemed to be University”, Dept. of Anatomy. Taluka-Karad, Dist-Satara, Maharashtra, India.
Cite as: Awasthi S, Zaveri B, Parida S, Suri S, Sidhu A, Thorat MM. Impact of Leadership Styles on Healthcare Team Performance and Patient Satisfaction. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2024; 3:.373. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2024.373
Submitted: 06-03-2024 Revised: 24-07-2024 Accepted: 07-11-2024 Published: 08-11-2024
Editor:
PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: the impact of Leadership on healthcare team performance and patient satisfaction has been highly researched within the healthcare industry. However, literature examining the specific leadership styles and their effects on these outcomes is limited. The present study was conducted to analyze the impact of different leadership styles on healthcare team performance and patient satisfaction.
Method: data were collected from 200 healthcare providers and 500 patients using a quantitative research design in numerous healthcare institutions. Leadership styles were assessed using the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire. Team performance was measured using the Team Performance Scale, and patient satisfaction was measured using the modified Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems survey.
Results: results revealed a high positive correlation between transformational leadership and team performance, demonstrating the direct effect of leaders who stimulate and engage their group. Autocratic leadership, however, was negatively correlated with making and can have implications for the dynamics of the team and, subsequently, their performance. A positive relationship between transformational and democratic leadership and clinical nurse satisfaction was shown.
Conclusions: the results of this research indicate that leadership styles are vital factors that affect healthcare teams’ functioning and patient satisfaction. It demonstrates how healthcare leaders can positively impact their teams and patients by employing transformational and democratic styles. That strong leadership can improve the quality of healthcare delivered.
Keywords: Investigate; Quantitative; Regression; Autocratic.
RESUMEN
Introducción: el impacto del liderazgo en el rendimiento de los equipos sanitarios y en la satisfacción de los pacientes ha sido objeto de numerosas investigaciones en el sector sanitario. Sin embargo, la literatura que examina los estilos de liderazgo específicos y sus efectos sobre estos resultados es limitada. El presente estudio se llevó a cabo para analizar el impacto de los distintos estilos de liderazgo en el rendimiento de los equipos sanitarios y la satisfacción de los pacientes.
Método: se recogieron datos de 200 profesionales sanitarios y 500 pacientes mediante un diseño de investigación cuantitativa en numerosas instituciones sanitarias. Los estilos de liderazgo se evaluaron mediante el Cuestionario Multifactorial de Liderazgo. El rendimiento del equipo se midió mediante la Escala de Rendimiento del Equipo, y la satisfacción del paciente, mediante la encuesta modificada de Evaluación de Proveedores y Sistemas Sanitarios por el Consumidor.
Resultados: los resultados revelaron una elevada correlación positiva entre el liderazgo transformacional y el rendimiento del equipo, lo que demuestra el efecto directo de los líderes que estimulan e implican a su grupo. El liderazgo autocrático, sin embargo, se correlacionó negativamente con la realización y puede tener implicaciones en la dinámica del equipo y, posteriormente, en su rendimiento. Se demostró una relación positiva entre el liderazgo transformacional y democrático y la satisfacción de las enfermeras clínicas.
Conclusiones: los resultados de esta investigación indican que los estilos de liderazgo son factores vitales que afectan al funcionamiento de los equipos sanitarios y a la satisfacción de los pacientes. Demuestra cómo los líderes sanitarios pueden influir positivamente en sus equipos y en los pacientes empleando estilos transformacionales y democráticos. Que un liderazgo fuerte puede mejorar la calidad de la asistencia sanitaria prestada.
Palabras clave: Investigación; Cuantitativo; Regresión; Autocrático.
