doi: 10.56294/hl2022110
ORIGINAL
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Leadership Development Programs in Healthcare Management
Evaluación de la eficacia de los programas de desarrollo del liderazgo en la gestión sanitaria
Kashish Gupta1
![]() , Jamuna. K. V2
, Jamuna. K. V2
![]() , Rakesh Mohanty3
, Rakesh Mohanty3
![]()
1Noida International University, Department of Biotechnology and Microbiology. Greater Noida, India.
2JAIN (Deemed-to-be University), Department of Forensic Science. Bangalore, India
3Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of Psychiatry, IMS and SUM Hospital. Bhubaneswar, India.
Cite as: Gupta K, Jamuna KV, Mohanty R. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Leadership Development Programs in Healthcare Management. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2022; 1:110. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2022110
Submitted: 08-08-2022 Revised: 26-10-2022 Accepted: 11-12-2022 Published: 12-12-2022
Editor: PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: the aim of the study was to investigate innovative health leadership models focusing on the improvement of the quality of life in post-acute care settings. It answered the increasing demand for successful leadership policies towards enhanced patient outcomes and service delivery.
Method: this researcher used a mixed-methods approach, performing quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews with healthcare professionals at multiple post-acute care facilities. The study reviewed data from 150 participants to assess the influence of individual leadership models on care quality and staff morale. These leadership models could include transformational, transactional, servant or a mixture of all.
Results: the results showed that patient quality of life in post-acute care settings was significantly enhanced by transformational leadership models. Facilities that implemented this model reported higher patient satisfaction scores and better overall health outcomes than those using transactional and servant leadership models. Staff reported higher job satisfaction and lower burnout rates in transformational leadership settings.
Conclusions: despite which transformational model was used, the study determined that transformational leadership was the best model for post-acute care settings because both patients and staff flourished in this environment. “Transformational Leadership in Healthcare: A 360-Degree Approach” offers a thorough overview of how focusing on empathy, communication, and empowerment can improve patient care and increase job satisfaction among health care workers. In fact, the study called for adoption of transformational leadership training programs that would use the skills to develop existing and future healthcare leaders and, subsequently, enhance quality of life in post-acute-care settings.
Keywords: Health; Leadership; Qualitative; Transformational; Empathy; Prioritizing.
RESUMEN
Introducción: el objetivo del estudio era investigar modelos innovadores de liderazgo sanitario centrados en la mejora de la calidad de vida en entornos de cuidados posagudos. Respondía así a la creciente demanda de políticas de liderazgo acertadas para mejorar los resultados de los pacientes y la prestación de servicios.
Método: este investigador utilizó un enfoque de métodos mixtos, realizando encuestas cuantitativas y entrevistas cualitativas a profesionales sanitarios de múltiples centros de cuidados posagudos. El estudio examinó los datos de 150 participantes para evaluar la influencia de los distintos modelos de liderazgo en la calidad asistencial y la moral del personal. Estos modelos de liderazgo podían ser transformacional, transaccional, de servicio o una mezcla de todos ellos.
Resultados: los resultados mostraron que la calidad de vida de los pacientes en los centros de cuidados posagudos mejoraba significativamente con los modelos de liderazgo transformacional. Los centros que aplicaban este modelo mostraban mayores índices de satisfacción de los pacientes y mejores resultados sanitarios generales que los que utilizaban modelos de liderazgo transaccional y de servicio. El personal se mostró más satisfecho con su trabajo y menos agotado en los entornos de liderazgo transformacional.
Conclusiones: a pesar del modelo de transformación utilizado, el estudio determinó que el liderazgo transformacional era el mejor modelo para los centros de cuidados posagudos, ya que tanto los pacientes como el personal prosperaban en este entorno. «Liderazgo transformacional en la atención sanitaria: A 360-Degree Approach» ofrece una visión exhaustiva de cómo centrarse en la empatía, la comunicación y la capacitación puede mejorar la atención al paciente y aumentar la satisfacción laboral de los trabajadores sanitarios. De hecho, el estudio aboga por la adopción de programas de formación en liderazgo transformacional que utilicen estas competencias para desarrollar a los actuales y futuros líderes sanitarios y, por consiguiente, mejorar la calidad de vida en los entornos de atención posaguda.
Palabras clave: Salud; Liderazgo; Cualitativo; Transformacional; Empatía; Priorización.
