doi: 10.56294/hl2022175
ORIGINAL
Emotional intelligence and its relationship with leadership: research keys
Inteligencia emocional y su relación con el liderazgo: claves de la investigación
Rolando Eslava-Zapata1 ![]() *, Edixon
Chacón-Guerrero2
*, Edixon
Chacón-Guerrero2 ![]() *, Rómulo Esteban Montilla3
*, Rómulo Esteban Montilla3 ![]() *
*
1Universidad Libre Colombia, Faculty of Economics, Administrative and Accounting Sciences. Cúcuta, Colombia.
2Universidad de Los Andes, Statistics Department. San Cristóbal, Venezuela.
3Saint’s Mary’s University, Department of Counseling and Human Services. San Antonio, United States.
Cite as: Eslava-Zapata R, Chacón-Guerrero E, Esteban Montilla R. Emotional intelligence and its relationship with leadership: research keys. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2022; 1:175. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2022175
Submitted: 30-07-2022 Revised: 08-10-2022 Accepted: 12-12-2022 Published: 13-12-2022
Editor: PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
Corresponding Author: Rolando Eslava-Zapata *
ABSTRACT
Introduction: in organizations, emotional intelligence is closely linked to work teams and its relationship with factors such as maturity, intellectual capital, high levels of wisdom to solve the different problems that occur in human relations, and the ability to bounce back in the face of adversity. In this sense, this paper aims to carry out a bibliometric analysis of emotional intelligence and its relationship with leadership to identify the keys to research.
Method: a bibliographic review is carried out in the Scopus database, considering the articles published in English between 2002 and 2022. In this regard, the documents are analyzed by year, author, country, research area, co-authorship, and co-occurrence.
Results: the results reveal the formation of two clusters. The first cluster is related to Emotional Intelligence, and the second cluster is related to Transformational Leadership. It is evident that Emotional Intelligence allows the leader to intuit the collaborators’ needs and search for the means to satisfy them; likewise, it is found that the transformational leader must promote change and empower people to become empowered.
Conclusions: emotional intelligence is a key factor for those who assume the role of leaders since it facilitates relationships with individuals and the understanding of emotions. The leadership style adopted should help manage the organization’s human resources to promote the team’s emotional growth and job satisfaction.
Keywords: Emotional Intelligence; Transformational Leadership; Job Satisfaction; Nurses.
RESUMEN
Introducción: en las organizaciones la inteligencia emocional está muy vinculada a los equipos de trabajo y su relación con factores como la madurez, el capital intelectual, los altos niveles de sabiduría para resolver los diferentes problemas que se dan en las relaciones humanas y la capacidad para reponerse ante las adversidades. En este sentido, este trabajo tiene por objetivo realizar un análisis bibliométrico sobre la Inteligencia emocional y su relación con el liderazgo a fin de identificar las claves de la investigación.
Método: se realiza una revisión bibliográfica en la base de datos Scopus considerando los artículo publicados en idioma inglés en el periodo 2002-2022. Al respecto, se realiza un análisis de los documentos por año, autor, país, área de investigación, coautoría y coocurrencia.
Resultados: los resultados revelan la formación de dos clústeres. El primer clúster está relacionado con la Inteligencia Emocional y el segundo clúster con el Liderazgo Transformacional. Se evidencia que La inteligencia emocional otorga al líder la capacidad de intuir las necesidades de los colaboradores y la búsqueda de los medios para satisfacerlas; asimismo, se encuentra que el líder transformacional debe promover el cambio y facultar a las personas para que se empoderen.
Conclusiones: la inteligencia emocional es un factor clave para quienes asuman el papel de líderes, puesto que esta facilita las relaciones con los individuos y la comprensión de las emociones. El estilo de liderazgo adoptado debe ayudar a gestionar los recursos humanos de la organización de cara a promover el crecimiento emocional del equipo y su satisfacción laboral.