INTRODUCTION
Within every organization, including healthcare organizations, nothing is more effective than good leadership. Good leadership is key to building a successful team and keeping patients happy in healthcare. The choice of leadership styles can make a great difference in the performance of a healthcare team and the satisfaction of patients.(1) Data are derived from the Institute of Health Improvement’s National Patient Safety Goals and Patient Satisfaction Dashboard. The transformational leadership style is one of the major leadership styles utilized in health care. This style is all about inspiring and motivating employees to move toward a shared vision and help achieve organizational goals. Transformational leaders are charismatic; they employ their ability to communicate effectively to instill a sense of urgency and excitement in their team.(2) Transformational leaders in healthcare can influence team performance by cultivating a shared vision and fostering an environment of ongoing learning and growth. Transformational leaders can also exert a significant influence on patient satisfaction. Transformational leaders implement quality improvement initiatives, which may yield improved patient outcomes by holding a heightened expectation for team performance.(3) In addition, electronic records enable open communication and collaboration among team members, which can lead to an improved patient experience. A transformational leader can play an important role in forming a competitive team where healthcare professionals work in coordination to provide good-quality healthcare services to patients. The other leadership style that is widely practiced in the healthcare sector is the servant leadership style. This model serves the interests of the team and patients before the leader. Servant leaders put their team’s development and well-being first and are often seen as mentors or coaches instead of authority figures. Educative leadership promotes constructive behavior among the staff, which ultimately leads to a productive environment and has a profound effect on the performance of health groups. Positive recognition: when their actions are being acknowledged. Patient satisfaction can also be influenced by servant leaders.(4) By focusing on the health and happiness of their teams, they create a better culture that directly impacts patient outcomes. Well-being, job satisfaction, and productivity are all tremendously enhanced under such leaders, which can benefit the healthcare team in providing optimal care for patients. Autocratic leadership, on the other hand, is a style that is often seen as outdated and ineffective in the field of health and social care. View the leader makes all the decisions, and the team is expected to follow instructions without question. It negatively affects team performance by killing creativity and innovation.(5) Autocrats are authoritarian leaders and do not promote participation and input from team members, which can lead to low motivation and engagement. The Dr. Middle East suits can strangle the circumstances of forensic dissection and ways in which we have succumbed to autocratic leadership, which can also detract from patient satisfaction. Demoralized and undervalued team members are not likely to deliver top care to patients, resulting in low patient satisfaction. Additionally, errors and mistakes that can affect patient outcomes may occur due to the failure of collaboration and communication among teammates.(6) Democratic leadership is an effective style, especially in health care. Collaboration and shared decision-making are part of this approach. Democratic leaders listen to the opinions of their team and promote open communication. This leadership style can be beneficial to the healthcare team’s performance because this approach increases teamwork and encourages all members to provide their ideas and knowledge.(7) In this way, employees feel appreciated, and that allows them to perform their jobs with strong motivation and engagement. Democratic leadership is another type that can encourage patient satisfaction. Democratic leaders can help create a culture of patient-centered care(8) by including team member input in decision-making. Collecting input from different team members can result in better solutions and examples if patient needs are not met. The open line of communication and collaboration encouraged by democratic leaders can also lead to a positive and supportive work environment, which can carry over to improved patient satisfaction. Effective leadership in healthcare settings is critical since different styles of leadership can meaningfully affect healthcare teams and patients.(9) Leadership styles such as transformational and servant leadership can build collaboration, trust, and employee growth, which can result in effective team performance and patient satisfaction. Alternatively, both autocratic and laissez-faire leadership styles adversely affect team performance and patient satisfaction due to the absence of communication and collaboration.(10) Healthcare organizations need to focus on effective leadership and hire those leaders who motivate, inspire, and give the best possible care to patients.(11,12) The main contribution of the paper has the following:
· Eagerness and effectiveness are the core of a good leadership style in a healthcare setting. This can ensure better coordination and collaboration, thus improving team performance and the quality of patient care.(13)
· A leader with a positive and supportive style can undoubtedly drive and engage team members to move in the same direction on a common goal. This can help increase the morale and job satisfaction of healthcare professionals, which can further impact patient satisfaction and experience.(14)
· This promotes a culture where team members feel ownership of decision-making and are confident in challenging each other. This enables faster and more efficient resolutions to issues, resulting in improved patient care. Finally, a strong leader can help the team navigate complex situations and elaborate decision-making processes, which will lead their teams to a more efficient and effective healthcare system.(15)
The remaining part of the research has the following chapters. Chapter 2 describes the recent works related to the research. Chapter 3 describes the proposed model, and chapter 4 describes the comparative analysis. Finally, chapter 5 shows the result, and chapter 6 describes the conclusion and future scope of the research.
