doi: 10.56294/hl2024.368
ORIGINAL
Integrating Environmental Health into Healthcare Management Practices
Integración de la salud ambiental en las prácticas de gestión sanitaria
Syed Fahar Ali1
![]() ,
Jayaprakash Lamoria2
,
Jayaprakash Lamoria2 ![]() ,
Suvendu Narayan Mishra3
,
Suvendu Narayan Mishra3 ![]() ,
Amit Kumar4
,
Amit Kumar4 ![]() ,
Ashmeet Kaur5
,
Ashmeet Kaur5 ![]() ,
Ravindra Shinde6
,
Ravindra Shinde6 ![]()
1SJMC, Noida International University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.
2Parul Institute of Management and Research-MBA, Parul University, Vadodara, Gujarat, India.
3IMS and SUM Hospital, Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of Psychiatry, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
4Centre of Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Punjab, India.
5Chitkara Centre for Research and Development, Chitkara University, Himachal Pradesh, India.
6Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Krishna Vishwa Vidyapeeth “Deemed to be University”, Dept. of Microbiology, Taluka-Karad, Dist-Satara, Maharashtra, India.
Cite as: Fahar Ali S, Lamoria J, Narayan Mishra S, Kumar A, Kaur A, et al. Integrating Environmental Health into Healthcare Management Practices. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2024; 3:.368. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2024.368
Submitted: 09-03-2024 Revised: 27-07-2024 Accepted: 18-11-2024 Published: 19-11-2024
Editor: PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: conveying Environmental Health in Healthcare Management Practices: Analysis of Systematic Review the authors systematically reviewed the existing literature for best practices and strategies for integrating ecological health into healthcare management.
Method: we performed an extensive search on the comprehensive database, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and Science Direct. However, these studies focused on integrating environmental health in healthcare management, either through the implementation of policy initiatives in educational settings or through organizational transitions.
Results: the review revealed emergent themes and strategies for integrating environmental health into healthcare management. These steps varied and ranged from forming environmental health committees to creating policies and protocols on how to address environmental health (e.g., incorporating ecological health-related goals and metrics in performance evaluations and providing staff training and education on environmental health, among others).
Conclusions: the culture of healthcare management can be acted upon to enhance environmental health, resulting in intelligent patient outcomes and illuminated healthcare practices. Nevertheless, additional research and evaluations of these integration movements have yet to assess their efficacy and identify areas for improvement.
Keywords: Healthcare Management; Databases; Staff Training; Ecological Health; Effectiveness.
RESUMEN
Introducción: transmisión de la salud ambiental en las prácticas de gestión sanitaria: Análisis de una revisión sistemática los autores revisaron sistemáticamente la bibliografía existente en busca de mejores prácticas y estrategias para integrar la salud ecológica en la gestión sanitaria.
Método: se realizó una extensa búsqueda en la base de datos exhaustiva, incluyendo PubMed, Google Scholar y Science Direct. Sin embargo, estos estudios se centraron en la integración de la salud ecológica en la gestión sanitaria, ya fuera mediante la aplicación de iniciativas políticas en entornos educativos o a través de transiciones organizativas.
Resultados: la revisión reveló temas y estrategias emergentes para integrar la salud ambiental en la gestión sanitaria. Estos pasos variaron y abarcaron desde la formación de comités de salud ambiental hasta la creación de políticas y protocolos sobre cómo abordar la salud ambiental (por ejemplo, la incorporación de objetivos y métricas relacionados con la salud ecológica en las evaluaciones de rendimiento y la formación y educación del personal en materia de salud ambiental, entre otros).
Conclusiones: se puede actuar sobre la cultura de la gestión sanitaria para mejorar la salud ambiental, lo que se traduce en resultados inteligentes para los pacientes y prácticas sanitarias iluminadas. No obstante, aún es necesario realizar más investigaciones y evaluaciones de estos movimientos de integración para valorar su eficacia e identificar áreas de mejora.
Palabras clave: Gestión Sanitaria; Bases de Datos; Formación del Personal; Salud Ecológica; Eficacia.
