doi: 10.56294/hl2024.366
ORIGINAL
Assessing the Role of Leadership in Promoting Patient-Centered Care
Evaluando el papel del liderazgo en la promoción de una atención centrada en el paciente
Axita Thakkar1
![]() ,
Surjeet Sahoo2
,
Surjeet Sahoo2 ![]() ,
Vivek Saraswat3
,
Vivek Saraswat3 ![]() ,
Jatin Khurana4
,
Jatin Khurana4 ![]() ,
Sujayaraj Samuel Jayakumar5
,
Sujayaraj Samuel Jayakumar5
![]() ,
Adarsh Kumar6
,
Adarsh Kumar6 ![]() ,
Atul Bhanudas Hulwan7
,
Atul Bhanudas Hulwan7 ![]()
1Parul Institute of Management and Research-MBA, Parul University, Vadodara, Gujarat, India.
2IMS and SUM Hospital, Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of Psychiatry, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India.
3Centre of Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Punjab, India.
4Chitkara Centre for Research and Development, Chitkara University, Himachal Pradesh-174103 India.
5JAIN (Deemed-to-be University), Department of Forensic science, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
6SJMC, Noida International University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.
7Krishna institute of Medical Sciences, Krishna Vishwa Vidyapeeth “Deemed to be University”, Department of Pathology, Taluka-Karad, Dist-Satara, Maharashtra, India.
Cite as: Thakkar A, Sahoo S, Saraswat V, Khurana J, Jayakumar SS, Kumar A, et al. Assessing the Role of Leadership in Promoting Patient-Centered Care. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2024; 3:.366. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2024.366
Submitted: 08-03-2024 Revised: 24-07-2024 Accepted: 19-11-2024 Published: 20-11-2024
Editor: PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: this study aimed to assess the role of leadership in promoting patient-centered care in healthcare organizations. Patient-centered care is an approach that focuses on meeting patients’ individual needs and preferences, thereby improving their overall experience and outcomes. Effective leadership is crucial in driving the implementation of patient-centered care in healthcare settings.
Method: the proposed development for assessing the role of leadership in promoting patient-centered care involves conducting research and gathering data on the effectiveness of leadership in promoting and implementing patient-centered care practices. A survey or questionnaire would be developed to gather data from healthcare professionals and patients on their perceptions of leadership’s role in promoting patient-centered care.
Results: effective leadership is essential in promoting patient-centered care. Transformational leadership, which emphasizes individualized consideration and intellectual stimulation, was found to be most beneficial in this context. This type of leadership empowers healthcare professionals to actively involve patients in their care actively, leading to higher patient satisfaction and improved outcomes. Servant leadership, which focuses on serving the needs of others, was also found to be effective in promoting patient-centered care.
Conclusions: this study highlights the crucial role of leadership in promoting patient-centered care. Healthcare organizations should focus on developing and nurturing transformational and servant leaders to drive the implementation of patient-centered care. By prioritizing patient needs and preferences and involving them in decision-making processes, leaders can create a culture of patient-centered care within their organizations, ultimately improving patient outcomes and experiences. Further research is needed to explore the specific leadership styles and strategies that are most effective in promoting patient-centered care.
Keywords: Organizations; Patient-Centered Care; Servant Leadership; Preferences; Decision-Making Processes.
RESUMEN
Introducción: este estudio pretende evaluar el papel del liderazgo en la promoción de la atención centrada en el paciente en las organizaciones sanitarias. La atención centrada en el paciente es un enfoque que se centra en satisfacer las necesidades y preferencias individuales de los pacientes, mejorando así su experiencia y resultados generales. Un liderazgo eficaz es crucial para impulsar la implantación de la atención centrada en el paciente en los centros sanitarios.
Método: el desarrollo propuesto para evaluar el papel del liderazgo en la promoción de la atención centrada en el paciente implica la realización de investigaciones y la recopilación de datos sobre la eficacia del liderazgo en la promoción y aplicación de prácticas de atención centrada en el paciente. Se elaboraría una encuesta o cuestionario para recabar datos de profesionales sanitarios y pacientes sobre su percepción del papel del liderazgo en la promoción de la atención centrada en el paciente.