Palabras clave: Inteligencia Emocional; Liderazgo Transformacional; Satisfacción Laboral; Enfermeras.
INTRODUCTION
Leadership goes beyond team management and decision-making, requiring a clear and deep understanding of people and human relationships.(1) Emotional intelligence, which emerged in the 1990s with Goleman, calls for transformational leadership that helps promote healthy and happy work environments.(2) Controlling emotions helps to control anxiety and enhances people's creative abilities for the development of competencies and sustainable growth of organizations.(3)
In organizations, emotional intelligence is closely linked to work teams and its relationship with factors such as maturity, intellectual capital, high levels of wisdom to solve problems in human relationships, and the ability to bounce back from adversity.(4) Tools such as coaching allow the development of self-knowledge, self-awareness, and self-regulation, allowing leaders to act intelligently in managing work teams.(5)
Leaders with high emotional intelligence can respond with empathy to the work team and build lasting personal relationships where trust and commitment prevail in developing all the objectives the organization proposes.(6) Influencing the emotions of the collaborators drives innovation and shared efforts in the same direction, which is fully aligned with the organizational mission.(7)
Therefore, emotional intelligence is a fundamental pillar of leadership since it enhances the effective management of the organization and the psychological and physical well-being of employees.(8) Keeping motivation at a high level is an essential challenge. It helps to maintain resilience in the face of difficulties and contributes to creating a healthy and cohesive environment.(9) In this sense, this work aimed to carry out a bibliometric analysis of emotional intelligence and its relationship with leadership to identify the keys to research.(10)
METHOD
The study followed a qualitative type of research. A literature review was conducted in the Scopus database considering articles published in the English language in the period 2002-2022, using the following search engine:
( TITLE-ABS-KEY ( “emotional intelligence” ) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY ( leadership ) ) AND PUBYEAR > 2001 AND PUBYEAR < 2023 AND ( LIMIT-TO ( DOCTYPE , “ar” ) ) AND ( LIMIT-TO ( LANGUAGE , “English” ) ) AND ( LIMIT-TO ( PUBSTAGE , “final” ) ) )
The results yielded 1030 published articles. In this regard, the documents were analyzed by year, author, country, research area, co-authorship, and co-occurrence using the VOSviewer program.
RESULTS
Table 1 shows that scientific production has increased in recent years. Research shows that emotional intelligence plays a fundamental role in leadership since it involves the control of emotions, which ultimately favors positive interpersonal relationships and facilitates conflict resolution.
|
Table 1. Documents by year |
|
|
Year |
Documents |
|
2022 |
95 |
|
2021 |
81 |
|
2020 |
99 |
|
2019 |
77 |
|
2018 |
71 |
|
2017 |
73 |
|
2016 |
50 |
|
2015 |
53 |
|
2014 |
52 |
|
2013 |
40 |
Table 2 shows the scientific production by country. The three countries with the highest scientific production are the United States (398), the United Kingdom (111), and Australia (69). It should be noted that the relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership has aroused international interest and is opening the way to other areas of study; for example, demonstrating the ability to inspire people, the way of communicating and empathy with the team can lead to a favorable change in organizational culture, promote personal growth of people and strengthen the health of employees.
|
Table 2. Documents by country |
||
|
N° |
Country |
Documents |
|
United States |
398 |
|
|
2 |
United Kingdom |
111 |
|
3 |
Australia |
69 |
|
4 |
India |
57 |
|
5 |
Canada |
52 |
|
6 |
Malaysia |
40 |
|
7 |
China |
36 |
|
8 |
South Africa |
31 |
|
9 |
Spain |
29 |
|
10 |
Pakistan |
24 |
Table 3 shows the results of documents per author. The three authors with the highest scientific production.