INTRODUCTION
One of the key drivers behind healthcare management practices is environmental health. Environmental Health Definition: The recognition of the environmental effects on human health and the promotion of human health through the absence or mitigation of impacts on the environment.(1) Embedding environmental health in our management of healthcare practice would benefit not only individual patients but also have a more significant impact on public health and the environment. We will discuss how environmental health is such an essential aspect of healthcare management, the extent to which this integration currently exists, and what can still be done for this integration.(2) The integration of environmental health into health care management addresses one of the significant issues of our time—the challenges to the environment and the associated risks to human health. In addition, the environment is essential for the promotion of individual and community health and well-being.(3)
Health effects of air pollution: Air pollution has been linked to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, while toxic chemical exposure can cause multiple health problems, from cancer to neurological disorders(4) by integrating environmental health into healthcare through management practices such as valid and effective healthcare services, identifying elements that pose threats to beneficial environmental factors, and reducing exposure of patients to these threats. Introducing environmental health to healthcare management could be a way to address health equity and social justice.(5) “For a lot of marginalized and low-income communities who don’t have access to good healthcare and for whom the health consequences of environmental devastation are becoming more and more of a reality, environmental hazards have been on the rise for some time. Addressing healthcare management challenges in these domains can promote both health equity and social justice, whereby not only all people have good access to a healthy environment but also access to needed healthcare services.(6)
Environmental health is still relatively nascent in its integration into healthcare management. Environmental health is not embedded in most healthcare organizations’ decisions and strategies. Implementing environmental health management systems in health organizations is one of the ways to tackle these challenges. An Environmental Health Management System (EHMS) is a tool introduced for the integration of Environmental Health aspects into policies and procedures by organizations. It offers a systematic method for the identification, assessment, and management of environmental risks within healthcare institutions.(7)
EHMS also helps healthcare organizations better understand their impacts and how to reduce them. Disseminating information and training opportunities on environmental health for healthcare professionals can also be supported in healthcare management practices.(8) Environmental health education can be integrated into the early curricula of healthcare-related disciplines (medicine, nursing, public health) to enhance the knowledge and skills of future healthcare professionals.(9) Another method is to provide professional development courses for current healthcare leaders that focus on training healthcare professionals on advances in environmental health and how to incorporate EV programs into healthcare service delivery. Payment and education efforts, collaboration between healthcare organizations and environmental health agencies, and effective integration are also crucial for the successful integration of EHMS.(10) Collectively, they can pool resources and knowledge to tackle environmental challenges and enhance the community’s health at large. The main contribution of the paper has the following
• Healthcare Facilities Management of environmental health information. Hazardous waste is untenable. Bacterial contamination can affect a large number of patients, and the recommendation to Aria Health helps. This can lower the prevalence of environmental-related diseases and subsequently enhance public health outcomes.
• Healthcare facilities can reduce operational costs by promoting waste reduction, energy efficiency, and other environmentally friendly practices. This can then translate into reduced healthcare expenses for patients and society as a whole.
• Embedding environmental health considerations in healthcare management practices will foster a more sustainable healthcare system. This means considering the long-term effects of healthcare activities on the environment and making positive efforts to minimize waste, save resources, and create a healthier place for patients and staff.
(1)integrated pest management (IPM) spreads a plan that seeks to control pests with a leap of insights and minimize the negatives on the habitat and health. Nonetheless, there are significant challenges to it’s (ensure Implementation, including high costs, lack of support from farmers, and low levels of knowledge and infrastructure in developing countries.(2) big data analytics-enabled transformation model (structured big data analytics embedded into business processes and business operations); encompasses the processes of identifying key data sources, deploying analytics tools, and leveraging insights for organizational advancement and decision-making. Cairncross, S., et al. Ecosystem and Environmental health engineering in the tropics.(3)
This involves designing and establishing efficient and sustainable systems to supply safe drinking water, adequate disposal of sewage, and vector control of these diseases. (4)have introduced a framework for assessing sustainability in healthcare systems (a suite of tools and processes used to evaluate the environmental, social and economic impact of healthcare systems). It offers metrics and indicators that allow for the analysis of how well healthcare systems are consistent with sustainability principles to foster sustainability. Bobb, J. F., et al. Statistical software is discussed to assess the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures through Bayesian kernel machine regression.(5) This enables a more complete assessment of the impact of multi-exposure on health.