INTRODUCTION
In an ever-evolving and challenging environment like the healthcare industry, the importance of evaluating the effect of healthcare management leadership development programs cannot be overstated.(1) In addition, the healthcare field requires leaders who can be flexible, adept in critical-thinking and making sound, strategic decisions, while balancing unique and complex organizational needs without compromising patient care.(2) It is needed to measure the achievements of leadership development programs, which are intended to develop such competence. How Does One Measure Leadership SuccessFactors – Improvement in Leadership Competencies One of the best ways to measure success is to assess the improvement in leadership competencies such as communication, strategic thinking, and emotional intelligence.(3) Assessment before and after the program, 360-degree feedback, and real-world metrics are valuable indicators of these areas. It could also be useful to look at studies that assess the impact of leadership programs on organizational metrics such as patient satisfaction, employee engagement, and operational efficiency to provide a more comprehensive picture of their effectiveness.(4) Therefore evaluation includes much more, such as feedback from participants. Familiarizing yourself with experiences of those who are already trained, shed light on the relevance and usefulness of the program.(5) Effective programs should recognize that both individual career paths and organizational needs are manifested, which serves to motivate attendees and aids in ensuring that the skills obtained through the program get applied. Lastly, there is need for long term follow-up to assess the changes and skills acquired through the leadership program, are sustained.(6) This is measured through upward career progression, retention tracking, and enhanced performance over time. Through this systematic assessment of each of these components, Organizations can validate that leadership development programs do not just fulfill their immediate training needs, but also align with an ethos that promotes ongoing enhancements in healthcare administration.(7)
Main Contribution following:
· Enhance Leadership Skills These assessments will help determine whether or not the programs are effective in improving the leadership skills of the healthcare professionals. Through measuring outcomes of different programs, organizations can recognize the skills their leaders are learning to be able to make strategic decisions, lead teams, or implement organizational change.(8)
· Monetary Value (ROI) Analysis Evaluations provide valuable insights related to the financial viability of leadership development initiatives. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of programs such as this can help health care organizations determine cost savings, which provides an ROI and rationale for spending on leadership training.(9)
· Customization and Continuous Improvement Assessing these programs also helps identify strengths and opportunities for improvement, enabling content to be tailored to meet the unique needs of healthcare leaders more effectively.(10) By continuously iterating upon and refining their leadership development initiatives, they are able to ensure that their programs remain appropriate and meaningful with respect to the ever-changing needs of the healthcare industry.
· This would require a cumbersome approach to measure effectiveness of healthcare management leadership development programs while meeting the desired objectives. First, a clear definition of the objectives of the program is necessary. These typically emphasize skills such as strategic thinking, decision-making, and team leadership located in health care contexts. We collect feedback from participants via surveys and interviews to gauge their satisfaction with the program and the value they find in it.
This is best assessed at the level of the organization itself: by measuring changes in employee engagement, turnover, and patient care. This involves collecting data over an extended period of time after training to track long-term effects and transformations. Leadership behaviors have to be aligned to the strategic direction of the organization therefore it is important to create a synergy between leadership development and an organization’s larger strategy. Finally, mechanisms for continuous improvement should be established to use the data collected to drive iterative improvements to the programs. This might mean a revision to the curriculum, a redesign with new learning modalities, or an effort to better align the program with changing healthcare challenges. This structured approach helps healthcare organizations identify areas for improvement, refining their leadership development strategies to ensure they effectively address the specific needs of their workforce, ultimately leading to better management and patient care outcomes.
The remaining part of the research has the following chapters. Chapter 2 describes the recent works related to the research. Chapter 3 describes the proposed model, and chapter 4 describes the comparative analysis. Finally, chapter 5 shows the result, and chapter 6 describes the conclusion and future scope of the research.