|
Table 3. Documents by author |
||
|
N° |
Author |
Documents |
|
Humphrey, R.H. |
11 |
|
|
2 |
Boyatzis, R.E. |
9 |
|
3 |
Stoller, J.K. |
7 |
|
4 |
Dartey-Baah, K. |
5 |
|
5 |
Dulewicz, V. |
5 |
|
6 |
Müller, R. |
5 |
|
7 |
Taylor, D.C. |
5 |
|
8 |
Ashkanasy, N.M. |
4 |
|
9 |
Dasborough, M.T. |
4 |
|
10 |
Ellis, P. |
4 |
Table 4 shows that the three main areas of research on emotional intelligence and its relationship with leadership are Business, Management, and Accounting (401), Social Sciences (357), and Medicine (216). There are physical and psychological benefits of emotional intelligence and leadership in the collaborators of organizations, since harmonious work environments increase job satisfaction and counteract burnout and frustration of people.
|
Table 4. Documents by area |
||
|
N° |
Subject area |
Documents |
|
Business, Management and Accounting |
401 |
|
|
2 |
Social Sciences |
357 |
|
3 |
Medicine |
216 |
|
4 |
Psychology |
161 |
|
5 |
Nursing |
118 |
|
6 |
Arts and Humanities |
61 |
|
7 |
Economics, Econometrics and Finance |
53 |
|
8 |
Engineering |
45 |
|
9 |
Decision Sciences |
38 |
|
10 |
Health Professions |
32 |
For co-authorship analysis, a criterion of a minimum of two papers per author and twenty-nine citations was considered. The results revealed that out of 989 authors, only 20 met the criterion. Table 5 shows the results of co-authorship per author. In this regard, it was found that the first three places in published papers were occupied by Martin J., Miao C. et al., and Boyatzis R.E. As for the authors with the most citations, the top three places are occupied by Müller R. et al., Boyatzis R.E. and Miao C. et al. It should be noted that the co-authorship map does not reveal co-authorship among the authors.
|
Table 5. Co-authorship by author |
||||
|
N° |
Author |
Documents |
Author |
Citations |
|
Martin J. |
4 |
Müller R. et al. |
461 |
|
|
2 |
Miao C. et al. |
4 |
Boyatzis R.E. |
370 |
|
3 |
Boyatzis R.E. |
3 |
Miao C. et al. |
358 |
|
4 |
Greenstein F.I. |
3 |
Humphrey R.H. |
337 |
|
5 |
Stoller J.K. |
3 |
Freshman B. et al. |
124 |
|
6 |
Blackmore J. |
2 |
Stoller J.K. |
121 |
|
7 |
Chan D.W. |
2 |
Vitello-Cicciu J.M. |
100 |
|
8 |
Chopra P.K. et al. |
2 |
Blackmore J. |
95 |
|
9 |
Chrusciel D. |
2 |
Lindebaum D. et al. |
87 |
|
10 |
Cliffe J. |
2 |
Mysirlaki S. et al. |
78 |
For the analysis of co-authorship by country, a minimum of eleven documents per country and one citation were considered. The results showed that out of 104 countries, only 19 countries met the criterion. The co-authorship map revealed that the two countries were unconnected, leaving seventeen countries. In this sense, two clusters were formed (figure 1). The first cluster identified with red is composed of Australia, Canada, Germany, Greece, Netherlands, South Africa, Spain, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The second cluster, identified with green color, comprises China, India, Malaysia, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Taiwan, and Turkey. The two clusters reveal the collaboration between European and American countries on the one hand and Asian countries on the other.