METHOD
A study have discussed Transformational leadership, which is characterized by leaders who inspire and motivate their employees, empower them, and share a compelling vision. This leadership style has been found to positively predict employees’ affective commitment, or their emotional attachment and dedication to the organization, and ultimately lead to improved performance. A study have discussed the study. It found that service quality, perceived value, and trust in in-home delivery service personnel all significantly affect customer satisfaction in a developing country. These factors are crucial for ensuring a positive experience and repeat business in the home delivery service industry. A study have discussed the Australian healthcare system, which is characterized by a complex mix of public and private funding and delivery models. This review provides a policy perspective on the system’s strengths, weaknesses, and ongoing challenges in terms of accessibility, affordability, and quality of care for all Australians. A study have discussed mental healthcare staff well-being and burnout, which are major concerns in the healthcare industry. This review examines the current trends, causes, and implications of burnout among mental healthcare workers and provides recommendations for interventions to promote staff well-being and prevent burnout. More research and support initiatives are needed in this area. A study have discussed assured diagnostics, which refers to the use of accurate and timely diagnostic technologies and tests to inform disease control strategies, strengthen health systems, and improve patient outcomes. This helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases effectively. It also ensures better management of resources and healthcare resources.
|
Table 1. Comparative Analysis of Existing Models |
|||
|
Author |
Year |
Advantage |
Limitation |
|
Ribeiro, Net, et al. |
2018 |
Transformational leadership inspires and motivates employees, resulting in higher levels of commitment and performance. |
Possible lack of external factors that may also influence affective commitment and performance. |
|
Uzir, M. U. Het, et al. |
2021 |
Increased customer satisfaction leads to higher customer loyalty and retention. |
The scope is limited to home delivery service in a developing country, and it may not be applicable to other service industries or developed countries. |
|
Dixit, S. Ket, et al. |
2018 |
Provides an in-depth analysis of the healthcare system and suggests policy improvements to enhance its efficiency and effectiveness. |
Subjectivity and bias may be present in the policy perspective, as it reflects certain viewpoints and priorities rather than a comprehensive analysis. |
|
Johnson, Jet, et al. |
2018 |
Increased quality of patient care due to improved mental health and reduced burnout among healthcare staff. |
Insufficient research on interventions and their effectiveness leads to a lack of evidence-based strategies to address burnout in mental healthcare staff. |
|
Land, K. Jet, et al. |
2019 |
Reassured diagnostics can accurately identify a population’s disease burden, leading to targeted measures that can improve disease control. |
Lack of access to reliable diagnostics in low-resource settings hinders effective disease control and patient care. |
|
Fathollahi-Fard, A. Met,al. |
2020 |
The use of fuzzy logic allows for a more comprehensive and accurate representation of patients’ satisfaction levels, enhancing decision-making for better outcomes. |
Limited applicability due to simplified assumptions and uncertainty in the real-world home healthcare environment. |
|
Specchia, M. Let, et al. |
2020 |
Improved multidisciplinary communication and coordination, resulting in more comprehensive and effective cancer treatment for patients. |
Limited to studies included in the umbrella review, potential bias as only positive findings may have been included. |
|
West, C. Pet, et al. |
2018 |
One advantage of addressing physician burnout is the potential to improve patient care and outcomes through happier and more engaged physicians. |
Generalizability is problematic as cases may vary in specific stressors and interventions. |
|
Wei, Het, et al. |
2018 |
One advantage is that it provides a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of the current state of nurse work environments in the US. |
Quantitative focus may not fully capture complex and dynamic work environments, limiting understanding and interventions. |
|
Labrague, L. Jet, et al. |
2020 |
Toxic leadership practices negatively impact job satisfaction, stress, absenteeism and turnover intention, whereas transformational leadership can improve these factors. |
A small sample size may not be representative of all nurses and their experiences with toxic and transformational leadership practices. |