METHOD
Musinguzi, C.,et,al. Leadership style has a significant impact on the motivation and job satisfaction of health workers and teamwork. Inspirational and transformational leadership supports a positive working environment, stimulating motivation and cooperation. This creates better job satisfaction and teamwork which is essential for providing quality healthcare and retaining qualified personnel in the health sector. Buchbinder, S. B.,et,al. of “Healthcare Management” discuss give an overview of the healthcare industry, particularly the principles of management, the operations, and the policies. This program emphasizes the skills required to lead healthcare organizations in a complex, rapidly changing environment; improve patient care; and meet current and future challenges in providing high-quality and cost-effective healthcare, covering leadership, strategic planning, ethics, law, and financial management. Gray, P.,et,al. have examined The realist review evaluates workplace interventions intended to improve healthcare workers’ mental health and wellbeing. Some key strategies are supportive leadership, peer support, and mindfulness training, highlighting that tailored approaches which align with both organizational contexts and individual needs are essential for cultivating a positive work environment. Guraya, S. Y.,et,al. On the other hand, Faculty development programs have a strong role in terms of the educators’ knowledge, skills, and professional competence. These programs are associated with increased knowledge, improved teaching practices, efficacy, and a better disposition toward educational innovations, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of faculty development programs on educational outcomes. Broadening professional development opportunities to the staff further increases academic outcomes and faculty satisfaction by __. Ginter, P. M.,et,al. have talked about The strategic management of healthcare organizations involves setting objectives, analyzing internal and external environments, formulating strategies, implementing plans, and evaluating outcomes to improve efficiency, quality, and patient satisfaction. It entails managing costs while delivering high-quality care, accommodating changes in regulations, and adopting new technology for a competitive edge.
|
Table 1. Comparative Analysis of Existing Models |
|||
|
Author |
Year |
Advantage |
Limitation |
|
Musinguzi, C.,et,al. |
2018 |
Effective leadership positively influences health worker motivation, job satisfaction, and teamwork, leading to improved patient care and organizational performance. |
One limitation is that diverse cultural contexts may affect how leadership styles impact motivation, job satisfaction, and teamwork among health workers. |
|
Buchbinder, S. B.,et,al. |
2019 |
It provides foundational knowledge and skills necessary for effectively managing healthcare organizations and improving overall patient care. |
One limitation of “Introduction to Health Care Management” is its broad scope, which can oversimplify complex management issues in healthcare settings. |
|
Gray, P.,et,al. |
2019 |
Effective leadership enhances motivation, job satisfaction, and teamwork among health workers, resulting in improved patient care and organizational performance. |
Effective leadership alone may not overcome systemic issues like resource shortages, which can limit improvements in healthcare outcomes. |
|
Guraya, S. Y.,et,al. |
2019 |
Improved faculty knowledge, skills, and competence, enhancing teaching quality and student outcomes through structured and effective professional development initiatives. |
Potential limitation: Limited generalizability due to variation in program content, implementation, and evaluation across different educational institutions and contexts. |
|
Ginter, P. M.,et,al. |
2018 |
One advantage is aligning organizational goals with patient care, ensuring efficient use of resources and improving overall healthcare quality. |
Limited adaptability to rapid changes in healthcare technology and regulations can hinder effective strategy implementation and organizational agility. |
|
Figueroa, C. A.,et,al. |
2019 |
An advantage is the ability to quickly identify and address global health workforce shortages, improving resource allocation and management efficiency. |
One limitation is the rapid review’s potential to overlook nuanced regional challenges due to its broad, global focus. |
|
Flynn, R.,et,al. |
2019 |
A realist evaluation identifies specific contextual factors and mechanisms, enhancing understanding of what enables or hinders sustainable lean interventions in pediatric healthcare. |
Realist evaluation may struggle with complex healthcare settings, making it difficult to isolate specific contexts and mechanisms accurately. |
|
Bolden, R.,et,al. |
2020 |
An advantage is enhanced collaboration across sectors, fostering integrated solutions and improved outcomes for complex public service challenges. |
Limited engagement from key stakeholders can hinder the successful implementation of systems leadership initiatives in public services. |
|
Robbins, B.,et,al. |
2020 |
Transformational leadership in healthcare fosters innovation, enhances team collaboration, improves patient outcomes, and empowers staff, leading to transformative organizational growth. |
Transformational leadership can overwhelm healthcare staff with constant change, potentially leading to burnout and decreased job satisfaction. |
|
Rawashdeh, A.,et,al. |
2018 |
Green human resource management enhances sustainability awareness, leading to better resource utilization and improved environmental performance in Jordanian health service organizations. |
One limitation is the potential lack of comprehensive data on long-term environmental impact specific to Jordanian health service organizations. |
