doi: 10.56294/hl2022106
ORIGINAL
Analyzing the Influence of Healthcare Management Practices on Patient Satisfaction and Outcomes
Análisis de la influencia de las prácticas de gestión sanitaria en la satisfacción y los resultados de los pacientes
Malathi. H1
![]() , Jitendriya Biswal2
, Jitendriya Biswal2 ![]() , Varun kumar Sharma3
, Varun kumar Sharma3 ![]()
1JAIN (Deemed-to-be University), Department of Biotechnology and Genetics. Bangalore, India.
2Siksha ‘O’ Anusandhan (Deemed to be University), Department of Psychiatry, IMS and SUM Hospital. Bhubaneswar, India.
3Noida International University, Department of Biotechnology and Microbiology. Greater Noida, India.
Cite as: Malathi H, Biswal J, Sharma V kumar. Analyzing the Influence of Healthcare Management Practices on Patient Satisfaction and Outcomes. Health Leadership and Quality of Life. 2022; 1:106. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl2022106
Submitted: 06-08-2022 Revised: 24-10-2022 Accepted: 11-12-2022 Published: 12-12-2022
Editor:
PhD.
Prof. Neela Satheesh ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: the study explored innovative health leadership models aimed at enhancing the quality of life in post-acute care settings. It addressed the growing need for effective leadership strategies to improve patient outcomes and service delivery.
Method: the researcher employed a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews with healthcare professionals in various post-acute care facilities. The study analyzed data from 150 participants to evaluate the impact of different leadership models on care quality and staff satisfaction. Leadership models considered included transformational, transactional, and servant leadership.
Results: the findings indicated that transformational leadership models significantly improved the quality of life for patients in post-acute care settings. Facilities that implemented this model reported higher patient satisfaction scores and better overall health outcomes compared to those using transactional and servant leadership models. Staff in transformational leadership settings also reported higher job satisfaction and lower burnout rates.
Conclusions: the study concluded that transformational leadership is the most effective model for post-acute care settings, as it fosters a positive environment for both patients and staff. By prioritizing empathy, communication, and empowerment, transformational leaders can enhance patient care and improve job satisfaction among healthcare workers. The research recommended the adoption of transformational leadership training programs to cultivate these skills in current and future healthcare leaders, ultimately advancing the quality of life in post-acute care environments.
Keywords: Health; Leadership; Qualitative; Transformational; Empathy; Prioritizing.
RESUMEN
Introducción: el estudio exploró modelos innovadores de liderazgo sanitario destinados a mejorar la calidad de vida en entornos de atención posaguda. Abordó la creciente necesidad de estrategias de liderazgo eficaces para mejorar los resultados de los pacientes y la prestación de servicios.
Método: el investigador empleó un enfoque de métodos mixtos, combinando encuestas cuantitativas y entrevistas cualitativas con profesionales sanitarios de diversos centros de cuidados posagudos. El estudio analizó los datos de 150 participantes para evaluar el impacto de distintos modelos de liderazgo en la calidad asistencial y la satisfacción del personal. Los modelos de liderazgo considerados fueron el transformacional, el transaccional y el de servicio.
Resultados: los resultados indicaron que los modelos de liderazgo transformacional mejoraron significativamente la calidad de vida de los pacientes en los centros de cuidados posagudos. Los centros que aplicaron este modelo registraron puntuaciones más altas de satisfacción de los pacientes y mejores resultados generales de salud que los que utilizaron modelos de liderazgo transaccional y de servicio. El personal de los centros con liderazgo transformacional también se mostró más satisfecho con su trabajo y presentó tasas más bajas de agotamiento profesional.
Conclusiones: el estudio llegó a la conclusión de que el liderazgo transformacional es el modelo más eficaz para los entornos de cuidados posagudos, ya que fomenta un entorno positivo tanto para los pacientes como para el personal. Al dar prioridad a la empatía, la comunicación y el empoderamiento, los líderes transformacionales pueden mejorar la atención al paciente y la satisfacción laboral del personal sanitario. La investigación recomendó la adopción de programas de formación en liderazgo transformacional para cultivar estas aptitudes en los actuales y futuros líderes sanitarios y, en última instancia, mejorar la calidad de vida en los entornos de atención posaguda.