Resultados: un liderazgo eficaz es esencial para promover la atención centrada en el paciente. El liderazgo transformacional, que hace hincapié en la consideración individualizada y la estimulación intelectual, resultó ser el más beneficioso en este contexto. Este tipo de liderazgo capacita a los profesionales sanitarios para implicar activamente a los pacientes en su atención, lo que conduce a una mayor satisfacción de los pacientes y a la mejora de los resultados. El liderazgo de servicio, que se centra en atender las necesidades de los demás, también resultó eficaz para promover una atención centrada en el paciente.
Conclusiones: este estudio destaca el papel crucial del liderazgo en la promoción de la atención centrada en el paciente. Las organizaciones sanitarias deberían centrarse en desarrollar y fomentar líderes transformadores y servidores para impulsar la implantación de la atención centrada en el paciente. Al dar prioridad a las necesidades y preferencias de los pacientes e implicarlos en los procesos de toma de decisiones, los líderes pueden crear una cultura de atención centrada en el paciente dentro de sus organizaciones y, en última instancia, mejorar los resultados y las experiencias de los pacientes. Es necesario seguir investigando sobre los estilos y estrategias de liderazgo más eficaces para promover la atención centrada en el paciente.
Palabras clave: Organizaciones; Atención Centrada en el Paciente; Liderazgo de Servicio; Preferencias; Procesos de Toma de Decisiones.
INTRODUCTION
Leadership plays a critical role in promoting patient-centered care in healthcare organizations.(1) Patient-centered care is a model of healthcare in which patients are actively involved in their own care and decision-making process, and their preferences and needs are at the center of all clinical decisions. It is an approach that focuses on the individual needs and values of patients rather than solely on their medical conditions.(2) It will explore the critical role that leadership plays in facilitating and promoting patient-centered care. One of the key ways in which leadership promotes patient-centered care is by creating a culture that prioritizes patient needs and advocates for their participation in their care. It involves creating a supportive and inclusive environment that encourages open communication, mutual respect, and partnership between healthcare providers and patients. Leaders must set the tone for this culture by modeling patient-centered practices and fostering a positive, collaborative relationship with patients.(3) Leaders must also ensure that patient-centered care is incorporated into the organization’s mission and values. By clearly communicating the importance of patient-centered care to all staff, leaders can create a shared understanding and commitment to this approach. It can include implementing policies and procedures that require patient involvement in decision-making, as well as providing training and resources to support staff in implementing patient-centered practices.(4) Effective communication is another crucial aspect of promoting patient-centered care, and leadership plays a vital role in facilitating this. Leaders must ensure that patients are informed and involved in their care by promoting open and honest communication between patients, their families, and healthcare providers. It can include encouraging patients to ask questions and share their concerns, as well as providing them with the necessary information to make informed decisions about their care.(5) Leadership has a responsibility to ensure that patient’s needs and preferences are considered and integrated into all aspects of the healthcare system. It can include involving patients in the design and evaluation of services, as well as offering options for patient-centered care, such as shared decision-making and care planning. By involving patients in these processes, leaders can create a healthcare system that respects and responds to the unique needs and values of each individual.(6) Leadership also plays a crucial role in promoting a patient-centered approach within the healthcare team. It involves fostering a collaborative and multidisciplinary approach to patient care, where all members of the team work together to support patients in achieving their goals and meeting their needs.(7) Effective leadership in this area involves promoting a culture of mutual trust and respect, encouraging open communication and teamwork, and recognizing and valuing the contributions of all healthcare team members. Leadership is essential in promoting patient-centered care through continuous quality improvement efforts. It involves regularly evaluating and monitoring the delivery of patient-centered care to identify areas for improvement and to ensure that patient’s needs are being met.(8) By actively seeking and responding to patient feedback, leaders can continuously strive to improve and enhance the patient’s experience and outcomes. Where patients have become more informed and engaged in their care, leadership must also embrace technological advancements and innovative practices to promote patient-centered care. It can include utilizing electronic health records and telehealth services to improve communication and access to care, as well as leveraging data and analytics to understand the needs and preferences of patients better.(9) Leadership plays an essential role in promoting patient-centered care in healthcare organizations. By creating a culture that prioritizes patient needs, ensuring effective communication, incorporating patient preferences into all aspects of care, fostering a collaborative healthcare team, and continuously striving for improvement, leadership can facilitate the transformation of healthcare into a patient-centered system.(10) It is only through effective leadership that patient-centered care can become the standard of care in healthcare organizations, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction. The main contribution of the paper has the following:
• Effective leadership can promote the adoption of a patient-centered mindset among healthcare staff, ensuring that patient needs and preferences are prioritized in all aspects of care. It can lead to a more positive healthcare experience for patients and improved health outcomes.