|
Table 1. Comparative Analysis of Existing Models |
|||
|
Author |
Year |
Advantage |
Limitation |
|
Deguine, J. P et al.(1) |
2021 |
One advantage is that it promotes environmentally-friendly pest control methods that minimize the use of harmful chemicals. |
Difficulty in fully implementing and coordinating all aspects of IPM due to diverse and complex pest control scenarios. |
|
Wang, Y et al.(2) |
2018 |
Improved data-driven decision-making, as all relevant data is gathered and analyzed together for a comprehensive view of the organization. |
Inability to accurately predict long-term impacts on business strategy and market volatility. |
|
Cairncross, S et al.(3) |
2018 |
Preventing and reducing the spread of waterborne diseases through improved sanitation and water management practices, leading to improved public health. |
Infrastructural deficiencies in water and sanitation systems hinder effective disease control efforts in tropical regions. |
|
AlJaberi, O. A et al.(4) |
2020 |
A standardized framework allows for more accurate and efficient comparison of sustainability between different healthcare systems. |
Subjectivity in selecting indicators and measurement methods may result in inconsistent and biased results. |
|
Bobb, J. F et al.(5) |
2018 |
The advantage is that it can accurately assess the impact of multiple exposures, taking into account their interrelated effects. |
Potential limitations include the need for extensive computational resources and difficulty interpreting complex models. |
|
Figure ueroa, C. A et al.(6) |
2019 |
Improved alignment and coordination of efforts to address pressing health issues and achieve better health outcomes. |
Limited resources and funding hinder the ability to address and implement effective solutions for global health leadership and workforce management. |
|
Santana, M. J et al.(7) |
2018 |
Improved patient satisfaction and outcomes through personalized care tailored to their specific needs and preferences. |
Lack of standardized guidelines for implementation. |
|
Hunter, R. F et al.(8) |
2019 |
Enhancing physical and mental health, promoting social interaction and equality, and providing a sense of connection to nature for urban residents. |
Data bias towards specific populations and failure to account for intersectionality in analysis. |
|
Chen, M et al.(9) |
2020 |
Improving efficiency and accuracy in medical diagnoses and treatment recommendations. |
Potential for bias and inaccuracy in decision-making due to limited understanding of the complex nature of healthcare. |
|
Eckelman, M. J et al.(10) |
2020 |
Increased awareness and understanding of the health risks associated with pollution leading to potential preventative measures and policies. |
Lack of cohesive national approach to address the issue and enforce regulations. |
Health leadership and workforce are challenged by myriad global priorities, such as escalating healthcare services, lack of trained workforce, lack of funds and resources, and the need for innovation with new technologies and changing healthcare needs globally. These do not happen without strong leadership, strategic planning, and good management to ensure quality and sustainable delivery of health care. explained the person-centered care in the health system. This is about understanding the specificities of the person and engaging them in their care. This can be realized by respecting a safe space where the person feels valued and is a key contributor to decisions.
(8)have addressed the environmental benefits of Urban green space interventions, including reducing air and noise pollution, enhancing biodiversity, cycling, and alleviating the heat island effect. They also have health benefits for inhabitants, such as encouraging physical activity and mental well-being. Moreover, it enhances social relationships and equity as it provides access and opportunities for different socio-economic statuses in urban settings. Artificial Intelligence Artificial intelligence in healthcare, a supplement to the alternative domains represented in the articles, primarily uses advanced algorithms and data analysis techniques that are capable of automating and improving processes and decision-making in the healthcare field.(9) Healthcare providers are lagging in implementing advanced technology infrastructure for a digital future — an opportunity to transform how care is delivered, reallocate innovative spending, improve patient outcomes and realize cost efficiencies. Healthcare pollution and public health damage in the United States: an update | European Journal of Public Health | Oxford Academic In October 2023, the most recent data on the state of healthcare pollution and its impact on public health, as well as strategies for addressing this ongoing problem, was released.