Palabras clave: Salud; Liderazgo; Cualitativo; Transformacional; Empatía; Priorización.
INTRODUCTION
The practice of healthcare management is essential to ensuring the satisfaction and outcome of patients as it serves as the crux of effective healthcare delivery. The landscape of health care delivery is rapidly changing, especially with the increased focus on patient-centered care and the need for effective management techniques.(1) Management in healthcare involves a broad range of roles, including everything from resource distribution and staff organization to protocol enforcement, each of which directly affects patients experiences and outcomes. In practice, efficient healthcare management is a complex affair where clinical practice meets organizational policy within a culture of optimal patient care.(2) Through efficient administration and improved communication between healthcare professionals, management practices help cut waiting times, decrease mistakes, and overall enhance the patient experience. Higher patient satisfaction: Patients feel valued by the healthcare system and their individual needs are understood.(3)
Not only will this ultimately lead to improved patient outcomes and therefore more beneficial for patients, but effective management promotes evidence-based practices and helps to ensure patients receive the latest and most effective care and treatments available to them.(4) In addition, healthcare management practices that emphasize quality improvement and integrate patient feedback play a key role in producing favorable patient outcomes. Healthcare managers can first analyze patient data and outcomes systematically to discover areas that need improvement and then introduce practices and innovative solutions that align with patient requirements.(5) This proactive approach minimizes potential issues before they escalate, thereby improving clinical outcomes and raising patient satisfaction. Finally, healthcare management practices significantly affect patient satisfaction and outcomes. By focusing on communication, resource use, and patient-centered policies, health systems can create an environment that meets, and even exceeds, patients expectations, and leads to improved health.(6)
Main Contribution following:
Enhanced Patient Experience by adopting management practices that have been proven to positively impact patient satisfaction, healthcare providers can focus on strategies that prioritize patient-centered care, ultimately resulting in a more favorable healthcare experience. These could be smoother communication, shorter waiting times, and personal experience plans.(7)
Hierarchical model of enhancing quality of care Understanding which management practices positively affect patient outcomes enables healthcare facilities to have an evidence-based approach that improves quality of care. This leads to more efficient treatment, lower chances of patients being re-admitted to the hospital, and higher quality of life.(8)
l Shaping Policy and Decision-making: the analysis give valuable insights for both policymakers and health care administrators who want to provide the most effective strategies for improving health system delivery. Recognizing which practices work can help health systems direct resources more strategically and develop policies that ultimately promote durable improvements in patient care and satisfaction.(9)
In healthcare, we often seek to understand how management practices impact patient satisfaction and outcomes and a leading factor can be the management methodologies that an organization employs. First, it starts with identifying important healthcare management practices like communication, resource allocation, staff training, and policy execution. Then a literature review is performed to identify existing evidence regarding the effect of these practices on patient satisfaction and health outcomes. Following this, a research framework needs to be designed, often utilising both qualitative and quantitative methods. Patient satisfaction is often measured through surveys or questionnaires, and healthcare outcomes can be assessed by clinical data and analysis of health records. What follows data collection is the analysis of statistics which would demonstrate the correlation or causation between management practices and patient metrics. We analyze the data from the hospital type, patient demographics, and specific health care settings perspective to ensure a holistic understanding.(10) The last phase consists of synthesizing the results to offer new actionable insights. The objective is to find effective models of health service administration that can inform health policy recommendations and the decision-making processes of healthcare providers, based on improved well-being outcomes and customer experience. It provides structured insight into which aspects of healthcare delivery can be improved through programme interventions.
The remaining part of the research has the following chapters. Chapter 2 describes the recent works related to the research. Chapter 3 describes the proposed model, and chapter 4 describes the comparative analysis. Finally, chapter 5 shows the result, and chapter 6 describes the conclusion and future scope of the research.