• Leaders can play a key role in designing and implementing systems and processes that support patient-centered care, such as providing staff training and resources, collecting and utilizing patient feedback, and integrating patients and their families in care planning and decision-making.
• Leaders can facilitate better communication and collaboration among healthcare teams, patients, and their families, promoting a partnership approach to care. This can help build trust, enhance the patient experience, and improve overall quality of care In decision-making processes.
Agha, A. Z et al.(1) have discussed that the VHA has implemented various strategies to improve patient-centered care and increase patient engagement. Clinical staffs have overcome barriers to patient engagement by utilizing effective communication techniques, promoting shared decision-making, and using technology to improve access to care. These efforts have resulted in improved patient satisfaction and better health outcomes. Fix, G. M et al.(2) have discussed that Patient-centered care is an approach to healthcare that prioritizes the individual needs and values of the patient. It involves active listening, shared decision-making, and collaboration between healthcare professionals and patients in order to provide personalized and holistic care. It recognizes the importance of the patient’s perspective in their care. Grover, S et al.(3) have discussed that patient-centered care is a healthcare approach that focuses on the individual needs of the patient rather than just their illness. It involves actively involving patients in their care decisions, providing information and education, and addressing their physical, emotional, and social needs. It can be implemented by putting the patient at the center of all healthcare interactions and tailoring treatments to their unique needs. Charosaei, F et al.(4) have discussed Effective strategies for implementing patient-centered care in cardiac care units involving patients in decision-making, emphasizing communication and education, promoting multidisciplinary collaboration, incorporating patient feedback and preferences, providing emotional support, and utilizing technology to improve accessibility and coordination. These strategies can ultimately improve outcomes and patient satisfaction in the cardiac care setting. Bachnick, S et al.(5) have discussed that Patient-centered care is an approach to healthcare that prioritizes the needs and preferences of the patient. Nurse work environment refers to the organizational and physical factors that impact nurses’ ability to provide quality care. Implicit rationing of nursing care occurs when nurses are unable to provide all necessary care due to limited resources or time.
|
Table 1. Comparative Analysis of Existing Models |
|||
|
Author |
Year |
Advantage |
Limitation |
|
Agha, A. Z et al.(1) |
2018 |
Better health outcomes through increased patient satisfaction, trust, and participation in their care. |
Limited resources and competing priorities may make it challenging for clinical staff to implement patient-centered care initiatives at the VHA fully. |
|
Fix, G. M et al.(2) |
2018 |
Promotes individualized and personalized approach to healthcare, leading to improved patient satisfaction and outcomes. |
Subjectivity in employee understanding may impact the consistency of implementation and effectiveness in achieving patient-centered care goals. |
|
Grover, S et al.(3) |
2022 |
Increased patient satisfaction and engagement in their own healthcare decisions. |
A lack of standardized definitions and measures leads to inconsistent implementation and difficulties in evaluating effectiveness. |
|
Charosaei, F et al.(4) |
2021 |
Improved patient satisfaction and outcomes through personalized and collaborative care, leading to better overall patient experience and health outcomes. |
One limitation is that patient-centered care can increase workload and require additional resources and training for staff. |
|
Bachnick, S et al.(5) |
2018 |
Improved patient outcomes, job satisfaction for nurses, and efficient allocation of limited resources in Swiss acute care hospitals. |
Patients may not always have the ability or resources to engage in patient-centered carefully. |
|
Stockdale, S. E et al.(6) |
2020 |
It ensures that the medical home transformation aligns with evidence-based practices and improves the overall quality of care for Veterans. |
Difficulty in capturing the complexities and nuances of implementation within a single fidelity measure. |
|
Alhalal, E et al.(7) |
2020 |
Improved patient satisfaction and outcomes due to personalized care tailored to specific needs and preferences. |
Actual patient satisfaction with care cannot be measured due to nurses’ subjective perceptions. |
|
Asif, M et al.(8) |
2019 |
Leadership can create a culture of accountability and teamwork, leading to improved communication and patient satisfaction. |
Difficulty in measuring and quantifying the impact of specific leadership practices on patient satisfaction and separating them from other factors. |
|
Zuraik, A et al.(9) |
2019 |
Improved understanding of patient needs and preferences, leading to more relevant and effective healthcare interventions. |
Patients are not always capable of providing accurate information due to language barriers or cognitive impairments. |
|
Kim, E. J et al.(10) |
2020 |