METHOD
The development we talk about here refers to the integration of principles, practices, and philosophy of ecological health in healthcare providers’ management activities. This would encompass establishing a framework and principles for identifying, evaluating, and managing environmental health hazards in health systems. One approach would be to form a working group or task force that would be responsible for coordinating the integration of environmental health with public health practices and developing policies and procedures for how ecological health would be managed moving forward. This would also include regular inspections and assessments/audits to identify potential hazards and risks. Healthcare staff would receive training and education programs to raise their awareness of environmental health issues and educate them on how to build preventative measures into their daily practices. This would also include advancing sustainability and green practices in the healthcare facility. To keep track of ecological health regulation updates, partnerships with local environmental agencies and organizations will be established to employ effective strategies for risk management purposes. Even the integration of environmental health into healthcare management practices will ultimately result in a more sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to healthcare, promoting the health and well-being of patients, staff, and the surrounding community. Figure 1 shows the Proposed Development Model.
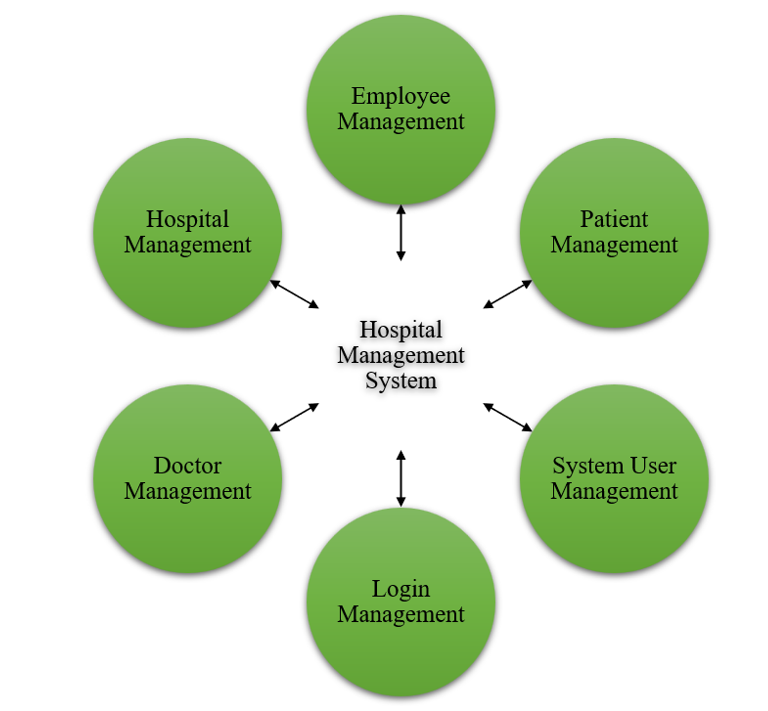
Figure 1. Proposed Development Model
A Hospital Management System is a unique source for managing the everyday operations of the hospitals and healthcare procedures. It makes things easier and automates tasks like registering patients, scheduling appointments, managing doctors and staff, managing inventory, and billing. You are based on modules like employee, patient, doctor, and user. Employee Management Module: This module is for the management of employees working in the hospital. Such activities include creating employees’ profiles, attendance and leaves monitoring and managing their schedules. It also allows for the management of employee pay, benefits and performance reviews:
⦁ Patient Management Module (TPM): handles patient registration, maintains the medical history, and manages appointments, both inpatient and outpatient. It also documents patient diagnosis, treatment and medication, enabling doctors to retrieve patient records more efficiently and deliver quality treatment. Part of hospital management software is doctor management to doctor and timetable management in hospitals. It allows doctors to create profiles, track their availability, and book appointments. It also addresses generating doctor schedules to ensure enough coverage for patient visits.
The system User Management module is the module that Manage access to the system and its modules. It specifies user roles and criteria that narrow access to sensitive data to authorized personnel. It also provides system administrators with the ability to watch user activity and maintain confidentiality and data security. This is an essential part of the operation of the hospitals. By facilitating communication between its various modules, it creates a better work environment for staff and a frictionless experience for patients.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Integrating ecological health into health systems management can reduce the impacts of facilities and the opportunity for associated health effects. Integrating environmental health into healthcare management practices can fulfill dual roles. Not only can they help healthcare facilities save costs by reducing waste and implementing sustainable practices, but they can also improve patient care and wellness. Here are both the answers and explanations of why cleaning cleanliness is vital in hospitals: The quality of care that a person wishes to provide to patients can also be improved with these cleaning agents, as a clean-tidy environment will help create a clean patient outcome. Environmental health and healthcare management can help raise awareness and educate people about the effects of environmental factors on their health. It can help many countries take preventive measures against hazardous ecological factors that may negatively affect the health of individuals. This can result in improved prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions associated with environmental factors.