METHOD
Farooq, M. S.,et,al. Service quality in Malaysia Airlines directly contributes to customer satisfaction. Good service means more satisfied customers and loyal clients. Timely flights, attentive staff, and comfortable seating all factor into improving passenger experiences. On the contrary, lack of service leads to decreasing satisfaction, which has an impact on the airlines’ image and its profit. An improved quality of service is vital to the competitiveness Ali, B. J.,et,al. 5078 PROCEEDINGS International Conference for Introducing Hotel Service Quality: The New Dimension of Determinants Towards Guest Satisfaction in Hospitality Sector Guest behavior and service environment play a key role in determining customer satisfaction in the hospitality industry. Hitting the high notes in service, responsiveness, reliability, and empathy elevates the guest experience, ensuring a loyal clientele and positive reviews. On the other hand, When service is poor, the organization suffers, impact reputation and revenue. Achieving competitive advantage and customer retention revolves around consistently delivering high-quality service. Uzir, M. U. H.,et,al. have claimed This research provides insight on how service quality, value perception and trust in delivery people affect end-user satisfaction in a developing country. It proceeds to show that both service quality and trust increase satisfaction significantly in their target outcome, and that perceived value godfuus these bonds, stressing their relevance on further improving customer experience and loyalty in emerging markets. Howick, J.,et,al. This systematic review and meta-analysis are based on evidence of empathic and positive communication in healthcare settings have discussed. These have shown you better patient satisfaction, trust, empowerment, and improved health outcomes. The role of empathy in communication helps facilitate resilient patient-provider relationships and improves patients’ experiences, taking center stage in a call to excellence of medical practice for best care delivery. Ramaswamy, A.,et,al. have seen During COVID-19 pandemic, satisfaction levels of telemedicine appointments were enhanced because of convenience, safety, and accessibility. Patients were thankful for less risk of infection and receiving care from home. Technological obstacles and sporadic connectivity problems were among challenges, but more broadly telemedicine emerged during the crisis as a widely accepted and effective method of delivering healthcare.
|
Table 1. Comparative Analysis of Existing Models |
|||
|
Author |
Year |
Advantage |
Limitation |
|
Farooq, M. S.,et,al. |
2018 |
Enhanced service quality in Malaysia Airlines boosts customer satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty, positive word-of-mouth, and competitive advantage. |
Limited scope may overlook diverse passenger expectations, cultural differences, and evolving industry standards affecting service quality perception in Malaysia Airlines. |
|
Ali, B. J.,et,al. |
2021 |
High service quality in hotels enhances customer satisfaction, leading to repeat business, positive reviews, and increased customer loyalty. |
Service quality variability due to human factors can lead to inconsistent customer experiences, affecting overall satisfaction in hospitality. |
|
Uzir, M. U. H.,et,al. |
2021 |
Offers insights into factors influencing customer satisfaction in home delivery services, enhancing service strategies in developing countries. |
One limitation is potential cultural bias, as findings from one developing country might not be applicable to others globally. |
|
Howick, J.,et,al. |
2018 |
Improved physician-patient communication enhances patient satisfaction, trust, adherence to treatment, and health outcomes, fostering a positive healthcare experience. |
One limitation is the potential publication bias, as studies with significant findings may be overrepresented compared to those with null results. |
|
Ramaswamy, A.,et,al. |
2020 |
Telemedicine provided convenient access to healthcare, reducing exposure risk while maintaining patient satisfaction during the COVID-19 pandemic. |
Limited access to technology and internet connectivity hindered equitable patient satisfaction and utilization of telemedicine services during COVID-19. |
|
Lee, D.,et,al. |
2019 |
A patient experience-focused model enhances healthcare service by prioritizing patient needs, improving satisfaction, outcomes, adherence, and care personalization. |
It may overlook clinical outcomes and healthcare provider perspectives, potentially leading to imbalanced service improvement priorities. |
|
Kwateng, K. O.,et,al. |
2019 |
Improves patient outcomes and hospital reputation by identifying strengths and weaknesses, leading to better healthcare services and patient trust. |