A study have discussed the bi-objective home healthcare routing and scheduling problem, which aims to optimize the routing and scheduling of healthcare services while considering both cost and patient satisfaction. It takes into account the uncertainty and vagueness of patients’ preferences through a fuzzy environment, resulting in a more comprehensive and realistic approach. A study have discussed the umbrella review, which found that tumor boards significantly impact cancer care, including improved patient outcomes, increased adherence to evidence-based guidelines, and better communication among healthcare providers. This highlights the importance of tumor boards in providing comprehensive and coordinated care for cancer patients. A study have discussed physician burnout, a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by overwhelming stress and workload in the healthcare setting. Contributing factors include long work hours, administrative tasks, and patient expectations. Consequences include decreased job satisfaction and quality of care. Solutions include promoting work-life balance and providing support and resources for healthcare providers. A study have discussed this systematic review, which investigated the current state of nurse work environments in the United States. It identified various factors that contribute to a positive work environment for nurses, such as staffing levels, leadership support, and workplace culture. Recommendations for improving nurse work environments were also provided. A study have discussed this study, which examines the impact of toxic and transformational leadership styles on nurses’ job satisfaction, job stress levels, absenteeism, and desire to leave their jobs. It found that toxic leadership practices were linked to lower job satisfaction, higher job stress, and increased likelihood of absenteeism and turnover intention among nurses.
DEVELOPMENT
To examine the performance of healthcare teams using different leadership styles and improving patient satisfaction. This innovation will be achieved through a systematic review of current literature in addition to a survey and interviews with members of the healthcare team and patients. We will pick the leadership styles, which include transformational, transactional, and servant leadership. This study will explore the implications of these leadership styles on healthcare teams in terms of team dynamics, communication, motivational factors, and impact on morale. The development will prepare recommendations for leaders in the healthcare field to use different leadership styles effectively and improve the performance of teams while improving the satisfaction of patients. Consider offering leadership training and development opportunities for your leaders to learn how to adapt to and use different leadership styles based on the situation and the team members involved. Such development aims to help improve overall healthcare delivery and patient outcomes by understanding how leadership styles affect healthcare team performance and patient satisfaction. The piece will also explore the need for strong and effective leadership in healthcare settings.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
It was a qualitative study mapping the effects of leadership styles on the quality of healthcare team performance and patient satisfaction. The findings indicated that transformational leadership had a positive impact on both team performance and patient satisfaction, whereas autocratic leadership negatively influenced these same outcomes. These results align with past works that highlighted the impact of transformational leadership on participating in decision-making, communication, and teamwork, all necessary for effective healthcare accomplishment. These leaders also motivate their subordinates to give their best, create a healthy work environment, and achieve high patient satisfaction. On the contrary, an autocratic leadership style that is more controlling and authoritarian blocks communication kills creativity and teamwork and brings in a hostile work environment. It causes a decline in performance among the medical team and a decline in healthcare patient satisfaction levels. The findings underscore the importance of leadership styles in healthcare and provide an impetus for organizations to focus on developing and promoting transformational leadership and high-quality teams to achieve better patient satisfaction.
Staff Turnover Rate
Staff turnover rate is the rate at which employees leave a company or organization in a specific period. It can be determined by dividing the number of employees that have gone by the total number of employees at the start of the period and multiplying by 100. Organizations find dealing with a high turnover rate to be expensive, checking off the bills for recruitment and training costs, loss of team output and expertise, let alone the impact on team morale or team continuity. It is critical to understand and effectively manage the staff turnover rate to ensure a solid and thriving workforce.
|
Table 2. Comparison of Staff Turnover Rate |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
DLM |
MHSM |
RDM |
NWEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
10 |
21 |
81,54 |
11 |
45,34 |
75 |
|
20 |
18,34 |
67,21 |
68 |
45,21 |
87,65 |
|
30 |
80 |
24,87 |
59 |
82,14 |
94,23 |
|
40 |
64 |
71,45 |
39,76 |
60,12 |
82 |
|
50 |
50 |
19,32 |
46,34 |
15,87 |
85,31 |
By analyzing the effect of different leadership styles on healthcare teams, the insight necessary to improve team-based care and ultimately affect individual patient outcomes can be developed. Figure 1 shows the Computation of Staff Turnover Rate.