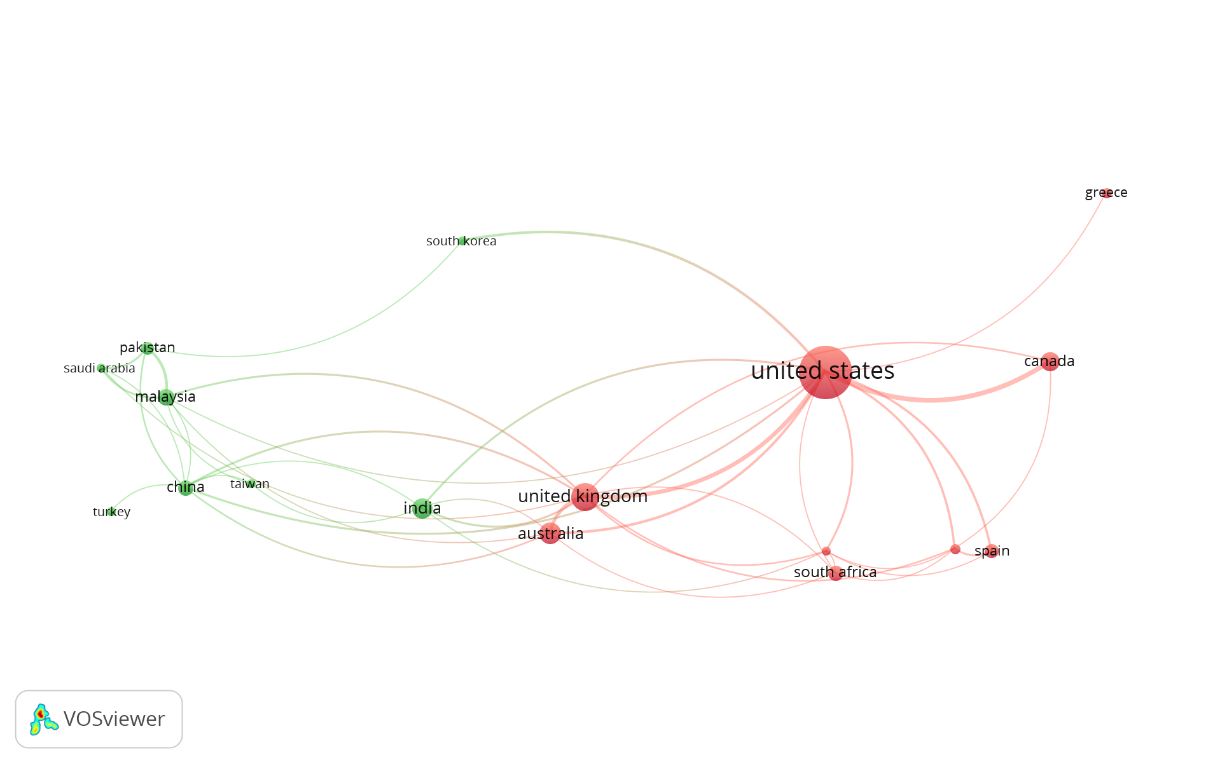
Figure 1. Cooccurrence of keywords by author
DISCUSSION
For the analysis of keyword co-occurrence per author, a minimum of twelve occurrences of the keywords was considered. The results revealed that out of 2032 keywords, only 19 words met the criterion. It should be noted that one word was added to the thesaurus program. Two distinct clusters were formed (figure 2).(11,12,13)
The first cluster identified with the color red is related to Emotional Intelligence. It is integrated by the words Coaching, Communication, competencies, Emotional Intelligence, Emotions, Empathy, Gender, Job Satisfaction, Leadership, Leadership Development, Management, Nurses, and Self-Awareness.
Research shows a relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership. Leaders who have high emotional intelligence are more efficient and effective in achieving organizational goals.(14) Several factors influence the development of emotional intelligence, including gender, age, and educational level.(15)
Acting wisely in human relations is the essence of emotional intelligence. This implies that the leader must learn to monitor his and others' emotions in order to guide behaviors and positively impact individuals' social and personal development.(16) Wisdom is accompanied by emotions, which lead the leader to act in a certain way depending on the situation and the human interactions that occur in the social context.(17)
Emotional intelligence gives the leader the ability to sense the collaborators' needs and search for ways to satisfy them; therefore, research has shown a positive relationship between leadership and the collaborator's performance and highlighted it as a fundamental element for personal and professional development.(18)
Leaders can manage their emotions by consciously understanding their own emotions, recognizing the emotions of others, regulating their own emotions to recover from challenging situations, and taking advantage of emotions to maintain a positive attitude that enhances the work team's performance. Leaders with greater emotional intelligence can cope better with different day-to-day situations, reflected in greater employee satisfaction and a positive organizational climate.(19)
The second cluster, identified with green color, is related to Transformational Leadership and is integrated by the words Intelligence, Leadership Effectiveness, Leadership Style, Performance, Transactional Leadership, and Transformational Leadership. Leadership has been studied from the point of view of hierarchical position and the process of social influence.