Figueroa, C. A.,et,al. have suggested This rapid review reiterates a need for appropriate health leadership and human resource for health management highlighting the management priorities in the settings such as resilience building, optimal resource utilization, and technology adaptation. Some of the main issues include workforce shortages, burnout, and inequitable access to care which have been worsened by global crises such as pandemics, and require responsive strategies to sustain health systems globally. Flynn, R.,et,al. Topics: A realist evaluation explores how contexts and mechanisms affect the successfulness and sustainability of a lean intervention in pediatric healthcare. This recognizes factors that facilitate or inhibit implementation, identifying what works in practice and where the barriers may lie. Hence, in the long run, it also aids to positively impact and maintain the efficiency and quality of healthcare in pediatric settings. Bolden, R.,et,al. discusses “Mobilizing change in public services”, a systems leadership development intervention designed to improve public sector leadership capabilities. The initiative aims to respond to complex 21st-century societal challenges, enhance service delivery, and drive efficient organisational change by developing collaboration, innovation, and adaptive leadership in public service professionals across a range of public service settings. Robbins, B.,et,al. discuss Transformational leadership in the healthcare context involves motivating and inspiring employees to enhance patient care and outcomes. Inspire innovation, flexibility, and a strong environment, allowing space for growth in both personal and professional aspects. Transformational leadership emphasizes the need for shared goals, which in turn leads to organizational transformation and improvement in the quality and efficiency of health services. Rawashdeh, A.,et,al. deal with Green human resource management in Jordan health services improve environmental performance; it is normal that the human resource management system integrated by the company with environmental measures and different human resources practices enhances environmental performance. It nurtures a sustainability culture, embodies resource-efficient behaviors, cultivates commitment to compliance of environmental standards, thereby enhancing Eco-efficiency and organizations image and lowering environmental footprints.
DEVELOPMENT
The proposed model for evaluating the effectiveness of leadership development programs in healthcare management involves a multi-dimensional approach that integrates both quantitative and qualitative measures. It begins with a needs assessment to identify specific leadership competencies required within the organization. Following the completion of the leadership program, the model employs Pre- and post-program assessments to quantitatively assess changes in participants’ leadership skills, using validated tools like 360-degree feedback and self-assessment surveys. In addition, the model uses qualitative assessment from general structured interviews and focus groups of participants and their peers and qualitative data on behavior change and skill use. In addition, the model focuses on organizational outcome by evaluating the change in key performance indicators (KPIs) that present a team effectiveness, staff engagement, patient satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Longitudinal studies in this area would be also beneficial to measure the longitudinal effect of leadership development. Feedback loops are inbuilt to ensure lifelong improvement, whereby the facilitators of the programmes can iterate modifications based on evaluation results. By considering all aspects of leadership development, this framework creates a strong foundation to measure the outcomes and impacts of leadership programmes, while also connecting such initiatives with the overall goals of the organization, ensuring leadership development efforts are directly improving management practices and patient care in healthcare systems. Figure 1 shows the development of proposed model.
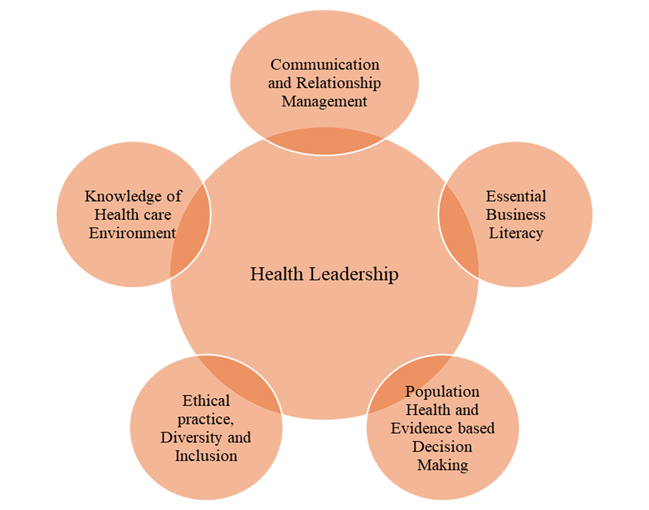
Figure 1. Development of proposed model
So it needs a model how to measure the effectiveness of leadership development programs in the healthcare management field. It starts with the specific organization needs assessment for identified leadership competencies. This model includes a measurement phase in which pre- and post-program assessments are employed to demonstrate quantitative evidence of the change in the participants’ leadership skills using validated 360-degree feedback and self-assessment surveys after the leadership program has been completed. Moreover, the model channels qualitative assessments via structured interviews and focus groups with both participants and their peers to extract context about behaviour change and the transference of skills to real-world contexts. In addition, the model explores not only the teams and systems of care but the total organizational impact reflected in the process through analysis of such outcomes and key performance indicators as team effectiveness, staff engagement, patient experience and operational efficiency. Longitudinal studies are needed to evaluate the longer-term effect of leadership development. Embedded in program design are feedback loops which enable program facilitators to iterate and improve according to the assessment results. This multi-dimensional approach also provides a better framework for measuring the effectiveness of directorial skills development initiatives and aligning them with organizational-level goals to ensure maximum ROI by connecting directorial skills development and enhanced healthcare management practices and improved patient care quality on the ground.