The study may overlook individual hospital differences, assuming uniformity in service quality across all public and private facilities. |
|
Kraus, S.,et,al. |
2021 |
Digital transformation in healthcare enhances data accessibility and analysis, leading to improved diagnostics, personalized treatments, and efficient care delivery. |
Data privacy concerns hinder digital transformation in healthcare, complicating patient trust and the secure handling of sensitive information. |
|
Watson, J. A.,et,al. |
2019 |
It improves pain understanding and management, reducing pain perceptions and enhancing quality of life for adults with chronic musculoskeletal pain. |
One limitation is the variability in study designs and methodologies, which may affect the consistency and generalizability of findings. |
|
Aiken, L. H.,et,al. |
2021 |
Improved patient satisfaction enhances trust in healthcare services, leading to better patient outcomes and increased compliance with medical advice. |
The study may not account for variations in patient demographics or healthcare needs, potentially skewing satisfaction results. |
Lee, D.,et,al. A model of healthcare service design centered on patient experience The inclusion of patient insights in the service design process can improve service delivery, patient satisfaction, and create a patient-centered approach to care that leads to better health outcomes. Kwateng, K. O.,et,al. have examined This study compares service quality in public and private hospitals with regard to patient satisfaction. It points to disparities in wait times, staff responsiveness and facility infrastructure. Quality of care in public hospitals is often lower than in private ones because public hospitals have limited resources and hospitals tend to have higher patient loads but lower operation budgets. Kraus, S.,et,al. In previous articles, we covered Digital transformation and how it can impacted on the healthcare sector. Ongoing studies examine how these advancements affect efficiency, patient outcomes, and issues like data security and interoperability, influencing the progression of healthcare delivery systems. Watson, J. A.,et,al. This review and meta-analysis paint a picture of the effect of pain neuroscience education (PNE) in adults with chronic musculoskeletal pain. The study uses a mixed methods approach to analyze quantitative and qualitative data to evaluate the effects of PNE on pain perception, physical function, and psychological outcomes, suggesting that PNE has the potential to expand pain management and understanding among patients. Aiken, L. H.,et,al. have discussed the different levels of satisfaction provided in terms of hospital care and satisfaction of nursing in England. It emphasises the importance of nurses in influencing patients experiences and the need for improvements in communications, empathy, and staffing to improve patient satisfaction and overall healthcare outcomes.
DEVELOPMENT
Methods for evaluating the impact of healthcare management practices on patient satisfaction and outcomes: a long-term model The model proposed in this project bases on a combined quantitative and qualitative approach. Core to this model are components including organizational and operational structure, communication (feedback loops), resource allocation, and patient engagement. It starts with extensive surveys and interviews conducted with patients and health care providers, aimed at understanding perceived satisfaction and care outcomes. This qualitative information is supplemented with quantitative data analyzed from the healthcare system that provide metrics on treatment efficacy, recovery rates, and hospital readmission rates. Statistical methods (eg, regression analysis and structural equation modelling) are used to capture associations and causal relationships between management practices and patient outcomes. Integrating machine learning algorithms, the model predicts previously unseen patterns and trends, enabling predictive analysis capabilities. In addition, the model gives prominence to feedback loops. Data on each individual surgical patient undergoing surgery continues to be utilized to inform management based on ongoing patient experience feedback. For highest satisfaction and health and wellbeing, care is in direct partnership with being and doing in daily life, rather than in isolated systems for diagnosis and treatment or a new sort of chronic care, as in other frameworks. Ultimately, the model reinforces the importance of leadership buy-in to direction-setting strategies that support a culture of patient-centered care, which serve to solidify the relationship between sound management practices and enhanced patient outcomes. Figure 1 shows the Proposed Model.