Increased patient engagement and empowerment, leading to improved health outcomes and better self-management of chronic conditions. |
Limited generalizability due to the non-inclusion of diverse patient populations and varying health conditions. |
Stockdale, S. E et al.(6) have discussed that fidelity is necessary for implementing quality improvement strategies for patient-centered medical homes in the Veterans Health Administration. It includes determining how closely the strategies are followed, measuring their effectiveness, and making adjustments as needed to ensure successful transformation. Alhalal, E et al.(7) have discussed that Patient-centered care is a fundamental aspect of nursing practice that aims to promote patient satisfaction and positive outcomes. The predictors of patient-centered care provision among nurses in acute care settings include communication skills, empathy, cultural competence, teamwork, and organizational support. These factors contribute to the delivery of high-quality and patient-centered care. Asif, M et al.(8) have discussed how Leadership plays a crucial role in enhancing patient satisfaction. Effective leaders establish a positive and patient-centered culture that prioritizes both administrative and medical quality. It includes implementing efficient processes, ensuring competent and caring staff, and fostering open communication with patients. A strong and capable leader can significantly improve the overall patient experience and satisfaction. Zuraik, A et al.(9) have discussed that engaging the patient is an approach to research that actively involves patients in the design, implementation, and dissemination of research studies. This patient-centered approach ensures that the research is relevant, meaningful, and responsive to the needs and preferences of patients, leading to improved healthcare outcomes. Kim, E. J et al.(10) have discussed Patient-centered mobile health technologies, which refer to digital tools and applications that prioritize patient needs and preferences in healthcare delivery. Evaluating these technologies requires clear definitions of patient-centeredness, robust methodologies, and measuring outcomes such as patient satisfaction, engagement, and health outcomes.
METHOD
The proposed development for assessing the role of leadership in promoting patient-centered care involves conducting research and gathering data on the effectiveness of leadership in promoting and implementing patient-centered care practices. A team of researchers and healthcare professionals will carry out this development. The first step would involve identifying the key components of patient-centered care and understanding how leadership can influence these components. It would include reviewing existing literature and conducting interviews with healthcare leaders who have successfully implemented patient-centered care in their organizations.
A survey or questionnaire would be developed to gather data from healthcare professionals and patients on their perceptions of leadership’s role in promoting patient-centered care. It would provide valuable insights into the current state of patient-centered care and the impact of leadership on its implementation. To further assess the role of leadership, case studies would be conducted in healthcare organizations that have successfully implemented patient-centered care. It would involve interviews with leaders and staff, as well as observations of their practices.
The data collected from these methods would then be analyzed to identify key themes and patterns that demonstrate the impact of leadership on promoting patient-centered care. This information would be used to develop guidelines and recommendations for healthcare leaders to promote and implement patient-centered care practices in their organizations effectively. Figure 1 shows the development model.
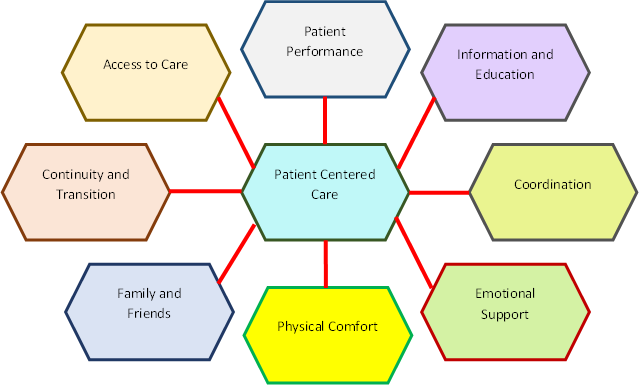
Figure 1. Development model
Patient-centered care is a holistic approach to healthcare that prioritizes the needs and preferences of the patient. Information and education are essential components of patient-centered care. It involves providing patients with detailed information about their health condition, treatment options, and potential outcomes. It also involves educating patients about how to manage their health and make informed decisions in their treatment. Emotional support is another critical aspect of patient-centered care. Patients often experience emotional distress and anxiety related to their health condition. It may involve listening to their concerns, addressing their fears, and providing reassurance and encouragement. Physical comfort is also crucial in patient-centered care. It consists of addressing the physical symptoms and discomfort that patients may experience as a result of their illness or treatment. Healthcare professionals must prioritize measures to alleviate pain, discomfort, and other physical symptoms to improve the overall well-being of the patient. Continuity and transition of care are essential components of patient-centered care. Patients must have access to uninterrupted care, especially during transitions between hospital and home or between various specialists. Access to care is a fundamental principle of patient-centered care. Healthcare providers must strive to eliminate barriers to care and promote equitable access for all patients.