Environmental Management System Compliance
This method of management, according to the best practices, allows for the determination, management, and minimization of the impact of the organization’s activities on the environment. The institution must prove compliance with applicable laws and regulations; The institution must have needed basic information and data on environmental performance; It must standardize monitoring, evaluation, and review processes for continuous improvement in environmental performance.
|
Table 2. Comparison of Environmental Management System Compliance |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
BDM |
GSCM |
HCISM |
IIRM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
50 |
17 |
9 |
15 |
6 |
6 |
|
100 |
5 |
21 |
8 |
24 |
25 |
|
150 |
11 |
16 |
14 |
18 |
28 |
|
200 |
7 |
10 |
19 |
4 |
57 |
|
250 |
12 |
22 |
20 |
13 |
79 |
An EMS can play a critical role in the healthcare industry by ensuring that healthcare facilities operate in an environmentally sustainable manner, with proper waste disposal, conservation of energy and water, and reduction of harmful pollutants. Figure 2 shows the computation of Environmental Management System Compliance.
Next, conceptualizing healthcare management practices that take into account environmental health is challenging yet also educational.
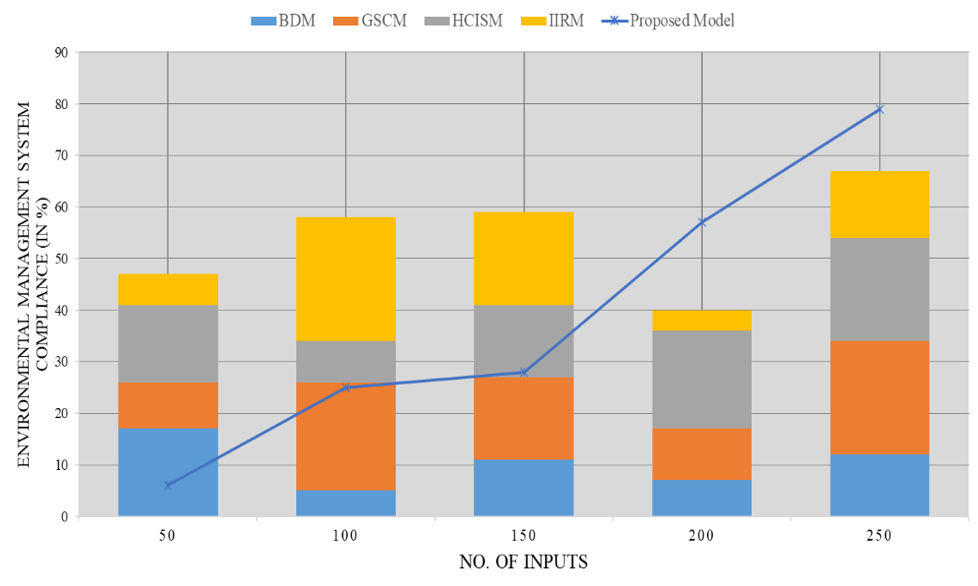
Figure 2. Computation of Environmental Management System Compliance
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction
Promoting environmental health within the health system’s management practices includes adopting practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing these practices can also help healthcare facilities minimize their carbon footprints and contribute to the global response to climate change.
|
Table 3. Comparison of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
BDM |
GSCM |
HCISM |
IIRM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
10 |
29 |
33 |
58 |
42 |
93 |
|
20 |
47 |
50 |
32 |
25 |
88 |
|
30 |
52 |
61 |
28 |
34 |
90 |
|
40 |
38 |
45 |
57 |
21 |
92 |
|
50 |
31 |
54 |
46 |
27 |
87 |
It can also result in cost reductions and better efficiency in healthcare operations. These facilities, in turn, allow patients to be educated to enhance environmental health, which will also reduce human health issues. Figure 3 shows the computation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction.