Examples range from building collaboration between providers, patients and stakeholders through engaging communication and relationship management. At the core, it is the ability to communicate clearly, actively listen, and conflict resolution in a way that ultimately builds trust and nurtures high-functioning professional relationships. It relates to understanding different ways of communicating and using technology to streamline communications. Financial management as well as strategic planning and operational efficiency sits at the heart of essential business literacy in healthcare. It helps professionals to make decisions based on data, optimize resources, and ensure sustainability. One of the biggest focuses here is on financial statement literacy, budget expertise, and exposure to risk management to align all of those with organizational mission. Through population trend analysis and evidence-based interventions, this operation is intended to improve health outcomes. It consists of collecting and processing data to identify health determinants and then creating interventions. The delivery of healthcare is aided by good research, clinical guidelines and best practices. Healthcare ethics describe a framework to work from in making decisions that affect people. It involves grappling with complex moral dilemmas, upholding patient confidentiality, and advancing equity in care. Introduction As part of a healthcare system, professionals are expected to knowethical standards to remain a part of the system. Diversity and inclusion operations work towards an entire healthcare industry that respects differences in gender, ethnicity, and cultural backgrounds. Issuing policies and implementing training programs to address disparities and enhance care delivery for patients Fostering an inclusive culture drives innovation, trust, and improves patient experience. Staying up to date with regulatory changes, technology, and healthcare policies is part of understanding the healthcare environment. Health professionals must understand increasingly complex systems, anticipate changes in industry trends, and align strategic approaches with regulatory and compliance measures in order to optimize healthcare delivery.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Get Your Custom Essay on The effectiveness of leadership development programs in the healthcare managementIndustry 1st June 2023 on The effectiveness of leadership development progr. Findings often underscore enhanced leadership skills like communication, decision-making, and strategic thinking that are vital for successful healthcare administration. Participants frequently describe enhanced conviction in their leadership potential and a greater capacity to direct teams to realize these organizational objectives. Examples of quantitative metrics could be improvements in scores related to team performance, patient satisfaction, and employee engagement — which can all be tied to better leadership practices. Higher quality leadership can also lead to increased staff retention, improved bottom-line performance, as successful leaders are able to better create effective and innovative operational practices. Move beyond basic description to help put these results in perspective in terms of the challenges faced in a healthcare setting, such as elevated stress, regulatory compliance and the complexities of providing evidence-based care. It should also consider how the effectiveness of this kind of program varies depending on how long the program lasts, how it is structured and how engaged participants are. Bear in mind that while leadership development programs add value, their impact is reliant first and foremost on long-term backing from management, inclusion of skills learned into broader goals, and the regular practice of those skills. Further studies should investigate longer-term effects, and determine what the most effective elements of the programs.
Competency Improvement
Evaluating the enhancement of Leadership and Management Skills: Measure the progress in participants’ leadership and management competencies. This can be assessed using Pre- and post-program competency evaluations, 360-degree feedback, and self-assessment surveys.
|
Table 2. Comparison of Competency Improvement |
||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
|||
|
ROI |
KPI |
BMC |
Proposed model |
|
|
20 |
22 |
39 |
56 |
73 |
|
40 |
26 |
42 |
61 |
78 |
|
60 |
30 |
46 |
64 |
82 |
|
80 |
34 |
50 |
69 |
86 |
|
100 |
38 |
53 |
74 |
89 |
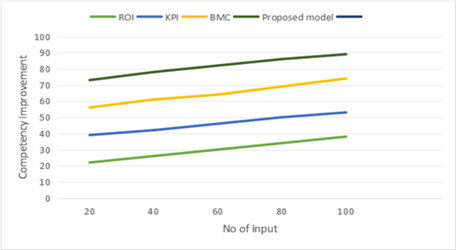
Figure 2. Computation of Competency Improvement
The focus should be on skills such as decision-making, strategic thinking, and team management to understand their capability improvements in real healthcare settings.