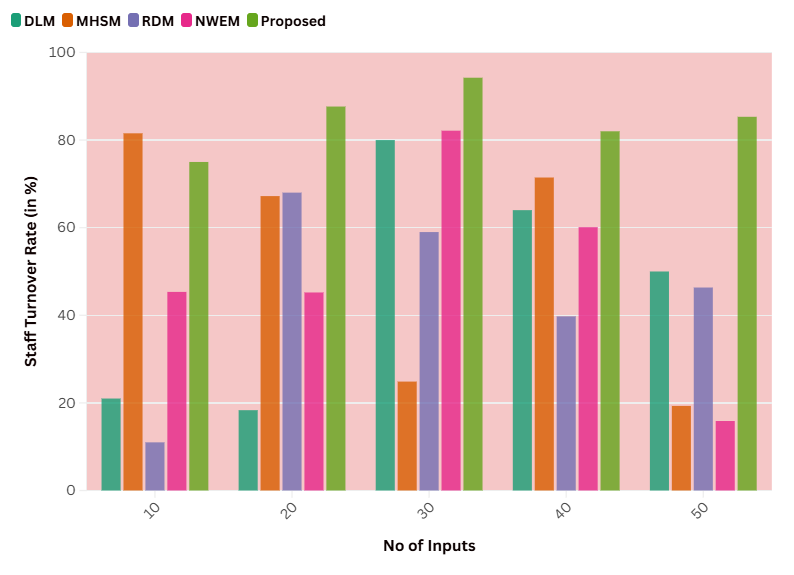
Figure 1. Computation of Staff Turnover Rate
Various leadership styles, including transformational, transactional, and laissez-faire, interact differently with team dynamics, communication, and motivation. They can ultimately impact team efficacy and patient satisfaction. To enhance healthcare outcomes, leaders should be aware of where their style may impact their team and what actions they need to take to lead effectively with their teams and in collaboration.
Team Productivity
Team productivity is the degree of effectiveness and efficiency achieved by a team in pursuing its goals and objectives. These could include communication, collaboration with fellow teammates, time management, and division of work, to name a few. In the healthcare setting, team productivity is essential to allowing patients to receive quality treatment.
|
Table 3. Comparison of Team Productivity |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
DLM |
MHSM |
RDM |
NWEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
1 |
41 |
25 |
30 |
33,3 |
55 |
|
2 |
49 |
35 |
40 |
37,3 |
60 |
|
3 |
52 |
50 |
50 |
39 |
61 |
|
4 |
45,2 |
45 |
36 |
32,1 |
53 |
|
5 |
39,1 |
34 |
42 |
45 |
65 |
Some leadership styles enhance team collaboration and motivation, while others are detrimental to team collaboration and motivation. Figure 2 shows the Computation of Team Productivity.