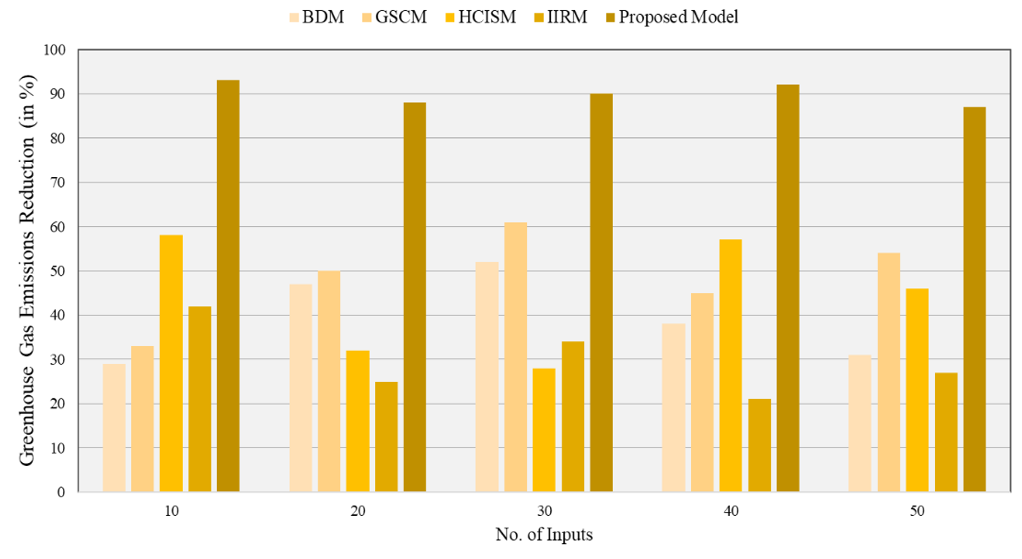
Figure 3. Computation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction
This is the information we need to see more of. I am excited to know that such a single-minded, ecologically aware healthcare system will, if anything, have less environmental impact as time goes on.
Sustainable Procurement
Sustainable procurement in health care is the systematic and progressive integration of environmental health considerations into the organization’s purchasing process, decisions, and procedures. This method involves calculating the environmental impact of items and services, searching for substitutes, and implementing programs that boost environmental performance. It also means encouraging suppliers to create sustainability in the supply chain.
|
Table 4. Comparison of Sustainable Procurement |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
BDM |
GSCM |
HCISM |
IIRM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
100 |
74 |
55 |
87 |
38 |
32 |
|
200 |
70 |
34 |
85 |
33 |
45 |
|
300 |
72 |
67 |
90 |
50 |
67 |
|
400 |
76 |
52 |
89 |
29 |
88 |
|
500 |
72 |
46 |
90 |
41 |
87 |
This means using eco-friendly products, reducing ecological risk and contributing to the sustainability of the healthcare sector. It requires healthcare managers, procurement practitioners and suppliers to work together to ensure sustainable priorities are taken into account and fulfilled. Figure 4 shows the computation of Sustainable Procurement.
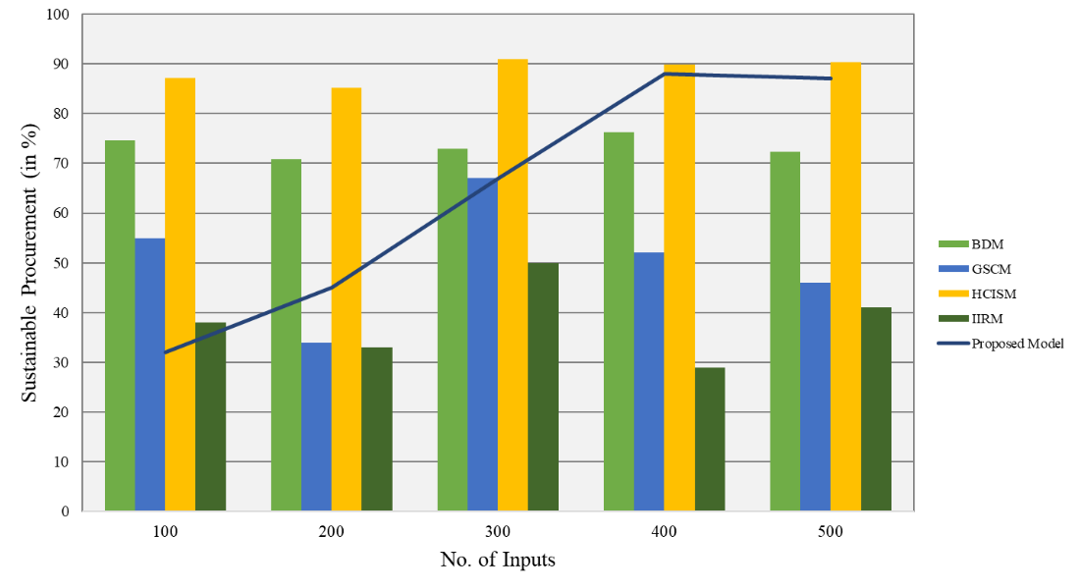
Figure 4. Computation of Sustainable Procurement
Engaging in environmental health procurement not only helps healthcare institutions become better stewards of the environment but it also creates a healthier, sustainable community.