In this sense, studies have generated four leadership theories: trait, behavioral, contingency, and transformational. Transformational leadership emerged in the 1970s with an approach that seeks to transform people and the organization, promoting the achievement of objectives without neglecting the essence of the individual as a human being.
Research has emphasized the need to inspire people and share a group vision to guide them to follow the same path in the organization. In this sense, organizational culture becomes a key element in the leader's behavior since aspects such as values, traditions, country, and, in general, cultural aspects condition their behavior.(20)
Therefore, the transformational leader must promote change and empower people to empower themselves. The idea is to delegate responsibilities and have them take on relevant tasks that lead them to work as a team; this will undoubtedly strengthen the motivation and commitment of employees, as well as give them the opportunity to recognize individual and group achievements.
In this context, transformational leadership promotes the development of the organization and its people; it is also based on the charismatic leadership model. Hence, transformational leadership encourages significant changes in the work team so that they transcend their personal objectives in favor of organizational objectives. Therefore, transformational leadership fosters trust, respect, and a healthy organizational culture for all collaborators.(21)
Transformational leadership involves transforming the environment through inspiration, which is transmitted to employees to prevent health problems such as stress, frustration, discouragement, or apathy. Therefore, the transformational leader must have a shared vision with the collaborators of the organizational objectives based on values such as justice, love, peace, and equality, among others.(22)
On the other hand, the overlay map shows the keys to emotional intelligence research and its relationship with leadership (Figure 2). The results reveal that research is focused on Job Satisfaction and Nurses. As markets become increasingly competitive and global, organizations are constantly transforming in an environment full of uncertainty. Therefore, leaders must implement strategies that go beyond strengthening competitiveness and extend to promoting job well-being.(23) The research analyzes cultural contexts to explain how leaders use emotional intelligence to manage diverse environments and employees' emotions.(24)
Job satisfaction is associated with employees' well-being in different aspects of life, such as health, nutrition, or education.(25) It has been proven that there is a relationship between social well-being and job satisfaction since they are connected from three points of view: psychological, economic, and human.(26) From the psychological point of view, the employee's perception of work stands out; from the economic point of view, labor variables stand out; and from the human point of view, productivity stands out.(27)