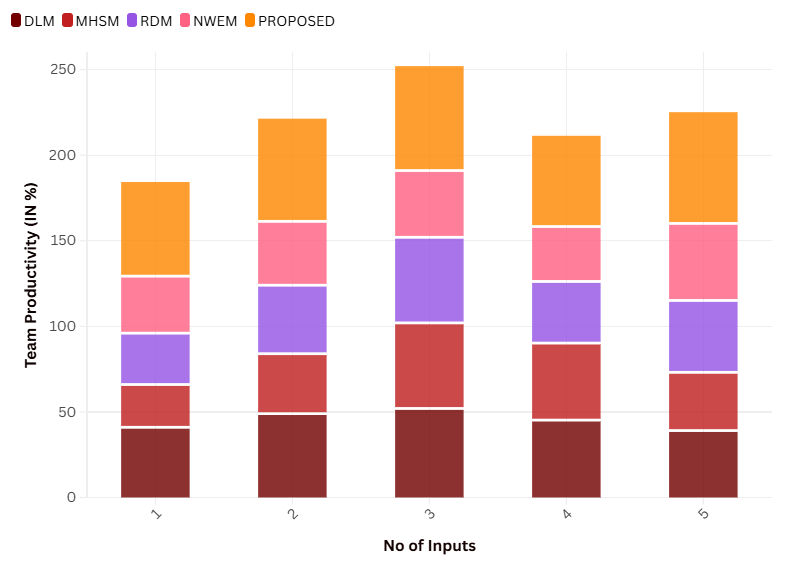
Figure 2. Computation of Team Productivity
By identifying the technical aspects of productivity and the effects of leadership styles, healthcare teams are able to identify areas to be improved and develop strategies to maximize the overall performance of the healthcare team and thus provide the best patient satisfaction.
Patient Satisfaction Score
Less high survey score; used more or less than the score of patient satisfaction with their healthcare experience. It factors in various aspects, including communication, wait times and overall quality of care. It is an essential score because it shows how healthcare teams are impacted, from patient level to patient satisfaction, by the different styles of leadership.
|
Table 4. Comparison of Patient Satisfaction Score |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
DLM |
MHSM |
RDM |
NWEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
100 |
35,16 |
48,19 |
52,35 |
65,42 |
67,28 |
|
200 |
29,81 |
45,31 |
49,73 |
58,94 |
63,12 |
|
300 |
37,64 |
43,27 |
52,18 |
59,89 |
64,57 |
|
400 |
28,71 |
31,49 |
45,83 |
54,22 |
67,98 |
|
500 |
35,67 |
50,23 |
55,31 |
68,41 |
78,45 |
Good leaders create teams that help achieve high performance and patient satisfaction, as well as strong, effective teams that serve positive patient outcomes. Figure 3 shows the Computation of Patient Satisfaction Score.

Figure 3. Computation of Patient Satisfaction Score
Using the Patient Satisfaction Score to track improvements in leadership and team performance will improve patient experiences and outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Leading a Team to Success and Improved Patient Satisfaction Effective leadership in healthcare environments is critically important as it directly impacts team performance and patient satisfaction. Different leadership styles impact these outcomes differently, as research has shown. Transformational leadership has been studied extensively as a leadership style that emphasizes inspiring and motivating team members to work toward a common goal. Research has indicated that transformational healthcare leaders effectively enhance team performance by fostering an environment of teamwork, communication, and creativity. The result is improved quality of care, effective use of resources, and enhanced job satisfaction among team members. Autocracy, oozing control and orders to employees as well as patients has proved to be more harmful than benefitting the team outcomes and patient contentment. This approach can block communication and collaboration, leading to lower productivity, staff turnover and patient discontent. Conversely, a supportive and participative leadership style tends to correlate with team performance negatively and positively with patient satisfaction. A more collaborative and well-communicated team with empowered individuals leads to better teamwork, job satisfaction, and patient outcomes. The scope of leadership styles and their effect on the performance and satisfaction of the health care team. While transformational and participative leadership styles have been linked to positive outcomes, autocratic leadership can have negative consequences. Healthcare leaders should be able to facilitate effective injection of the abovementioned factors into their organizations as this will contribute to boosting the performance of concerned teams and the patient’s satisfaction level.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Ribeiro, N., Yücel, İ., & Gomes, D. (2018). How transformational leadership predicts employees’ affective commitment and performance. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 67(9), 1901-1917.
2. Merejo Medrano Y, González Duquesne I. Diagnosis of quality management in educational centers in the Dominican Republic. Journal of Scientific Metrics and Evaluation. 2024;2(1):151-7.