CONCLUSION
The inclusion of environmental health in healthcare management practices can lead to numerous benefits for healthcare facilities as well as patients. By identifying and addressing the ecological determinants of health, it can help. Ultimately, it can improve patient outcomes and decrease healthcare costs. These encompass decreasing exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants, providing a safer, healthier living and working environment, and preventing environmental hazards that result in chronic diseases. The integration of ecological health into healthcare management practices should increase the sustainability and resilience of healthcare facilities through the adoption of environmentally conscious practices and policies. It contributes to environmental protection and lowers operational and maintenance costs at healthcare facilities. Including environmental health in healthcare management procedures is a critical block in the course of action of promoting well-being and health for individuals and the community. It is a significant component of delivering effective healthcare services and must be a focal point for healthcare organizations, regulators, and healthcare providers. With us being able to do this hand in hand, we can help create a better world to make sure that the general wellness of the patients is at a better place.
REFERENCES
1. Deguine JP, Aubertot JN, Flor RJ, Lescourret F, Wyckhuys KA, Ratnadass A. Integrated pest management: good intentions, hard realities. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development. 2021;41(3):38.
2. Wang Y, Kung L, Wang WYC, Cegielski CG. An integrated big data analytics-enabled transformation model: Application to health care. Information & Management. 2018;55(1):64-79.
3. Cairncross S, Feachem R. Environmental health engineering in the tropics: Water, sanitation and disease control. Routledge; 2018.
4. AlJaberi OA, Hussain M, Drake PR. A framework for measuring sustainability in healthcare systems. International Journal of Healthcare Management. 2020.
5. Bobb JF, Claus Henn B, Valeri L, Coull BA. Statistical software for analyzing the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures via Bayesian kernel machine regression. Environmental Health. 2018;17:1-10.
6. Figure ueroa CA, Harrison R, Chauhan A, Meyer L. Priorities and challenges for health leadership and workforce management globally: A rapid review. BMC Health Services Research. 2019;19:1-11.
7. Santana MJ, Manalili K, Jolley RJ, Zelinsky S, Quan H, Lu M. How to practice person‐centred care: A conceptual framework. Health Expectations. 2018;21(2):429-40.
8. Hunter RF, Cleland C, Cleary A, Droomers M, Wheeler BW, Sinnett D, et al. Environmental, health, wellbeing, social and equity effects of urban green space interventions: A meta-narrative evidence synthesis. Environment International. 2019; 130:104923.
9. Chen M, Decary M. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: An essential guide for health leaders. Healthcare Management Forum. 2020;33(1):10-8.
10. Eckelman MJ, Huang K, Lagasse R, Senay E, Dubrow R, Sherman JD. Health care pollution and public health damage in the United States: An update. Health Affairs. 2020;39(12):2071-79.
FINANCING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Syed Fahar Ali, Jayaprakash Lamoria, Suvendu Narayan Mishra, Amit Kumar, Ashmeet Kaur, Ravindra Shinde.
Research: Syed Fahar Ali, Jayaprakash Lamoria, Suvendu Narayan Mishra, Amit Kumar, Ashmeet Kaur, Ravindra Shinde.
Writing - original draft: Syed Fahar Ali, Jayaprakash Lamoria, Suvendu Narayan Mishra, Amit Kumar, Ashmeet Kaur, Ravindra Shinde.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Syed Fahar Ali, Jayaprakash Lamoria, Suvendu Narayan Mishra, Amit Kumar, Ashmeet Kaur, Ravindra Shinde.