Retention and Career Progression
Career Tracking: measure participant retention levels in your organization and their career trajectory after completing the program.
|
Table 3. Comparison of Retention and Career Progression |
||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
|||
|
ROI |
KPI |
BMC |
Proposed model |
|
|
10 |
35 |
52 |
69 |
82 |
|
20 |
39 |
56 |
73 |
84 |
|
30 |
43 |
60 |
77 |
85 |
|
40 |
47 |
64 |
81 |
87 |
|
50 |
51 |
68 |
85 |
88 |
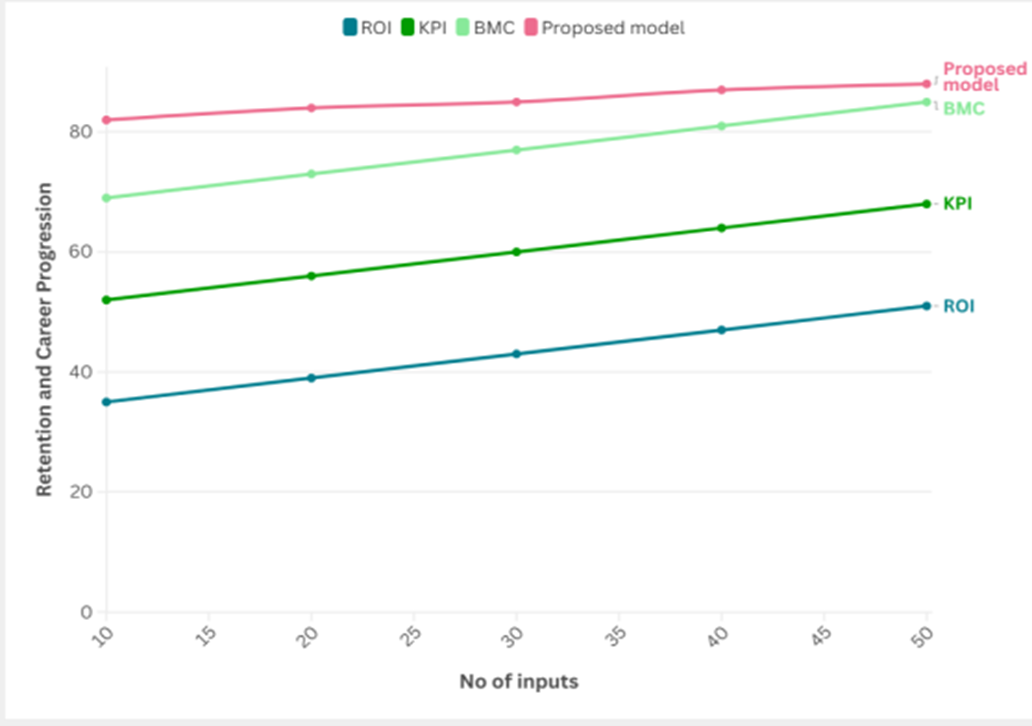
Figure 3. Computation of Retention and Career Progression
This encompasses promotions, elevation in responsibilities, or shift into vital roles. This will help ascertain if the knowledge and skills gained are actually being put to use and are recognized, signifying the program’s value in furthering one’s personal and professional advancement.