Research has also shown that working conditions and attention paid to employees improve productivity in the organization. In fact, the interaction between individuals is one of the most important factors in achieving job satisfaction, much more important than other variables such as security or affiliation; it has also been shown that job satisfaction varies according to individuals' individual needs.(28)
Research is also explaining emotional intelligence in the nursing field, envious of its importance in achieving good patient relations and care. Nurses' emotional competencies have a strong therapeutic power that contributes to improving patient care and the quality of care offered.(29)
Nurses apply holistic care in their work practice, comprising humanized care based on empathy, trust, and communication, which allows them to offer comprehensive care; however, it is the human, emotional, and spiritual aspects that will enhance their work with human beings.(30)
The emotional intelligence of nurses has a positive impact on patient care and mental health. Studies open a range of opportunities to study the effects of stress, workload, economic conditions, and job protection, among other variables, on patient care and nurse performance.(31)
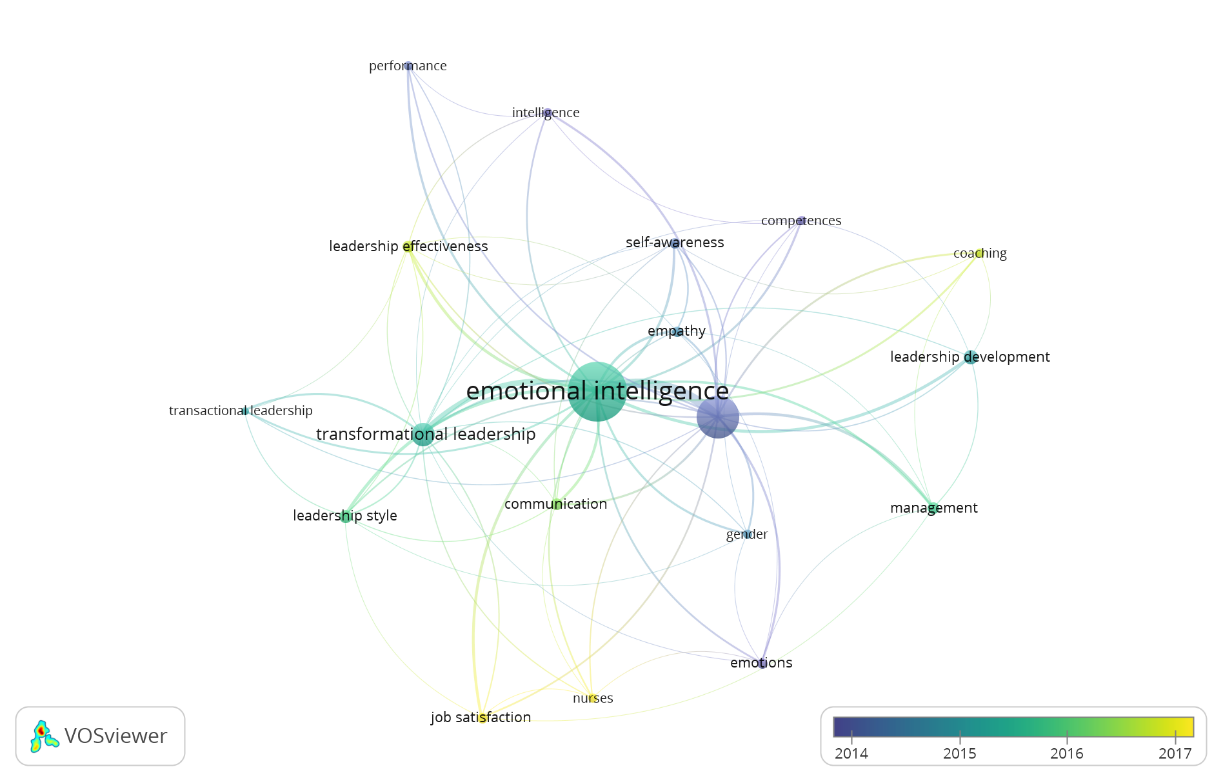
Figure 2. Overlay keywords by author
CONCLUSIONS
Leadership is a social phenomenon built through the interaction of people, and people yield power to others through their charisma or experience. Therefore, emotional intelligence is presented as a construct of study since it helps to achieve transformational behaviors that facilitate leadership. Leaders with good emotional control are able to foster trust and respect from followers and understand the emotions of others.
Emotional intelligence is related to leadership since it provides the ability to understand the emotions and needs of collaborators and effectively satisfy them. Therefore, it is emphasized that leaders with high emotional intelligence tend to be more successful and effective.
Emotional intelligence is a key factor for those who assume the role of leaders since it facilitates relationships with individuals and the understanding of emotions. The leadership style adopted, whether democratic, charismatic, or situational, should help manage the organization's human resources and promote the emotional growth of the team and their job satisfaction.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Rojas-Concepción AA, Herrera-Miranda GL, Arteaga-Prado Y. Pedagogical model for the methodological work of the General Integral Medicine specialization. Salud, Ciencia Y Tecnología. 2022; 2: p. 72.