RESULTSAND DISCUSSION
The result of the assessment shows that leadership plays a crucial role in promoting patient-centered care. It was found that effective leadership is essential for creating a patient-centered culture within healthcare organizations. Leaders who prioritize patient-centeredness and model the behavior themselves can influence their team members to do the same. It leads to better communication and collaboration and ultimately improves the quality of care delivered to patients. The results also highlighted the importance of leadership in setting policies and procedures that support patient-centered care. Leaders who prioritize patient needs and preferences when making decisions and developing guidelines can help ensure that patient-centered care remains a top priority. These findings emphasize the critical role of leadership in shaping the delivery of care and improving patient outcomes. Healthcare organizations should invest in leadership development programs that focus on promoting patient-centered care principles and practice.
Empowerment of Patients
Empowerment of patients is the process of enabling patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions and take control of their health. It involves providing patients with access to information, resources, and support to make informed choices and manage their conditions effectively. It can include patient education, shared decision-making, and involving patients in the design and evaluation of healthcare services.
|
Table 2. Comparison of Empowerment of Patients |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
BMCM |
QIM |
VHAM |
MHTM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
15 |
41,23 |
42,89 |
46,11 |
44,57 |
69,02 |
|
30 |
42,78 |
43,24 |
44,96 |
41,82 |
62,18 |
|
45 |
43,67 |
44,53 |
41,98 |
46,35 |
63,45 |
|
60 |
44,12 |
45,17 |
42,84 |
43,71 |
60,76 |
|
75 |
45,89 |
46,41 |
43,27 |
42,56 |
64,89 |
Leadership plays a crucial role in promoting patient-centered care by creating a culture of empowerment, setting clear expectations for patient involvement, and providing training and resources to healthcare staff. Figure 2 shows the Computation of Empowerment of Patients.

Figure 2. Computation of Empowerment of Patients
Effective leadership also involves advocating for patient rights and promoting a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers. Through strong leadership, patients are empowered to take an active role in their care, leading to better health outcomes and increased satisfaction with healthcare services.
Staff Engagement and Retention
This involves creating a positive work environment, providing opportunities for professional growth and development, and ensuring fair compensation and work-life balance to keep employees motivated and committed to their jobs.
|
Table 3. Comparison of Staff Engagement and Retention |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
BMCM |
QIM |
VHAM |
MHTM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
20 |
43,45 |
42,76 |
41,91 |
46,23 |
35,23 |
|
21 |
41,68 |
44,87 |
46,49 |
42,32 |
29,63 |
|
22 |
46,13 |
41,94 |
42,73 |
45,68 |
30,79 |
|
23 |
42,78 |
43,28 |
45,92 |
41,57 |
33,14 |
|
24 |
45,89 |
46,37 |
43,52 |
44,81 |
31,67 |
Leadership plays a crucial role in promoting patient-centered care by setting the tone for the organization’s culture and values, encouraging open communication and collaboration among staff, and implementing policies and practices that prioritize patient needs and satisfaction. Figure 3: shows the Computation of Staff Engagement and Retention.