Organizational Impact
Measuring Changes in Organizational Performance Metrics: demonstrate changes in KPIs including patient satisfaction scores, team productivity, or financial performance.
|
Table 4. Comparison of Organizational Impact |
||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
|||
|
ROI |
KPI |
BMC |
Proposed model |
|
|
10 |
20 |
37 |
54 |
71 |
|
20 |
24 |
41 |
58 |
76 |
|
30 |
28 |
45 |
62 |
80 |
|
40 |
33 |
49 |
67 |
84 |
|
50 |
36 |
52 |
72 |
87 |
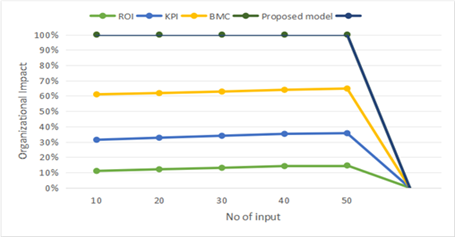
Figure 4. Computation of Organizational Impact
The effect of enhanced leadership on the organization as a whole: this parameter measures the overall impact of better leadership on the effectiveness of the organization and helps one see how better leadership can lead to fulfilling the strategic vision of healthcare organization.
CONCLUSIONS
The critical evaluation of leadership development programs in healthcare management elucidates some of the key take away messages regarding their viability. They usually work to enhance leadership capabilities, streamline decision-making, and foster organizational culture that promotes innovation and collaboration within healthcare organizations. First, holistic programs, combining theory, skills and experience work much better. Experiential exercises or simulations that replicate real-world scenarios allow leaders to apply leadership principles in the workplace. Second, the most important support always comes from the senior management, irrespective of the program, which has great bearing on how effective, these programs are, in the context of the organization culture. Yes, the alignment of leadership development initiatives with strategic goals and the support of senior leaders for these initiatives produce a greater impact on the performance of skills learned in participants. And, iterative testing and improvements on such initiatives can only occur through continuous tracking and feedback mechanisms. This process continually evaluates the training approach in identifying gaps and ensures that it adapts to the ever-evolving challenges of healthcare management. Moreover, its long-term effect is enhanced by building a support peer network of fellow learners that sustain learning and collaboration beyond the period of engagement in the program. In general, the success of leadership development initiatives in the area of healthcare management relies on how they are designed, executed, and assessed. All these aspects guide and feature leaders who will be able to generate beneficial alterations in healthcare habits and results.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Musinguzi, C., Namale, L., Rutebemberwa, E., Dahal, A., Nahirya-Ntege, P., & Kekitiinwa, A. (2018). The relationship between leadership style and health worker motivation, job satisfaction and teamwork in Uganda. Journal of healthcare leadership, 21-32.
2. Buchbinder, S. B., Shanks, N. H., & Kite, B. J. (2019). Introduction to health care management. Jones & Bartlett Learning.
3. Gray, P., Senabe, S., Naicker, N., Kgalamono, S., Yassi, A., & Spiegel, J. M. (2019). Workplace-based organizational interventions promoting mental health and happiness among healthcare workers: A realist review. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(22), 4396.
4. Guraya, S. Y., & Chen, S. (2019). The impact and effectiveness of faculty development program in fostering the faculty’s knowledge, skills, and professional competence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Saudi journal of biological sciences, 26(4), 688-697.
5. Ginter, P. M., Duncan, W. J., & Swayne, L. E. (2018). The strategic management of health care organizations. john wiley & sons.
6. Figueroa, C. A., Harrison, R., Chauhan, A., & Meyer, L. (2019). Priorities and challenges for health leadership and workforce management globally: a rapid review. BMC health services research, 19, 1-11.
7. Flynn, R., Rotter, T., Hartfield, D., Newton, A. S., & Scott, S. D. (2019). A realist evaluation to identify contexts and mechanisms that enabled and hindered implementation and had an effect on sustainability of a lean intervention in pediatric healthcare. BMC health services research, 19, 1-12.
8. Bolden, R., Gulati, A., & Edwards, G. (2020). Mobilizing change in public services: insights from a systems leadership development intervention. International Journal of Public Administration.
9. Robbins, B., & Davidhizar, R. (2020). Transformational leadership in health care today. The Health Care Manager, 39(3), 117-121.
10. Rawashdeh, A. (2018). The impact of green human resource management on organizational environmental performance in Jordanian health service organizations. Management Science Letters, 8(10), 1049-1058.
FINANCING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Kashish Gupta, Jamuna. K. V, Rakesh Mohanty.
Data curation: Kashish Gupta, Jamuna. K. V, Rakesh Mohanty.
Formal analysis: Kashish Gupta, Jamuna. K. V, Rakesh Mohanty.
Drafting - original draft: Kashish Gupta, Jamuna. K. V, Rakesh Mohanty.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Kashish Gupta, Jamuna. K. V, Rakesh Mohanty.