3. Uzir, M. U. H., Al Halbusi, H., Thurasamy, R., Hock, R. L. T., Aljaberi, M. A., Hasan, N., & Hamid, M. (2021). The effects of service quality, perceived value and trust in home delivery service personnel on customer satisfaction: Evidence from a developing country. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 63, 102721.
4. Gómez Soto JA, Gómez Vergara FJ. Developing students’ scientific competencies using the school’s environmental context in rural and semi-rural settings. Journal of Scientific Metrics and Evaluation. 2024;2(1):89-115.
5. Dixit, S. K., & Sambasivan, M. (2018). A review of the Australian healthcare system: A policy perspective. SAGE open medicine, 6, 2050312118769211.
6. Johnson, J., Hall, L. H., Berzins, K., Baker, J., Melling, K., & Thompson, C. (2018). Mental healthcare staff well‐being and burnout: A narrative review of trends, causes, implications, and recommendations for future interventions. International journal of mental health nursing, 27(1), 20-32.
7. Abreu Fuentes JR, Ponce Pastor RM. Pedagogical Tact: Phenomenology in Education from Community and Family Perspectives. Journal of Scientific Metrics and Evaluation. 2024;2(1):49-68.
8. Alarcón Osorio D, Gonzales Soria MB. Left-wing epistemology and right-wing ethics in public universities. Journal of Scientific Metrics and Evaluation. 2024;2(1):31-47.
9. Land, K. J., Boeras, D. I., Chen, X. S., Ramsay, A. R., & Peeling, R. W. (2019). Reassured diagnostics to inform disease control strategies, strengthen health systems and improve patient outcomes. Nature microbiology, 4(1), 46-54.
10. Fathollahi-Fard, A. M., Ahmadi, A., Goodarzian, F., & Cheikhrouhou, N. (2020). A bi-objective home healthcare routing and scheduling problem considering patients’ satisfaction in a fuzzy environment. Applied soft computing, 93, 106385.
11. Velázquez-Hernández M, Marín González D, Paumier Durán AG, Carcasés Lores L, Landrove-Escalona EA, Godínez Linares R. Scientific production of Cardiology in Cuban student medical journals in the period 2019-2023. Journal of Scientific Metrics and Evaluation. 2024;2(1):137-50.
12. Specchia, M. L., Frisicale, E. M., Carini, E., Di Pilla, A., Cappa, D., Barbara, A., ... & Damiani, G. (2020). The impact of tumor board on cancer care: evidence from an umbrella review. BMC health services research, 20, 1-14.
13. West, C. P., Dyrbye, L. N., & Shanafelt, T. D. (2018). Physician burnout: contributors, consequences and solutions. Journal of internal medicine, 283(6), 516-529.
14. Wei, H., Sewell, K. A., Woody, G., & Rose, M. A. (2018). The state of the science of nurse work environments in the United States: A systematic review. International journal of nursing sciences, 5(3), 287-300.
15. Labrague, L. J., Nwafor, C. E., & Tsaras, K. (2020). Influence of toxic and transformational leadership practices on nurses’ job satisfaction, job stress, absenteeism and turnover intention: A cross‐sectional study. Journal of nursing management, 28(5), 1104-1113.
FINANCING
No financing.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Data curation: Supriya Awasthi, Bijal Zaveri, Sonali Parida, Sahil Suri, Amritpal Sidhu, M. M. Thorat.
Methodology: Supriya Awasthi, Bijal Zaveri, Sonali Parida, Sahil Suri, Amritpal Sidhu, M. M. Thorat.
Software: Supriya Awasthi, Bijal Zaveri, Sonali Parida, Sahil Suri, Amritpal Sidhu, M. M. Thorat.
Drafting - original draft: Supriya Awasthi, Bijal Zaveri, Sonali Parida, Sahil Suri, Amritpal Sidhu, M. M. Thorat.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Supriya Awasthi, Bijal Zaveri, Sonali Parida, Sahil Suri, Amritpal Sidhu, M. M. Thorat.