2. Gómez-Ortiz EJ, Peñaranda-Soto E. El nuevo liderazgo y la transformación de las organizaciones del siglo XXI. Revista Gestión y Desarrollo Libre. 2020; 5(9): p. 217-235.
3. González NG. Leadership styles and organizational climate perceived by the nursing staff of a public hospital in Bahía Blanca1. Salud, Ciencia Y Tecnología. 2021; 1: p. 5.
4. Medina-Altamirano N, Enriquez-Gavilan N, Tenorio-Molina G, Quispe-Solano M, Ticona-Larico W, López-Gómez C. The quality educational service and learning by competencies of the students of the Productive Technical Centers of the UGEL N. 01, district of Villa el Salvador, Lima, 2019. Salud, Ciencia Y Tecnología - Serie De Conferencias. 2022; 1: p. 13.
5. Quiroz-Leal S. Tipos de liderazgo: una perspectiva liberadora desde la consejería profesional. Revista Gestión y Desarrollo Libre. 2021; 6(12): p. 1-20.
6. Ruiz-Díaz-de-Salvioni VV. Estrategias innovadoras para un aprendizaje continuo y efectivo durante emergencias sanitarias en Ciudad del Este. Región Científica. 2022; 2(1): p. 202238.
7. Quiroz-Leal S. La función gerencial: un análisis del liderazgo desde la Consejería Profesional. Revista Gestión y Desarrollo Libre. 2019; 4(7): p. 112-134.
8. Santander-Rodríguez KV, Alcayhuamán-Gil S, Sánchez-Rojas B, Suárez-Obregón ES, Osorio-Meniz PD. Reading comprehension strategies in elementary education: a bibliometric review. Salud, Ciencia Y Tecnología - Serie De Conferencias. 2022; 1: p. 256.
9. Pérez-Gamboa AJ, Gómez-Cano CA, Sánchez-Castillo V. Decision making in university contexts based on knowledge management systems. Data and Metadata. 2022; 1: p. 92.
10. Eslava-Zapata R, Omaña-Guerrero JA, Sierra-Narváez FJ, Mogrovejo-Andrade JM. Estilos de liderazgo: un estudio en Latinoamérica, Estados Unidos y Europa. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología. 2022; 3: p. 1.8.
11. Alcedo-Salamanca Y, Martínez-Nieto D, Weky L. Comunidades de aprendizaje, trabajo colaborativo y pensamiento complejo: retos para la transformación de la docencia universitaria en el siglo XXI. Revista Gestión y Desarrollo Libre. 2021; 6(11): p. 76-106.
12. Ramírez-Moncada JA, Rodríguez-Torres E, Zamora-Reyes JR. Estrategias recreativas para suplir las carencias de niños y jóvenes en situaciones de la Covid-19 en el municipio Morón (Cuba). Región Científica. 2022; 2(1): p. 202228.
13. Sanabria-Martínez MJ. Construir nuevos espacios sostenibles respetando la diversidad cultural desde el nivel local. Región Científica. 2022; 1(1): p. 20222.
14. Eslava-Zapata R, Montilla RE, Guerrero EC, Gómez-Cano CA, Gómez-Ortiz E. Social Responsibility: A bibliometric analysis of research state and its trend. Data and Metadata. 2022; 2: p. 117.
15. Norena-Chavez D, Thalassinos EI. Transactional Leadership and Innovative Behavior as Factors Explaining Emotional Intelligence: A Mediating Effect. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2022; 15(12): p. 545.
16. Ramos-Prieto M. Characteristics of the educational styles of parents/guardians of maladjusted children. Salud, Ciencia Y Tecnología - Serie De Conferencias. 2022; 1: p. 18.
17. Hsu N, Newman DA, Badura KL. Emotional Intelligence and Transformational Leadership: Meta-Analysis and Explanatory Model of Female Leadership Advantage. Journal of Intelligence. 2022; 10(4): p. 104.
18. Yen SJ. Can Emotional Intelligence Be Fostered? The Perspective of Social Learning Theory. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 2022; 16: p. 862360.