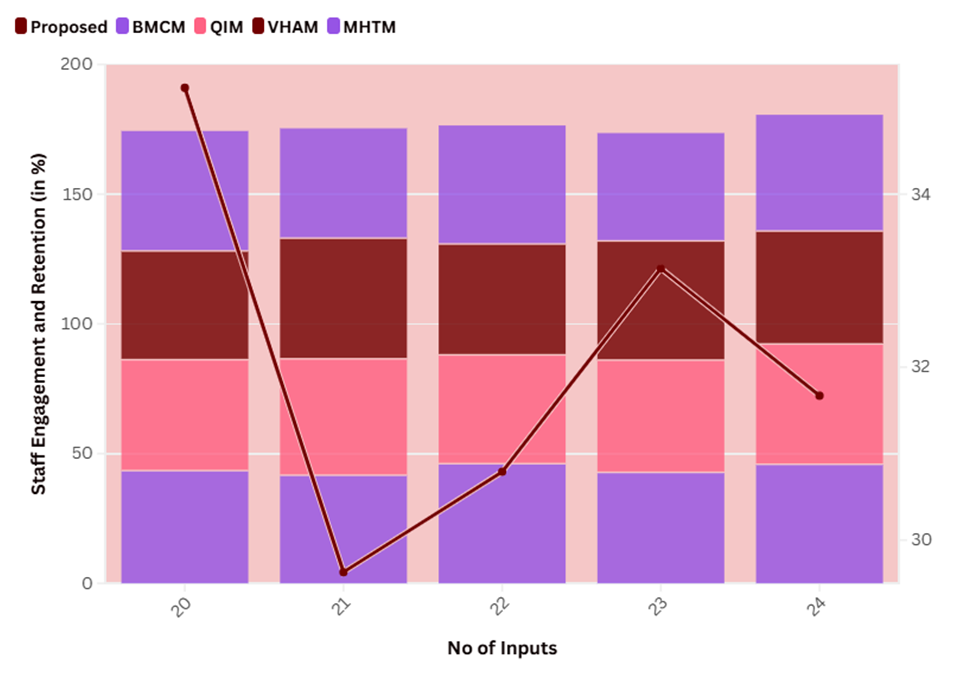
Figure 3. Computation of Staff Engagement and Retention
Effective leadership also involves actively involving patients in decision-making processes, promoting a culture of continuous improvement, and fostering a sense of empathy and compassion among staff towards patients. It ultimately leads to improved patient experiences and outcomes.
Patient-Centered Practices
Patient-centered practices focus on providing healthcare that is centered on the needs, preferences, and values of the patient. This approach includes involving patients in their care, promoting shared decision-making, and providing care that is respectful, compassionate, and culturally competent. A critical factor in promoting patient-centered care is the role of leadership.
|
Table 4. Comparison of Patient-Centered Practices |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
BMCM |
QIM |
VHAM |
MHTM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
40 |
44,21 |
46,13 |
45,97 |
43,56 |
35,29 |
|
80 |
46,75 |
44,81 |
42,35 |
45,83 |
33,57 |
|
120 |
43,18 |
46,62 |
45,41 |
42,27 |
29,18 |
|
160 |
45,92 |
41,28 |
46,54 |
46,36 |
31,04 |
|
200 |
46,54 |
45,47 |
43,67 |
45,11 |
34,82 |
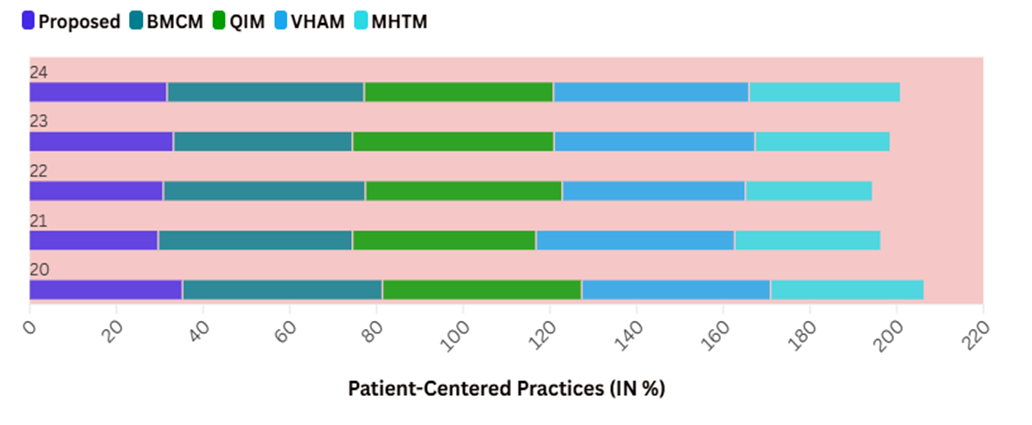
Figure 4. Computation of Patient-Centered Practices
Effective leadership is necessary to create a culture within a healthcare organization that prioritizes patient-centeredness. Figure 4 shows the Computation of Patient-Centered Practices.