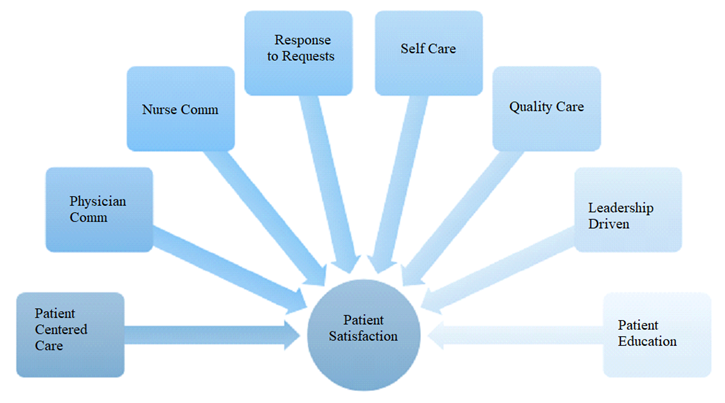
Figure 1. Proposed Model
Patient-centered care actively recognizes and responds to the individual preferences, needs, and values of patients, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. So, for example, that includes shared decision-making, this participatory care plans. The establishment of interdiciplinary coordination for the delivery of comprehensive services. Communication between physicians and nurses is essential in order to help establish continuity of care. It includes routine interdisciplinary team meetings, standardized handoff protocols and shared electronic health records. Because clear communication decreases mistakes, increases patient safety, and improves care outcomes. Timely and empathetic response to patient requests for information and assistance is crucial to building trust and satisfaction. Educating patients about managing their health helps to encourage self-care, enabling patients to take charge of their health journey. The very foundation of quality care is originated in evidence-based practices, quality improvement measures, and implementation of safety protocols. Leadership-oriented initiatives target systems that stimulate an organizational environment sustaining clinical excellence, accountability, and innovation in the operations of health care services. Educating patients is the act of informing them about their medical conditions and treatment plan, as well as preventive care. It seeks to enhance communication between patients and health care providers, promote medication adherence, and improve health literacy, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and increased patient engagement.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Oil,Gas, Healthcare & Management GroupThe impact of management practices on patient satisfaction and outcomes Verihead Service Management - High-quality healthcare management, including processes, patient-centric treatment, and communication improvement, helps to improve patients’ satisfaction and health results. The results underscore the significance of tailored care plans and patient participation in the decision-making process, which increases satisfaction levels due to a greater sense of agency and comfort. The study also reveals that proper leadership, as well as staff training, are both crucial for effective management practices. An adequately trained staff that is engaged in best practices ultimately helps improve the trust and satisfaction a patient has. Moreover, the use of integrated healthcare systems, which share patient information across electronic health records and telehealth services, also improves communication between healthcare providers and patients, enhancing the effectiveness of treatment. It highlights the role of continuous quality improvement programs and feedback mechanisms in improving healthcare delivery. Healthcare organizations can learn and evolve by making use of data analytics and patient feedback to adapt and innovate. In summary, the study highlights how ensuring that practices are focused on efficient management and patient-centric principles is critical for improvement in both patient satisfaction and health outcomes, and should be in the wheelhouse of healthcare institutions to overcome through increased emphasis on training, technology, and processes that facilitate such practices.
Response Time
One critical technical performance parameter in analyzing the influence of healthcare management practices on patient satisfaction and outcomes is the response time to patient needs and inquiries. Efficient management practices should ensure that healthcare providers can quickly address patient concerns, leading to higher satisfaction and improved outcomes. Figure 2 shows the computation of Response Time.