19. Gesto-Rodríguez J. El proceso comunicacional entre directivos y docentes en educación primaria: una valoración dialéctica. Revista Gestión y Desarrollo Libre. 2022; 7(14): p. 1-26.
20. Lepez CO, Eiguchi K. Labor market insertion, management and training by competencies: a current view in the Argentine context. Data and Metadata. 2022; 1: p. 67.
21. Lee CC, Li YS, Yeh WC, Yu Z. The Effects of Leader Emotional Intelligence, Leadership Styles, Organizational Commitment, and Trust on Job Performance in the Real Estate Brokerage Industry. Frontiers in Psychology. 2022; 13: p. 881725.
22. Huikko-Tarvainen S. Elements of perceived good physician leadership and their relation to leadership theory. Leadership in Health Services. 2022; 35(1).
23. Quiroz-Leal S, Eslava-Zapata R, Sánchez-Castillo V. Influential aspects in teacher motivation towards working with students with disabilities. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2022; 1: p. 99.
24. Neffe C, Wilderom CP, Lattuch L. Emotionally intelligent top management and high family firm performance: Evidence from Germany. European Management Journal. 2022; 40(3): p. 372-383.
25. Eslava-Zapata R, Chacón-Guerrero E, Gómez-Ortiz E, Mogrovejo-Andrade J. Decision-making in organizations: process and strategies. Data and Metadata. 2022; 1: p. 1-5.
26. Quiroz-Leal S, Eslava-Zapata R. Teacher motivation: An empirical study with teachers educating students with identified disabilities in a diverse classroom environment. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias. 2023; 2: p. 1-12.
27. Semenets-Orlova I, Shevchuk R, Plish V, Grydiushko I, Maistrenko K. Innovative Approaches to Development of Human Potential in Modern Public Administration. Economic Affairs. 2022; 67(04s): p. 915-926.
28. Cai B, Shafait Z, Chen L. Teachers’ Adoption of Emotions-Based Learning Outcomes: Significance of Teachers’ Competence, Creative Performance, and University Performance. Frontiers in Psychology. 2022; 13: p. 812447.
29. Stelmaszczuk J. Leadership style and organizational performance indicators from the nursing staff’s perspective. Salud, Ciencia Y Tecnología. 2021; 1: p. 10.
30. Teame K, Debie A, Tullu M. Healthcare leadership effectiveness among managers in Public Health institutions of Addis Ababa, Central Ethiopia: a mixed methods study. BMC Health Services Research. 2022; 22: p. 540.
31. Blickle G, Kranefeld I, Wihler A, Kückelhaus BP, Menges JI. It Works Without Words: A Nonlinguistic Ability Test of Perceiving Emotions With Job-Related Consequences. European Journal of Psychological Assessment. 2022; 38(3): p. 210–223.
FINANCING
The authors did not receive financing for the development of this research. Thanks to Universidad Libre Colombia Seccional Cúcuta for the technical support provided.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Rolando Eslava-Zapata.
Data curation: 2022.
Formal analysis: Rolando Eslava-Zapata.
Research: Rolando Eslava-Zapata.
Methodology: Rómulo Esteban Montilla, Edixon Chacón-Guerrero.
Project management: Rómulo Esteban Montilla, Edixon Chacón-Guerrero.
Resources: Rómulo Esteban Montilla, Edixon Chacón-Guerrero.
Software: Rolando Eslava-Zapata.
Supervision: Rómulo Esteban Montilla, Edixon Chacón-Guerrero.
Validation: Rómulo Esteban Montilla, Edixon Chacón-Guerrero.
Display: Rolando Eslava-Zapata, Rómulo Esteban Montilla, Edixon Chacón-Guerrero.
Drafting - original draft: Rolando Eslava-Zapata.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Rolando Eslava-Zapata, Rómulo Esteban Montilla, Edixon Chacón-Guerrero.