Leaders must encourage and model behaviors that prioritize patient preferences and establish policies and initiatives to support patient involvement in their care. They must also ensure that staff are adequately trained and supported in providing patient-centered care.
CONCLUSION
Leadership plays a vital role in promoting patient-centered care. This type of leadership is characterized by strong values, effective communication, and the ability to empower and engage both patients and healthcare team members. Transformational leadership is particularly effective in promoting patient-centered care, as it focuses on inspiring and motivating others towards a shared vision of providing patient-centered care. Effective leaders in healthcare must also have a deep understanding of patients’ needs and perspectives and be able to advocate for their rights and preferences. They should also prioritize the development of a patient-centered culture in their organizations and encourage continuous improvement and innovation in this area. Strong leadership is essential in driving and sustaining patient-centered care and should be nurtured and supported in healthcare organizations. Through effective leadership, patients can receive more personalized and compassionate care, leading to better outcomes and overall satisfaction. Further research and initiatives should focus on developing and implementing strategies to promote effective leadership in healthcare and its crucial role in delivering patient-centered care.
REFERENCES
1. Ribeiro N, Yücel İ, Gomes D. How transformational leadership predicts employees’ affective commitment and performance. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management. 2018;67(9):1901-17.
2. Miao R, Cao Y. High-performance work system, work well-being, and employee creativity: Cross-level moderating role of transformational leadership. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019;16(9):1640.
3. Al-Husseini S, Elbeltagi I. Evaluating the effect of transformational leadership on knowledge sharing using structural equation modelling: the case of Iraqi higher education. International Journal of Leadership in Education. 2018;21(4):506-17.
4. Bagheri A, Akbari M. The impact of entrepreneurial leadership on nurses’ innovation behavior. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2018;50(1):28-35.
5. Puni A, Mohammed I, Asamoah E. Transformational leadership and job satisfaction: the moderating effect of contingent reward. Leadership & Organization Development Journal. 2018;39(4):522-37.
6. Bosak J, Kilroy S, Chênevert D, Flood PC. Examining the role of transformational leadership and mission valence on burnout among hospital staff. Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance. 2021;8(2):208-27.
7. Phong LB, Hui L, Son TT. How leadership and trust in leaders foster employees’ behavior toward knowledge sharing. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal. 2018;46(5):705-20.
8. Alghamdi MG, Topp R, AlYami MS. The effect of gender on transformational leadership and job satisfaction among Saudi nurses. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2018;74(1):119-27.
9. Zuraik A, Kelly L. The role of CEO transformational leadership and innovation climate in exploration and exploitation. European Journal of Innovation Management. 2018;22(1):84-104.
10. Kim EJ, Park S. Transformational leadership, knowledge sharing, organizational climate and learning: an empirical study. Leadership & Organization Development Journal. 2020;41(6):761-75.
FUNDING
The authors did not receive funding for the development of this research.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Axita Thakkar, Surjeet Sahoo, Vivek Saraswat, Jatin Khurana, Sujayaraj Samuel Jayakumar, Adarsh Kumar, Atul Bhanudas Hulwan.
Research: Rakesh Axita Thakkar, Surjeet Sahoo, Vivek Saraswat, Jatin Khurana, Sujayaraj Samuel Jayakumar, Adarsh Kumar, Atul Bhanudas Hulwan.
Methodology: Axita Thakkar, Surjeet Sahoo, Vivek Saraswat, Jatin Khurana, Sujayaraj Samuel Jayakumar, Adarsh Kumar, Atul Bhanudas Hulwan.
Writing - original draft: Axita Thakkar, Surjeet Sahoo, Vivek Saraswat, Jatin Khurana, Sujayaraj Samuel Jayakumar, Adarsh Kumar, Atul Bhanudas Hulwan.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Axita Thakkar, Surjeet Sahoo, Vivek Saraswat, Jatin Khurana, Sujayaraj Samuel Jayakumar, Adarsh Kumar, Atul Bhanudas Hulwan.