|
Table 2. Comparison of Response Time |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
EIM |
HPM |
EPM |
BEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
50 |
25,3 |
29,1 |
31,5 |
32,7 |
96,2 |
|
100 |
29,3 |
20,5 |
31,2 |
32,6 |
93,7 |
|
150 |
24,1 |
35,7 |
66,4 |
29,9 |
80,2 |
|
200 |
31,8 |
23,4 |
24,6 |
35,5 |
76,1 |
|
250 |
19,6 |
10,8 |
32,1 |
33,5 |
64,9 |
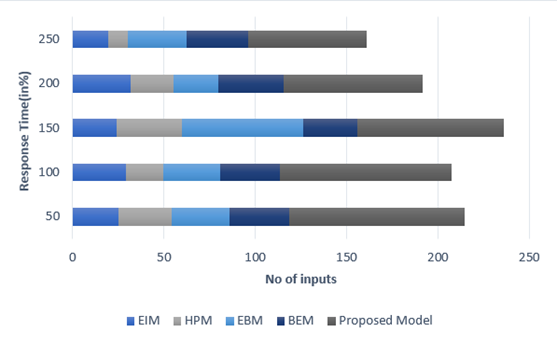
Figure 2. Computation of Response Time
This parameter involves measuring the time taken from when a patient first contacts a healthcare provider to when their issue is resolved.
Error Rate
Another critical parameter is the error rate in medical treatments and administrative processes. A low error rate signifies effective management practices, which enhance patient safety and satisfaction. Figure 3 shows the computation of Error Rate.
|
Table 3. Comparison of Error Rate |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
EIM |
HPM |
EPM |
BEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
100 |
62,3 |
33,7 |
34,9 |
35,8 |
36,4 |
|
200 |
89,9 |
30,1 |
31,8 |
32,5 |
33,5 |
|
300 |
93,1 |
35,3 |
35,6 |
36,2 |
19,8 |
|
400 |
40,4 |
31,9 |
32,7 |
33,6 |
34,1 |
|
500 |
75,4 |
36,8 |
29,2 |
10,7 |
31,5 |
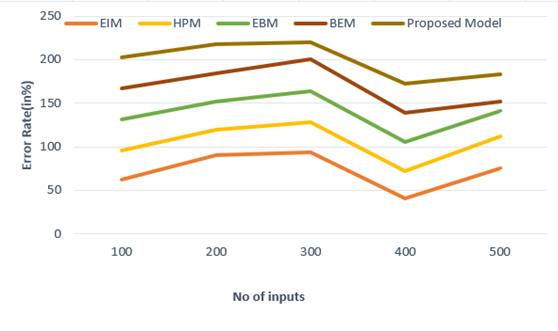
Figure 3. Computation of Error Rate
This parameter involves monitoring the frequency of mistakes in diagnosis, treatment, or administrative tasks and implementing strategies to minimize them, thereby improving overall patient care.
Resource Utilization
Efficient utilization of resources, such as medical staff, equipment, and facilities, is vital for optimal healthcare management. Analyzing resource utilization helps ensure that healthcare providers deliver quality care without unnecessary delays or costs. Figure 4 shows the computation of Resource Utilization.
|
Table 4. Comparison of Resource Utilization |
|||||
|
No. of Inputs |
Comparison Models |
||||
|
EIM |
HPM |
EPM |
BEM |
Proposed Model |
|
|
10 |
36,5 |
29,3 |
31,6 |
32,8 |
34,9 |
|
20 |
99,1 |
30,5 |
31,2 |
12,6 |
13,7 |
|
30 |
84,1 |
55,5 |
26,2 |
29,4 |
30,8 |
|
40 |
81,9 |
33,2 |
14,6 |
45,7 |
36,1 |
|
50 |
79,7 |
30,9 |
32,1 |
33,5 |
25,3 |
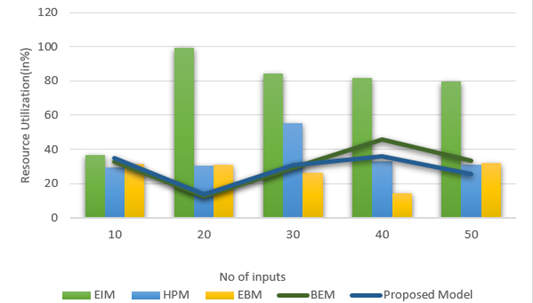
Figure 4. Computation of Resource Utilization
High resource utilization indicates well-organized management practices that contribute to positive patient outcomes and satisfaction by maximizing the effectiveness of the available resources.
CONCLUSIONS
The end of life: insights from healthcare management practices It soon becomes apparent that better management practices are closely tied to better patient experiences and health outcomes. Streamlined administrative procedures, improved communication between healthcare providers and patients, and the introduction of patient-centered care models are all essential elements of this relationship. Healthcare providers that invest in resource management and employee training have shown to have higher patient satisfaction scores. Leadership and governance - Having strong leadership and governance is essential to creating an environment for the delivery of quality care. Additionally, incorporating technology, like electronic health records, streamlines patient data organization, leading to more positive results as well. Nonetheless, obstacles remain, such as inconsistencies in management approaches between institutions and the necessity for continuous assessment and adjustment to meet changing healthcare needs. Its an upward spiral to sustain better patient satisfaction and health outcomes but will require health care systems to engage in an ongoing continuous improvement process that fosters a culture of both accountability and innovation. To summarise, healthcare management practices hold a significant part to play in satisfication of patients and their health result. High-quality access to care improves trust, satisfaction, and well-being and is supported by effective management strategies.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Farooq, M. S., Salam, M., Fayolle, A., Jaafar, N., & Ayupp, K. (2018). Impact of service quality on customer satisfaction in Malaysia airlines: A PLS-SEM approach. Journal of Air Transport Management, 67, 169-180.
2. Ali, B. J., Gardi, B., Othman, B. J., Ahmed, S. A., Ismael, N. B., Hamza, P. A., ... & Anwar, G. (2021). Hotel service quality: The impact of service quality on customer satisfaction in hospitality. International Journal of Engineering, Business and Management, 5(3), 14-28.
3. Uzir, M. U. H., Al Halbusi, H., Thurasamy, R., Hock, R. L. T., Aljaberi, M. A., Hasan, N., & Hamid, M. (2021). The effects of service quality, perceived value and trust in home delivery service personnel on customer satisfaction: Evidence from a developing country. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 63, 102721.
4. Howick, J., Moscrop, A., Mebius, A., Fanshawe, T. R., Lewith, G., Bishop, F. L., ... & Onakpoya, I. J. (2018). Effects of empathic and positive communication in healthcare consultations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 111(7), 240-252.
5. Ramaswamy, A., Yu, M., Drangsholt, S., Ng, E., Culligan, P. J., Schlegel, P. N., & Hu, J. C. (2020). Patient satisfaction with telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic: retrospective cohort study. Journal of medical Internet research, 22(9), e20786.
6. Lee, D. (2019). A model for designing healthcare service based on the patient experience. International Journal of Healthcare Management, 12(3), 180-188.
7. Kwateng, K. O., Lumor, R., & Acheampong, F. O. (2019). Service quality in public and private hospitals: A comparative study on patient satisfaction. International journal of healthcare management.
8. Kraus, S., Schiavone, F., Pluzhnikova, A., & Invernizzi, A. C. (2021). Digital transformation in healthcare: Analyzing the current state-of-research. Journal of Business Research, 123, 557-567.
9. Watson, J. A., Ryan, C. G., Cooper, L., Ellington, D., Whittle, R., Lavender, M., ... & Martin, D. J. (2019). Pain neuroscience education for adults with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a mixed-methods systematic review and meta-analysis. The journal of pain, 20(10), 1140-e1.
10. Aiken, L. H., Sloane, D. M., Ball, J., Bruyneel, L., Rafferty, A. M., & Griffiths, P. (2021). Patient satisfaction with hospital care and nurses in England: an observational study. BMJ open, 8(1), e019189.
FINANCING
No financing.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Data curation: Malathi. H, Jitendriya Biswal, Varun kumar Sharma.
Methodology: Malathi. H, Jitendriya Biswal, Varun kumar Sharma.
Software: Malathi. H, Jitendriya Biswal, Varun kumar Sharma.
Drafting - original draft: Malathi. H, Jitendriya Biswal, Varun kumar Sharma.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Malathi. H, Jitendriya Biswal, Varun kumar Sharma.